Summary
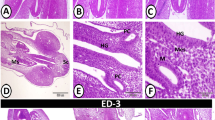
The villi of the caecal mucosa in postnatal rats were studied using both scanning electron and light microscopy.
On the day of birth, numerous villi of various sizes and shapes were present on the caecal mucosa. After the 5th day, the villi decreased very rapidly in length and in number. A strong constriction was observed at the basal region of the caecal villi. During postnatal days 5 ∼ 9 the villi probably separated and disappeared from the caecal mucosa. No villi were observed in rats that were over 10 days of age.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker SJ, Mathan VI, Cherian V (1963) The nature of the villi in the small intestine of the rat. Lancet 1:860
Burke JA, Holland P (1976) The epithelial surface of the monkey gastrointestinal tract. A scanning electron-microscopic study. Digestion 14:68–76
Gustafsson BE, Maunsbach AB (1971) Ultrastructure of the enlarged cecum in germfree rats. Z Zellforsch 120:555–578
Helander HF (1973) Morphological studies on the development of the rat colonie mucosa. Acta Anat 85:153–176
Henrikson C (1973) Ultrastructural aspects of mouse cecal epithelium. Z Zellforsch 140:445–449
Hilton WA (1902) The morphology and development of intestinal folds and villi in vertebrates. Am J Anat 1:459–504
Kavin H, Hamilton DG, Greasley RE, Eckert JD, Zuidema G (1970) Scanning electron microscopy. A new method in the study of rectal mucosa. Gastroenterology 59:426–432
Lewis FT (1912) The development of the large intestine. In: E Keibel and FP Mall (eds) Manual of Human Embryology Vol II pp 393–399
Ono K (1976a) Ultrastructure of the surface principal cells of the large intestine in postnatal developing rats. Anat Embryol 149:155–171
Ono K (1976b) Alkaline phosphatase activity of the large intestinal principal cells in postnatal developing rats.: Acta Histochem 57:312–319
Ono K (1977) Absorption of horseradish peroxidase by the principal cells of the large intestines of postnatal developing rats.: Anat Embryol 151:53–62
Ono K, Takashio M (1978) Scanning electron microscopic studies of ileal epithelial cells in suckling rats. Anat Embryol 153:1–8
Scherman D (1898) Über die Rückbildung der Darmzotten des Meerschweinchens. Verh d Phys med Gesellsch zu Würzburg NF 32:1–9
Takashio M, Yamauchi A (1975) A further comment on the osmium-thiocarbohydrazide-osmium staining methods for the scanning electron microscope specimens, p. 548 10th Int Cong Anat, Tokyo
Takeuchi A, Zeller JA (1972) Scanning electron microscopic observations on the surface of the normal and spirochete-infested colonie mucosa of the rhesus monkey. J Ultrastruct Res 40:313–324
Voigt J (1899) Beitrag zur Entwicklung der Darmschleimhaut. Anatomische Hefte XII Bd I, Abt. 38. Heft 51–68
Wille K-H (1975) Über die Schleimhautoberfläche des Blinddarmes einiger Haussäuger. Eine rasterelektronenmikroskopische Untersuchung. Zbl Ver Med C 4:265–273
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ono, K. Changes of the caecal villi during postnatal development in rats. Cell Tissue Res. 208, 253–259 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00234875
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00234875