Abstract
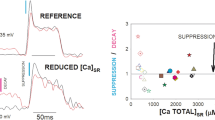
Ca2+-dependent inhibition of native and isolated ryanodine receptor (RyR) calcium release channels from sheep heart and rabbit skeletal muscle was investigated using the lipid bilayer technique. We found that cytoplasmic Ca2+ inhibited cardiac RyRs with an average K m = 15 mm, skeletal RyRs with K m = 0.7 mm and with Hill coefficients of 2 in both isoforms. This is consistent with measurements of Ca2+ release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) in skinned fibers and with [3H]-ryanodine binding to SR vesicles, but is contrary to previous bilayer studies which were unable to demonstrate Ca2+-inhibition in cardiac RyRs (Chu, Fill, Stefani & Entman (1993) J. Membrane Biol. 135, 49–59). Ryanodine prevented Ca2+ from inhibiting either cardiac or skeletal RyRs. Ca2+-inhibition in cardiac RyRs appeared to be the most fragile characteristic of channel function, being irreversibly disrupted by 500 mm Cs+, but not by 500 mm K+, in the cis bath or by solublization with the detergent CHAPS. These treatments had no effect on channel regulation by AMP-PNP, caffeine, ryanodine, ruthenium red, or Ca2+-activation. Ca2+-inhibition in skeletal RyRs was retained in the presence of 500 mm Cs+. Our results provide an explanation for previous findings in which cardiac RyRs in bilayers with 250 mm Cs+ in the solutions fail to demonstrate Ca2+-inhibition, while Ca2+-inhibition of Ca2+ release is observed in vesicle studies where K+ is the major cation. A comparison of open and closed probability distributions from individual RyRs suggested that the same gating mechanism mediates Ca2+-inhibition in skeletal RyRs and cardiac RyRs, with different Ca2+ affinities for inhibition. We conclude that differences in the Ca2+-inhibition in cardiac and skeletal channels depends on their Ca2+ binding properties.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahern, G.P., Junankar, P.R., Dulhunty, A.F. (1994). Single channel activity of the ryanodine receptor calcium release channel is modulated by FK-506. FEBS Lett. 352:194–197
Airey, J.A., Beck, C.F., Murakami, K., Tanksley, S.J., Deerinck, T.J., Ellisman, M.H., Sutko, J.L. (1990). Identification and localization of two triad junctional foot protein isoforms in mature avian fast twitch skeletal muscle. J. Biol. Chem. 265:14187–14194
Ashley, C.C., Mulligan, I.P., Lea, T.J. (1991). Ca2+ and activation mechanisms in skeletal muscle. Q. Rev. Biophys. 24:1–73
Ashley, R.H., Williams, A.J. (1990). Divalent cation activation and inhibition of single calcium release channels from sheep cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum. J. Gen. Physiol. 95:981–1005
Brandt, N.R., Caswell, A.H., Wen, S.R., Talvenheimo, J.A. (1990). Molecular interactions of the junctional foot protein and dihydropyridine receptor in skeletal muscle triads. J. Membrane Biol. 113:237–251
Caswell, A.H., Brandt, N.R., Brunschwig, J.P., Purkerson, S. (1991). Localization and partial characterization of the oligomeric disulfide-linked molecular weight 95,000 protein (triadin) which binds the ryanodine and dihydropyridine receptors in skeletal muscle triadic vesicles. Biochemistry 30:7507–7513
Chamberlain, B.K., Volpe, P., Fleischer, S. (1984). Calcium-induced calcium release from purified cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles. General characteristics. J. Biol.Chem. 259:7540–7546
Chen, S.R., Zhang, L., MacLennan, D.H. (1992). Characterization of a Ca2+ binding and regulatory site in the Ca2+ release channel (ryanodine receptor) of rabbit skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. J. Biol. Chem. 267:23318–23326
Chu, A., Dixon, M.C., Saito, A., Seiler, S., Fleischer, S. (1988). Isolation of sarcoplasmic reticulum fractions referable to longitudinal tabules and junctional terminal cisternae from rabbit skeletal muscle. Methods Enzymol. 157:36–46
Chu, A., Fill, M., Stefani, E., Entman, M.L. (1993). Cytoplasmic Ca2+ does not inhibit the cardiac muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum ryanodine receptor Ca2+ channel, although Ca2+-induced Ca2+ inactivation of Ca2+ release is observed in native vesicles. J. Membrane Biol. 135:49–59
Chung, S.H., Moore, J.B., Xia, L.G., Premkumar, L.S., Gage, P.W. (1990). Characterization of single channel currents using digital signal processing techniques based on Hidden Markov Models. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Biol. 329:265–285
Collins, K.D., Washabaugh, M.W. (1985). The Hofmeister effect and the behavior of water at interfaces. Q. Rev. Biophys. 18:323–422
