Summary
-
1.
In sheep anaesthetized with fluothane, electrical stimulation of the superior laryngeal nerve (SLN), which contains most of the afferent fibres for swallowing, evokes potentials in the medial part of the ipsilateral thalamic VPM (nucleus ventro-postero-medialis) within about 5 msec. This region constitutes the secondary synaptic relay for the laryngeal impulses projecting to the frontal cortex concerned with swallowing.
-
2.
SLN fibres are synaptically connected with cells of the NTS (nucleus of the tractus solitarius), 2–4 mm rostral to the obex (see Car and Jean, 1971). Coagulation of this region abolishes reflexly and cortically induced swallowing, but does not influence the thalamic or cortical responses induced by SLN stimulation.
-
3.
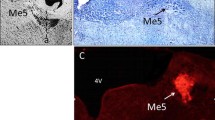
SLN stimulation evokes potentials with a short latency (2 msec) in a restricted pontine area localized 5 mm from the midline and above the trigeminal motor nucleus, just in front of the central emergence of the facial nerve (i.e. about 12 mm rostral to obex). Restricted coagulation of this pontine region eliminates both the thalamic and the cortical projection of SLN.
-
4.
Repetitive stimulation (2 V; 0.2 msec; 20–30 Hz) of this same pontine region produces rhythmic swallowing with characteristics quite similar to those of swallowing induced by SLN or bulbar stimulation.
-
5.
Other data show that SLN fibres, or at least part of them, bifurcate after entering the brain stem (about 6 mm in front of the obex), and give a caudal branch, which reaches the bulbar swallowing centre (3 mm rostral to the obex) by running through the tractus solitarius; and a rostral branch terminating in the pons where the primary synaptic relay for the ascending laryngeal pathway is localized.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aström, K.E.: On the central course of afferent fibres in the trigeminal, facial, glossopharyngeal, and vagal nerves and their nuclei in the mouse. Acta physiol. scand. 29, Suppl.106, 209–320 (1953)
Bernard, R.A., Nord, S.G.: A first order synaptic relay for taste fibers in the pontine brain stem of the cat. Brain Res. 30, 349–356 (1971)
Car, A.: La commande corticale du centre déglutiteur bulbaire J. Physiol. (Paris) 62, 361–386 (1970)
Car, A.: Etude macrophysiologique et microphysiologique de la zone déglutitrice du cortex frontal. J. Physiol. (Paris) 63, 183A (1971)
Car, A., Jean, A.: Potentiels évoqués dans le rhombencéphale du mouton par la stimulation du nerf laryngé supérieur. Contribution à l'étude de la localisation du Centre déglutiteur. J. Physiol. (Paris) 63, 715–730 (1971)
Car, A.: La commande corticale de la déglutition. I: sa voie d'expression. J. Physiol. (Paris) 66, 531–551 (1973a)
Car, A.: La commande corticale de la déglutition. II: point d'impact bulbaire de la voie corticifuge déglutitrice. J. Physiol. (Paris) 66, 553–576 (1973b)
Car, A., Jean, A., Roman, C.: Mise en évidence d'un relais pontique pour les projections ascendantes du nerf laryngé supérieur. J. Physiol. (Paris) 67, 254A (1973)
Cottle, M.K.: Degeneration studies of primary afferents of IXth and Xth cranial nerves in the cat. J. comp. Neurol. 122, 329–345 (1964)
Culberson, J.L., Kimmel, D.L.: Central distribution of primary afferent fibers of the glossopharyngeal and vagal nerves in the opossum, Didelphis Virginiana. Brain Res. 44, 325–335 (1972)
Dell, P., Olson, R.: Projections thalamiques, corticales et cérébelleuses des afférences vagales. C.R. Soc. Biol. (Paris) 145, 1084–1088 (1951)
Dell, P.: Corrélations entre le système végétatif et le système de la vie de relation. Mésencéphale, diencéphale et cortex cérébral. J. Physiol. (Paris) 44, 471–557 (1952)
Doty, R.W.: Neural organization of deglutition. Handbook of Physiology, section VI, vol. IV, alimentary canal, pp. 1861–1902. Washington: American Physiological Society 1968
Emmers, R.: Separate relays of tactile, pressure, thermal, and gustatory modalities in the cat thalamus. Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. (N.Y.) 121, 527–531 (1966)
Jean, A.: Localisation et activité des neurones déglutiteurs bulbaires. J. Physiol. (Paris) 64, 227–268 (1972a)
Jean, A.: Effet de lésions localisées du bulbe rachidien sur le stade oesophagien de la déglutition. J. Physiol. (Paris) 64, 507–516 (1972b)
Jean, A., Car, A., Roman, C.: Comparison of activity in pontine versus medullary neurones during swallowing. Exp. Brain Res. 22, 211–220 (1975)
Karamanlidis, A.N., Voogd, J.: Trigemino-thalamic fibre connections in the goat. An experimental anatomical study. Acta anat. (Basel) 75, 596–622 (1970)
Kerr, F.W.L.: Facial, vagal and glossopharyngeal nerves in the cat. Arch. Neurol. (Chic.) 6, 264–281 (1962)
Klüver, A., Barrera, E.: A method for the combined staining of cells and fibres in the nervous system. J. Neuropath. exp. Neurol. 12, 400–403 (1953)
Mizuno, N.: Projection fibers from the main sensory trigeminal nucleus and the supratrigeminal region. J. comp. Neurol. 139, 457–472 (1970)
Morest, D.K.: Experimental studies of the projections of the nucleus of the tractus solitarius and the area postrema in the cat. J. comp. Neurol. 130, 277–300 (1967)
Ramón y Cajal, S.: Histologie du système nerveux de l'Homme et des Vertébrés. Tomme I, 986 p. Madrid: Consejo Sup. Invest. Cient. 1909
Rhoton, A.L.: Afferent connections of the facial nerve. J. comp. Neurol. 133, 89–100 (1968)
Richard, P.: Atlas stéréotaxique du cerveau de brebis “Préalpes du Sud”. Paris: INRA Edit. 1967
Richard, P., Auffray, P., Albe-Fessard, D.: Activités thalamiques évoquées par des stimulations somatiques chez le mouton anesthésié au chloralose. Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol. 23, 401–409 (1967)
Siegfried, J., Kunze, U.: Les projections thalamiques du nerf vague chez le chat. Helv. physiol. Acta 23, C49-C51 (1965)
Torvik, A.: The ascending fibers from the main trigeminal sensory nucleus. Amer. J. Anat. 100, 1–15 (1957)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Car, A., Jean, A. & Roman, C. A pontine primary relay for ascending projections of the superior laryngeal nerve. Exp Brain Res 22, 197–210 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00237689
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00237689