Summary
The projections of four different sub-areas within the anterior limbic cortex, all yielding vocalization when electrically stimulated, were compared in six squirrel monkeys by the autoradiographic tracing technique.
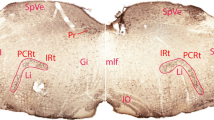
Areas of convergence of the projections from all four vocalization loci were the cortex within the anterior cingulate sulcus, a zone following the inferior thalamic peduncle from the central amygdaloid nucleus through the substantia innominata into the midline thalamus, a second zone following the periventricular fibre system from the anterior diencephalon to the caudal midbrain and dorsolateral pontine tegmentum and, finally, the tail of the caudate nucleus. Except for the latter, all of these brain structures produce vocalization when electrically stimulated. The call types elicitable from these projection areas are sometimes different from those elicitable from the anterior limbic cortex. It is hypothesized that the anterior limbic cortex controls vocalization directly, independently of the specific motivational state underlying it.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- a:
-
nucl. accumbens
- aa:
-
area anterior amygdalae
- ab:
-
nucl. basalis accessorius amygdalae
- ac:
-
nucl. centralis amygdalae
- an:
-
nucl. anterior thalami
- anl:
-
ansa lenticularis
- aq:
-
substantia grisea centralis
- ba:
-
nucl. basalis amygdalae
- bc:
-
brachium conjunctivum
- ca:
-
nucl. caudatus
- cc:
-
corpus callosum
- cent:
-
centrum medianum
- ci:
-
capsula interna
- cl:
-
claustrum
- coa:
-
commissura anterior
- coi:
-
colliculus inferior
- csp:
-
tractus cortico-spinalis
- gc:
-
gyrus cinguli
- gl:
-
corpus geniculatum laterale
- gm:
-
corpus geniculatum mediale
- gp:
-
globus pallidus
- gpm:
-
griseum periventriculare mesencephali
- gr:
-
gyrus rectus
- gts:
-
gyrus temporalis superior
- h:
-
campus Foreli
- ha:
-
nucl. habenularis
- hip:
-
hippocampus
- hy:
-
hypothalamus
- lap:
-
nucl. lateralis posterior thalami
- lem:
-
lemniscus medialis
- m:
-
corpus mamillare
- md:
-
nucl. medialis dorsalis thalami
- os:
-
nucl. olivaris superior
- p:
-
pedunculus cerebri
- po:
-
griseum pontis
- pro:
-
area praeoptica
- pu:
-
nucl. pulvinaris thalami
- put:
-
putamen
- re:
-
formatio reticularis
- s:
-
septum
- sm:
-
stria medullaris
- sn:
-
substantia nigra
- st:
-
stria terminalis
- tp:
-
cortex temporalis anterior
- va:
-
nucl. ventralis anterior thalami
- vpl:
-
nucl. ventralis postero-lateralis th.
- vpm:
-
nucl. ventralis postero-medialis th.
- III:
-
N. oculomotorius
References
Botez, M.J., Barbeau, A.: Role of subcortical structures and particularly of the thalamus in mechanisms of speech and language. Int. J. Neurol. (Montevideo) 8, 300–320 (1971)
Emmers, R., Akert, K.: A stereotaxic atlas of the brain of the squirrel monkey (Saimiri sciureus). Madison: University of Wisconsin Press 1963
Jürgens, U.: Reinforcing concomitants of electrically-elicited vocalizations. Exp. Brain Res. 26, 203–214 (1976a)
Jürgens, U.: Projections from the cortical larynx area in the squirrel monkey. Exp. Brain Res. 25, 401–411 (1976b)
Jürgens, U., Ploog, D.: Cerebral representation of vocalization in the squirrel monkey. Exp. Brain Res. 10, 532–554 (1970)
Jürgens, U., Ploog, D.: Zur Evolution der Stimme. Arch. Psychiat. Nervenkr. 222, 117–137 (1976)
Müller-Preuss, P., Jürgens, U.: Projections from the “cingular” vocalization area in the squirrel monkey. Brain Res. 103, 29–43 (1976)
Rubens, A.B.: Aphasia with infarction in the territory of the anterior cerebral artery. Cortex 11, 239–250 (1975)
Sutton, D., Larson, C., Lindeman, R.C.: Neocortical and limbic lesion effects on primate phonation. Brain Res. 71, 61–75 (1974)
Winter, P., Ploog, D., Latta, J.: Vocal repertoire of the squirrel monkey (Saimiri sciureus), its analysis and significance. Exp. Brain Res. 1, 359–384 (1966)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The study was carried out in accordance with the “Guiding Principles in the Care and Use of Primates” approved by the Council of the American Physiological Society.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jürgens, U., Müller-Preuss, P. Convergent projections of different limbic vocalization areas in the squirrel monkey. Exp Brain Res 29, 75–83 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00236876
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00236876