Fabiato, A. (1985). Time and calcium dependence of activation and inactivation of calcium-induced release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum of a skinned canine cardiac Purkinje cell. J. Gen. Physiol. 85:247–289
Fettiplace, R., Gordon, L.G.M., Hladky, S.B., Requena, J., Zingsheim, H.P., Haydon, D.A., Methods of Membrane Biol. In: Methods of Membrane Biol, E.D. Korn, editor, pp. 1–75. Plenum Press, New York 1975
Fruen, B.R., Mickelson, J.R., Shomer, N.H., Roghair, T.J., Louis, C.F. (1994). Regulation of the sarcoplasmic reticulum ryanodine receptor by inorganic phosphate. J. Biol. Chem. 269:192–198
Herrmann-Frank, A., Varsanyi, M. (1993). Enhancement of Ca2+ release channel activity by phosphorylation of the skeletal muscle ryanodine receptor. FEBS Lett. 332:237–242
Ikemoto, N., Ronjat, M., Meszaros, L.G., Koshita, M. (1989). Postulated role of calsequestrin in the regulation of calcium release from sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biochemistry 28:6764–6771
Imagawa, T., Smith, J.S., Coronado, R., Campbell, K.P. (1987). Purified ryanodine receptor from skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum is the Ca2+-permeable pore of the calcium release channel. J. Biol. Chem. 262:16636–16643
Jayaraman, T., Brillantes, A.M., Timerman, A.P., Fleischer, S., Erdjuent-Bromage, H. Tempst, P., Marks, A.R. (1992). FK-506 binding protein associated with the calcium release channel (ryanodine receptor). J. Biol. Chem. 267:9474–9477
Lai, F.A., Anderson, K., Rousseau, E., Lui, Q.Y., Meissner, G. (1988). Evidence for a Ca2+ channel within the ryanodine receptor complex from cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 151:441–449
Laver, D.R., Walker, N.A. (1991). Activation by Ca2+ and block by divalent ions of the K+ channel in the membrane of cytoplasmic drops from Chara australis. J. Membrane Biol. 120:131–139
Lindsay, A.R., Williams, A.J. (1991). Functional characterisation of the ryanodine receptor purified from sheep cardiac muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1064:89–102
Lindsay, A.R., Manning, S.D., Williams, A.J. (1991). Monovalent cation conductance in the ryanodine receptor-channel of sheep cardiac muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum J. Physiol. Lond. 439:463–480
Ma., J. (1995). Desensitization of the skeletal muscle ryanodine receptor: Evidence of hetergeneity of calcium release channels. Biophys. J. 68:893–899
Marty, I., Robert, M., Villaz, M., De Jongh, K.S., Lai, Y., Catterall, W.A., Ronjat, M. (1994). Biochemical evidence for a complex in-volving dihydropyridine receptor and ryanodine receptor in triad junctions of skeletal muscle. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91:2270–2274
Meissner, G. (1986). Ryanodine activation and inhibition of the Ca2+ release channel of sarcoplasmic reticulum. J. Biol. Chem. 261:6300–6306
Menegazzi, P., Larini, F., Treves, S., Guerrini, R., Quadroni, M., Zorzato, F. (1994). Identification and characterization of three calmodulin binding sites of the skeletal muscle ryanodine receptor. Biochemistry 33:9078–9084
Miller, C., Racker, E. (1976). Ca++-induced fusion of fragmented sarcoplasmic reticulum with artificial planar bilayers. Cell 9:283–300
Moczydlowski, E., Alvarez, O., Vergara, C., Latorre, R. (1985). Effect of phospholipid surface charge on the conductance and gating of a Ca2+-activated K+ channel in planar lipid bilayers. J. Membrane Biol. 83:273–282
Moczydlowski, E., Latorre, R. (1983). Gating kinetics of Ca2+-activated K+ channels from rat muscle incorporated into planar lipid bilayers. Evidence for two voltage-dependent Ca2+ binding reactions. J. Gen. Physiol. 82:511–542
Mueller, P., Rudin, D.O., Tien, H.T., Westcott, W.C. (1962). Reconstitution of cell membrane structure in vitro and its transformation into an excitable system. Nature 194:979–981
Murayama, T., Ogawa, Y. (1992). Purification and characterization of two ryanodine-binding protein isoforms from sarcoplasmic reticulum of bullfrog skeletal muscle. J. Biochem. Tokyo. 112:514–522
Nabauer, M., Callewaert, G., Cleemann, L., Morad, M. (1989). Regulation of calcium release is gated by calcium current, not gating charge, in cardiac myocytes. Science 244:800–803
Otsu, K., Willard, H.F., Khanna, V.J., Zorzato, F., Green, N.M., MacLennan, D.H. (1990). Molecular cloning of cDNA encoding the Ca++ release channel (Ryanodine receptor) of rabbit cardiac muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. J. Biol. Chem. 265:13472–13483
Peng, M., Fan, H., Kirley, T.L., Caswell, A.M., Schwartz, A. (1994). Structural diversity of triadin in skeletal muscle and evidence of its existence in heart. FEBS Lett. 348:17–20
