Summary
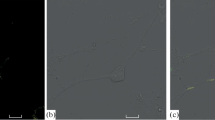
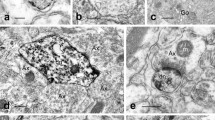
The distribution of fluorescence in the rat brain after i.p. or intracerebral (i.c.) injections of a fluorescent dihydroisoquinoline derivate of dopamine was studied. After low i.p. doses (50 mg/kg of body weight) the fluorescence was totally confined to the capillary endothelial cells in the cerebral cortex, neostriatum, and substantia nigra (SN). After large i.p. doses (500 mg/kg) fluorescent material was also present in the neuropil of all the regions studied and some cells of the cerebral cortex and SN. After injections to the neostriatum or SN fluorescence was observed in the endothelial cells and some small to medium-sized rounded cells in both regions. A conspicious dark area contrasting with the background fluorescence was constantly present around capillaries, and this area was in contact with nonfluorescent multibranched cells of astrocytic type. In fluorescent cells the fluorescence was present both in the cytoplasm and the nucleus.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bertler, Å., Falck, B., Rosengren, E.: The direct demonstration of a barrier mechanism in the brain capillaries. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol 20, 317–321 (1964)
Bertler, Å., Falck, B., Rosengren, E.: The localization of monoaminergic blood-brain barrier mechanisms. In: Pharmacol. Rev. Vol. 18, part 1. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins 1966
Björklund, A., Flack, B., Owman, C.: In: The Thyroid and Biogenic Amines; Methods in Investigative and Diagnostic Endocrinology (eds. J.E. Rall and I.J. Kopin). Vol. 1, p. 318. Amsterdam: North Holland 1972
Cohen, G.: Tetrahydroisoquinoline alkaloids in the adrenal medulla after perfusion with “blood concentrations” of (14C)acetaldehyde. Biochem Pharmacol 20, 1757–1761 (1971)
Cohen, G., Collins, M.: Alkaloids from catecholamines in adrenal tissue: Possible role in alcoholism. Science 167, 1749–1751 (1970)
Cohen, G., Katz, S.: 6,7-dihydroxytetrahydroisoquinoline: evidence for in vivo inhibition of intraneuronal monoamine axidase. J Neurochem 25, 719–722 (1975)
Cohen, G., Mytilineou, C., Barret, R.: 6,7-dihydroxytetrahydroisoquinoline: uptake and storage by peripheral sympathetic nerve of the rat. Science 175, 1269–1272 (1972)
Collins, M., Bigdeli, M.: Tetrahydroisoquinolines in vivo. I. Rat brain formation of salsolinol, a condensation product of dopamine and acetaldehyde, under certain conditions during ethanol intoxication. Life Sci 16, 585–602 (1975)
Collins, A., Cashaw, J., Davis, V.: Dopamine derived tetrahydroisoquinoline alkaloids — inhibitors of neuroamine metabolism. Biochem Pharmacol 22, 2337–2348 (1973)
Collins, M., Cohen, G.: Tissue catecholamines condense with acetaldehyde to form isoquinoline alkaloids. Amer Chem Soc, 156th Nat. Mtg., Abst. 274 (1968)
Costall, B., Naylor, R., Pinder, R.: Hyperactivity induced by tetrahydroisoquinoline derivates injected into the nucleus accumbens. Eur J Pharmacol 39, 153–160 (1976)
Davis, V., Walsh, M.: Alcohol, amines and alkaloids: A possible biochemical basis for alcohol addiction. Science 167, 1005–1007 (1970)
Giovine, A., Renis, M., Bertolino, A.: In vivo and in vitro studies on the effect of tetrahydropapaveroline and salsolinol on COMT and MAO activity in rat brain. Pharmacology 14, 86–94 (1976)
Greenberg, R., Cohen, G.: Tetrahydroisoquinolines and the catecholamine-binding granules of the adrenal medulla. Eur J Pharmacol 18, 292–294 (1972)
Heikkilä, R., Cohen, G., Dembiec, D.: Tetrahydroisoquinoline alkaloids: Uptake by rat brain homogenates and inhibition of catecholamine uptake. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 179, 250–258 (1971)
König, J.F.R., Klippel, R.A.: The rat brain: a stereotaxic atlas of the forebrain and lower parts of the brainstem. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins 1963
Majchrowicz, E., Mendelson, J.: Blood methanol levels in alcoholics during experimentally induced ethanol intoxication. Fed Proc 29, 649 (1970)
Partanen, S.: Fluorescence histochemical demonstration of the uptake of dopamine-derived dihydroisoquinoline in the hypothalamic neurons. Experientia 33, 653–655 (1977)
Samorajski, T., Marks, B.: Localization of tritated norepinephrine in mouse brain. J Histochem Cytochem 10, 392–399 (1962)
Sandler, M., Carter, S., Hunter, K., Stern, G.: Tetrahydroisoquinoline alkaloids: in vivo metabolites of L-DOPA in man. Nature 241, 439–443 (1973)
Simon, P., Goujet, M., Chermat, R., Boissier, J.: Etude pharmacologique d'un métabolite présumé de la dopamine, la tetrahydropapavéroline. Therapie XXVI, 1175–1192 (1971)
Sippel, H.: The acetaldehyde content in rat brain during ethanol metabolism. J Neurochem 23, 451–452 (1974)
Svensson, L.-A., Björklund, A., Lindwall, O.: Studies on the fluorophore forming reactions of various catecholamines and tetrahydroisoquinolines with glyoxylic acid. Acta Chem Scand B 29, 341–348 (1975)
Trepanier, D., Sunders, S.: 3–4-dihydroisocarbostril and 1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline derivates of ephedrine. J Med Chem 16, 342–347 (1973)
Turner, A., Baker, K., Algeri, S., Frigerio, A., Garattini, S.: Tetrahydropapaveroline: Formation in vivo and in vitro in rat brain. Life Sci 14, 2247–2257 (1974)
Walsh, M., Davis, V., Yamanaka, Y.: Tetrahydropapaveroline: An alkaloid metabolite of dopamine in vitro. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 174, 388–400 (1970)
Weil-Malherbe, H., Whitby, L., Axelrod, J.: The uptake of circulating (3H)norepinephrine by the pituitary gland and various areas of the brain. J Neurochem 8, 55–64 (1963)
Yamanaka, Y.: Effect of salsolinol on rat brain and liver monoamine oxidase. Japan J Pharmacol 21, 833–836 (1971)
Yamanaka, Y., Walsh, M. and Davis, V.: Salsolinol, an alkaloid derivate of dopamine formed in vitro during alcohol metabolism. Nature 227, 1143–1144 (1970)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Panula, P., Partanen, S. & Kaakkola, S. Fluorescence histochemical observations on the distribution of exogenous dihydroisoquinoline in the rat brain. Exp Brain Res 34, 155–164 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00238348
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00238348