Summary
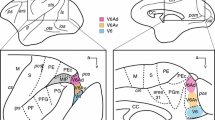
Degeneration density and topography in the thalamus of the squirrel monkey was studied following lesions in the septal area, fornix, and cingulate gyrus. It was found that the hippocampus projects more fibers to the anteroventral nucleus of the thalamus and the cingulate gyrus projects fewer fibers to it than does the septal area. The septal fibers to the anteromedial nucleus were more marked than were its projections to the anteroventral nucleus. The hippocampus and cingulate gyrus did not show this preferential projection. The thalamus is a more prominent target of limbic connections than heretofore realized. They appear to quantitatively rival known limbic-hypothalamic pathways. Therefore, in order to understand the total influence of the limbic system on cerebral function, one must consider its effects on thalamic perceptive mechanisms as well as effects on the hypothalamus.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Ac:
-
Anterior commissure
- Am:
-
Anteromedial nucleus of the thalamus
- Av:
-
Anteroventral nucleus of the thalamus
- Cb:
-
Cerebellum
- Cc:
-
Corpus callosum
- Cd:
-
Caudate nucleus
- Cg:
-
Cingulate gyrus
- Dm:
-
Dorsal medial nucleus of the thalamus
- Fx:
-
Fornix
- Gp:
-
Globus pallidus
- Ic:
-
Anterior limb of internal capsule
- It:
-
Inferior thalamic peduncle
- Ld:
-
Lateral dorsal nucleus of the thalamus
- Mb:
-
Mammillary body
- Oc:
-
Optic chiasm
- Of:
-
Orbital-frontal cortex
- Ot:
-
Olfactory tract
- Se:
-
Septum
- Sm:
-
Stria medullaris thalami
- Ti:
-
Temporal isocortex
References
Clemente, C.D., Sterman, M.B.: Limbic and other forebrain mechanisms in sleep induction and behavioral inhibition. Progr. Brain Res. 27, 34–47 (1967).
Domino, E.F., McCarthy, D.A., Deneau, G.A.: General anesthesia in infrahuman primates. Fed. Proc. 28, 1500–1509 (1969).
Emmers, R., Akert, K.: A Stereotaxic Atlas of the brain of the Squirrel Monkey. Madison: University of Wisconsin Press 1963.
Pink, R.P., Heimer, L.: Two methods for selective silver impregnation of degenerating axons and their synaptic endings in the central nervous system. Brain Res. 4, 369–374 (1967).
Grastyan, E.: Towards a better understanding of human emotion. Impact Sci. Soc. 18, 187–205 (1968).
Guillery, R.W.: Afferent fibers to the dorso-medial thalamic nucleus in the cat. J. Anat. (Lond.) 93, 403–419 (1959).
Livingston, K.E., Escobar, A.: Anatomical bias of the limbic system concept. Arch. Neurol. (Chic.) 24, 17–21 (1971).
Nauta, W.J.H.: Neural associations of the amygdaloid complex in the monkey. Brain 85, 505–520 (1962).
—, Gygax, P.A.: Silver impregnation of degenerating axons in the central nervous system: a modified technic. Stain Technol. 92, 91–93 (1954).
—, Haymaker, W.: Hypothalamic nuclei and fiber connections, pp. 136–209. In: The Hypothalamus. Ed. by W. Haymaker, E. Anderson. and W.J.H. Nauta. Springfield: Thomas 1969.
Papez, J.W.: A proposed mechanism of emotion. Arch. Neurol. Psychiat. (Chic.) 38, 725–744 (1937).
Pribram, K.H.: Neocortical function in behavior, pp. 151–172. In: Biological and Biochemical Bases of Behavior. Ed. by H.F. Harlow, and C.N. Woolsey. Madison: University of Wisconsin Press 1958.
Powell, E.W.: Septal efferents revealed by axonal degeneration in the rat. Exp. Neurol. 8, 406–422 (1963).
—: Septal efferents in the cat. Exp. Neurol. 14, 328–337 (1966).
—, Furlong, L.D., Hatton, J.B.: Influence of the septum and inferior colliculus on medial geniculate body units. Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol. 29, 74–82 (1970).
—, Hoelle, D.F.: Septo-tectal projections in the cat. Exp. Neurol. 18, 177–183 (1967).
—, Schnurr, R.: Silver impregnation of degenerating axons; comparisons of postoperative intervals, fixatives and staining methods. Stain Technol. 47, 95–100 (1972).
Powell, T.P.S., Guillery, R.W., Cowan, W.M.: A quantitative study of the fornix-mamillothalamic system. J. Anat. (Lond.) 91, 419–437 (1957).
Raisman, G.: The connexions of the septum. Brain 89, 317–348 (1966).
Simmons, H.J., Powell, E.W.: A quantitative analysis of septothalamic projections in the squirrel monkey. Anat. Rec. 166, 378 (1970).
—: Septomammillary projections in the squirrel monkey. Acta anat. (Basel) 82, 159–178 (1972).
Van Buren, J.M., Borke, R.C.: Hippocampal projections to the nucleus dorsalis superficialis (lateralis dorsalis) in man. Anat. Rec. 166, 392 (1970).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This research was supported by NSF Grant GB32170.
The author wishes to thank Drs. Charles Long of the Department of Psychology, Memphis State University and Herbert Schapiro of the Department of Anatomy, University of Tennessee Medical School for their critical review of the manuscript, and Dr. Carmine Clemente for his suggestions.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Powell, E.W. Limbic projections to the thalamus. Exp Brain Res 17, 394–401 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00234102
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00234102