Perrin, D.D., Sayce, I.G. (1967). Computer calculation of equilibrium concentrations in mixtures of metal ions and complexing species. Talanta 14:833–842
Pessah, I.N., Waterhouse, A.L., Casida, J.E. (1985). The calciumryanodine receptor complex of skeletal and cardiac muscle. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 128:449–456
Rardon, D.P., Cefali, D.C., Mitchell, R.D., Seiler, S.M., Hathaway, D.R., Jones, L.R. (1990). Digestion of cardiac and skeletal muscle junctional sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles with calpain II. Effects on the Ca2+ release channel. Circ. Res. 67:84–96IS
Rousseau, E. (1989). Single chloride-selective channel from cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum studied in planar lipid bilayers. J. Membrane Biol. 110:39–47
Rousseau, E., Meissner, G. (1989). Single cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-release channel: activation by caffeine. Am. J. Physiol. 256:H328-H333
Rousseau, E., Smith, J.S., Henderson, J.S., Meissner, G. (1986). Single channel and 45Ca2+ flux measurements of the cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium channel. Biophys. J. 50:1009–1014
Rousseau, E., Smith, J.S., Meissner, G. (1987). Ryanodine modifies conductance and gating behavior of single Ca2+ release channel. Am. J. Physiol. 253:C364-C368
Shomer, N.H.; Louis, C.F.; Fill, M.; Litterer, L.A.; Mickelson, J.R. (1993). Reconstitution of abnormalities in the malignant hyperthermiasusceptible pig ryanodine receptor Am. J. Physiol. 264:C125-C135
Sigworth, F.J., Sine, S.M. (1987). Data transformations for improved display and fitting of single-channel dwell time histograms. Biophys. J. 52:1047–1054
Sitsapesan, R., Montgomery, R.A., MacLeod, K.T., Williams, A.J. (1991). Sheep cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium-release channels: modification of conductance and gating by temperature. J. Physiol. Lond. 434:469–488
Sitsapesan, R., Williams, A.J. (1990). Mechanisms of caffeine activation of single calcium-release channels of sheep cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum. J. Physiol. Lond. 423:425–439
Sitsapesan, R., Williams, A.J. (1994). Gating of the native and purified cardiac SR Ca2+-release channel with monovalent cations as permeant species. Biophys. J. 67:1484–1494
Smith, J.S., Coronado, R., Meissner, G. (1986). Single channel measurements of the calcium release channel from skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. Activation by Ca2+ and ATP and modulation by Mg2+. J. Gen. Physiol. 88:573–588
Timerman, A.P., Jayaraman, T., Wiederrecht, G., Onoue, H., Marks, A.R., Fleischer, S. (1994). The ryanodine receptor from canine heart sarcoplasmic reticulum is associated with a novel FK-506 binding protein. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 198:701–706
Tinker, A., Lindsay, A.R., Williams, A.J. (1992). A model for ionic conduction in the ryanodine receptor channel of sheep cardiac muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. J. Gen. Physiol. 100:495–517
Tsien, R.Y. (1980). New calcium indicators and buffers with high selectivity against magnesium and protons; Design, synthesis, and properties of prototype structures. Biochemistry 19:2396–2404
White, S.H., Thompson, T.E. (1973). Capacitance, area, and thickness variations in thin lipid films. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 323:7–22
Witcher, D.R., Kovacs, R.J., Schulman, H., Cefali, D.C., Jones, L.R. (1991). Unique phosphorylation site on the cardiac ryanodine receptor regulates calcium channel activity. J. Biol. Chem. 266:11144–11152
Woodhull, A.M. (1973). Ionic blockage of sodium channels in nerve. J. Gen. Physiol. 61:687–708
Zahradnikova, A., Palade, P. (1993). Procaine effects on single sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ release channels. Biophys. J. 64:991–1003
Zimanyi, I., Pessah, I.N. (1991). Comparison of [3H]ryanodine receptors and Ca++ release from rat cardiac and rabbit skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 256:938–946
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The authors wish to thank Heather Domaschenz for assisting with the experiments and P.W. Gage for his critical assessment of the manuscript. The research was supported by an Australian Research Council Senior Research Fellowship and a grant from the National Heart Foundation.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Laver, D.R., Roden, L.D., Ahern, G.P. et al. Cytoplasmic Ca2+ inhibits the ryanodine receptor from cardiac muscle. J. Membarin Biol. 147, 7–22 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00235394
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00235394