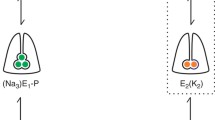Abstract
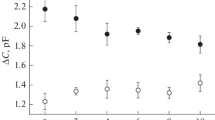
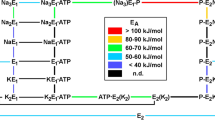
Ion binding at the extracellular face of the Na,K-ATPase is electrogenic and can be monitored by the styryl dye RH 421 in membrane fragments containing a high density of the Na,K-pumps. The fluorescent probe is noncovalently bound to the membrane and responds to changes of the local electric field generated by binding or release of cations inside the protein. Due to the fact that K+ binding from the extracellular side is an electrogenic reaction, it is possible to detect the amount of ions bound to the pump as function of the aqueous concentration. The results are in contradiction to a second order reaction, i.e., a simultaneous binding of two K+ ions. A mathematical model is presented to discuss the nature of the two step binding process. On the basis of this model the data allow a quantitative distinction between binding of the first and the second K+ ion. The temperature dependence of ion binding has been investigated. At low temperatures the apparent dissociation constants differ significantly. In the temperature range above 20°C the resulting apparent dissociation constants for both K+ ions merge and have values between 0.2 and 0.3 mm, which is consistent with previous experiments. The activation energy for the half saturating concentration of K+ is 22 kJ/mol. Additional analysis of the titration curve of K+ binding to the state P — E2 by the Hill equation yields a Hill coefficient, nHill, of 1.33, which is in agreement with previously published data.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Apell, H.-J. 1989. Electrogenic properties of the Na,K-pump. J. Membrane Biol. 110:103–114
Apell, H.-J., Nelson, M.T., Marcus, M.M., Läuger, P. 1986. Effects of ATP, ADP and inorganic phosphate on the transport rate of the Na+,K+-pump. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 857:105–115
Bühler, R., Stürmer, W., Apell, H.-J., Läuger, P. 1991. Charge translocation by the Na,K-pump: I. Kinetics of local field changes studied by time-resolved fluorescence measurements. J. Membrane Biol. 121:141–161
Clarke, R.P., Schrimpf, P., Schöneich, M. 1992. Spectroscopic investigations of the potential-sensitive membrane probe RH 421. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1112:142–152
Forbush III, B. 1987. Rapid release of 42K and 86Rb from an occluded state of the Na,K-pump in the presence of ATP or ADP. J. Biol. Chem. 262:11116–11127
Forbush III, B. 1988. Occluded ions and Na,K-ATPase. In: The Na+,K+-Pump, Part A: Molecular Aspects. J.C. Skou, J.G. Nørby, A.B. Maunsbach and M. Esmann, editors. Prog. Clin. Biol. Res. 268A, pp. 229–248. A.R. Liss, New York.
Gache, C., Rossi, B., Lazdunski, M. 1967. (Na+,K+)-activated adenosinetriphosphatase of axonal membranes, cooperativity and control. Eur. J. Biochem. 65:293–306
Glynn, I.M. 1985. The Na+,K+-transporting adenosine triphosphatase. In: The Enzymes of Biological Membranes. A.N. Martonosi, editor. Vol. 3 (2nd.), pp. 35–114. Plenum, New York
Glynn, I.M., Richards, D.E. 1982. Occlusion of rubidium ions by the sodium-potassium pump: Its implications for the mechanism of potassium transport. J. Physiol. 330:17–43.
Grinvald, A., Hildesheimer, R., Farber, I.C., Anglister, L. 1982. Improved fluorescent probes for the measurements of rapid changes in membrane potential. Biophys. J. 39:301–308
Heyse, S., Wuddel, I., Apell, H.-J., Stürmer, W. 1994. Partial reactions of the Na,K-ATPase: Determination of rate constants. J. Gen. Physiol. 104:197–240
Jørgensen, P.L. 1974. Isolation of the (Na+ + K+)-ATPase. Methods Enzymol. 32:277–290
Karlish, S.J.D., Stein, W.D. 1982. Passive rubidium fluxes mediated by Na,K-ATPase reconstituted into phospholipid vesicles when ATP-and phosphate-free. J. Physiol. 328:295–316
Läuger, P. 1991. In: Electrogenic Ion Pumps. pp. 168–224. Sinauer, Sutherland, MA
Läuger, P., Apell, H.-J. 1986. A microscopic model for the currentvoltage behavior of the Na,K-pump. Eur. Biophys. J. 13:309–321
Lowry, O.H., Rosenbrough, N.J., Farr, A.L., Randall, R.J. 1951. Protein measurements with the folin phenol reagents. J. Biol. Chem. 193:265–275
Marcus, M.M., Apell, H.-J., Roudna, M., Schwendener, R.A., Weder, H.-G. and Läuger, P. 1986. (Na+ + K+)-ATPase in artificial lipid vesicles: influence of lipid structure on pumping rate. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 845:270–278
Rakowski, R.F., Vasilets, L.A., LaTona, J., Schwarz, W. 1991. A negative slope in the current-voltage relationship of the Na+/K+ pump in Xenopus oocytes produced by reduction of external [K+]. J. Membrane Biol. 121:177–187
Sachs, J.R. 1980. The order of release of sodium and addition of potassium in the sodium-potassium pump reaction mechanism. J. Physiol. 273:489–514
Sachs, J.R., Welt, L.G. 1967. The concentration dependence of active potassium transport in the human red blood cell. J. Clin. Invest. 46:65–76
Sagar, A., Rakowski, R.F. (1994). Access channel model for the voltage dependence of the forward-running Na+/K+ pump. J. Gen. Physiol. (in press)
Schwartz, A., Nagano, K., Nakao, M., Lindenmeyer, G.E., Allen, J.C. 1971. The sodium- and potassium-activated adenosinetriphosphatase system. Methods Pharmacol. 1:361–388
Stürmer, W., Bühler, R., Apell, H.-J., Läuger, P. 1991. Charge translocation by the Na,K-pump: II. Ion binding and release at the extracellular face. J. Membrane Biol. 121:163–176
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The authors would like to thank G. Witz for technical assistance. This work has been financially supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (SFB 156).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bühler, R., Apell, H.J. Sequential potassium binding at the extracellular side of the Na,K-Pump. J. Membarin Biol. 145, 165–173 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00237374
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00237374