Summary
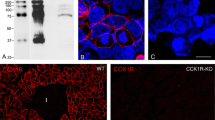
The cellular localization of the vitamin D-dependent calcium-binding protein (CaBP) in the duodenum of rat was studied using indirect immunofluorescence and immunoperoxidase staining methods. Specific positive reaction product, indicative of the presence of CaBP, was exclusively located within the villous part of the duodenal mucosa. Moreover, CaBP was detected mainly within the supranuclear region of the cytoplasm of absorptive cells and also at the level of their basal laminae. CaBP was not demonstrable either in the nuclei or associated with the brush border membrane of absorptive cells. Also, CaBP was neither detectable in goblet cells nor in sub-epithelial layers. When the specific anti-CaBP antiserum was replaced by nonimmune rabbit serum or when it was preabsorbed on a CaBP-Sepharose conjugate, no positive immunostaining was seen. Together with recent biochemical data our observations agree well with the view that CaBP may act as an intracellular “buffer” by protecting the cell against too high Ca2+ concentrations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnold, B.M., Kuttner, M., Willis, D.M., Hitchman, A.J.W., Harrison, J.E., Murray, T.M.: Radioimmunoassay studies of intestinal calcium-binding protein in the pig. The distribution of intestinal CaBP in pig tissues. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 53, 1135–1140 (1975)
Arnold, B.M., Kovacs, K., Murray, T.M.: Cellular localization of intestinal calcium-binding protein in pig duodenum. Digestion 14, 77–84 (1976)
Bikle, D.D., Zolock, D.T., Morrissey, R.L., Herman, R.H.: Independence of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3-mediated calcium transport from de novo RNA and protein synthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 253, 484–488 (1978)
Cambiaso, C.L., Goffinet, A., Vaerman, J.P., Heremans, J.F.: Glutaraldehyde-activated aminohexyl-derivative of Sepharose 4B as a new versatile immunoabsorbent. Immunochemistry 12, 273–278 (1975)
Emtage, J.S., Lawson, D.E.M., Kodicek, E.: Vitamin D-induced synthesis of mRNA for calcium-binding protein. Nature 246, 100–101 (1973)
Feher, J.J., Wasserman, R.H.: Evidence for a membrane-bound fraction of chick intestinal calcium-binding protein. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 540, 134–143 (1978)
Friedlander, E.J., Henry, H.L., Norman, A.W.: Studies on the mode of action of calciferol. J. Biol. Chem. 252, 8677–8683 (1977)
Gabe, M.: Techniques histologiques. Paris: Masson et Cie 1968
Graham, A.C., Karnovsky, M.J.: The early stages of absorption of injected horseradish peroxidase in the proximal tubules of mouse kidney: ultrastructural cytochemistry by a new technique. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 14, 291–325 (1966)
Helmke, K., Federlin, K., Piazolo, P., Stroder, J., Jeschke, R., Franz, H.E.: Localization of calcium-binding protein in intestinal tissue by immunofluorescence in normal, vitamin D-deficient and uraemic subjects. Gut 15, 875–879 (1974)
Hitchman, A.J.W., Harrison, J.E.: Calcium-binding proteins in the duodenal mucosa of the chick, rat, pig and human. Can. J. Biochem. 50, 758–765 (1972)
Marche, P., Pradelles, P., Gros, C., Thomasset, M.: Radioimmunoassay for a vitamin D-dependent calcium-binding protein in rat duodenal mucosa. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 76, 1020–1026 (1977)
Morrissey, R.L., Bucci, T.J., Empson, R.N., Lufkin, E.G.: Calcium-binding protein: its cellular localization in jejunum, kidney and pancreas. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 149, 56–60 (1975)
Morrissey, R.L., Empson, R.N., Zolock, D.T., Bikle, D.D., Bucci, T.J.: Intestinal response to 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol. A timed study of the intracellular localization of calcium-binding protein. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 538, 34–41 (1978)
Piazolo, P., Schleyer, M., Franz, H.E.: Isolation and purification of a calcium-binding protein from human tissues. Hoppe Seylers Z. Physiol. Chem. 352, 1480–1486 (1971)
Spencer, R., Charman, M., Wilson, P.W., Lawson, D.E.M.: The relationship between vitamin D-stimulated calcium transport and intestinal calcium-binding protein in the chicken. Biochem. J. 170, 93–101 (1978)
Taylor, A.N., McIntosh, J.E.: Light and electron microscopic immunoperoxidase localization of chick intestinal vitamin D-induced calcium-binding protein. In: Vitamin D. Biochemical, chemical and clinical aspects related to calcium metabolism (Norman, A.W., Schaefer, K., Coburn, J.W., De Luca, H.F., Fraser, D., Grigoleit, H.G., Herrath, D., eds.), pp. 303–312. Berlin, New York: Walter de Gruyter 1977
Taylor, A.N., Wasserman, R.H.: Immunofluorescent localization of vitamin D-dependent calcium-binding protein. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 18, 107–115 (1970)
Trier, J.: Structure of the mucosa of the small intestine as it relates to intestinal function. Fed. Proc. 26, 1391–1404 (1967)
Wasserman, R.H., Corradino, R.A., Feher, J.J., Ambrecht, HJ.: Temporal patterns of response of the intestinal calcium absorptive system and related parameters to 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol. In: Vitamin D. Biochemical, chemical and clinical aspects related to calcium metabolism (Norman, A.W., Schaefer, K., Coburn, J.W., De Luca, H.F., Fraser, D., Grigoleit, H.G., v. Herrath, D.V., eds.), pp. 331–340. Berlin, New York: Walter de Gruyter 1977
Wasserman, R.H., Corradino, R.A., Fullmer, C.S., Taylor, A.N.: Some aspects of vitamin D action; calcium absorption and the vitamin D-dependent calcium-binding protein. In: Vitamins and hormones (Harris, R.S., Munson, P.L., Diczfalusy, E., Glover, J., eds.), pp. 299–324. New-York: Academic Press 1974
Wasserman, R.H., Corradino, R.A., Taylor, A.N.: Vitamin D-dependent calcium-binding protein: purification and some properties. J. Biol. Chem. 243, 3978–3993 (1968)
Wasserman, R.H., Feher, J.J.: Vitamin D-dependent calcium-binding proteins. In: Calcium-binding proteins and calcium function (Wasserman, R.H., Corradino, R.A., Carafoli, E., Kretsinger, R.H., MacLennan, D.H., Siegel, F.L., eds.), pp. 293–302. New-York: North-Holland 1977
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marche, P., Le Guern, C. & Gassier, P. Immunocytochemical localization of a calcium-binding protein in the rat duodenum. Cell Tissue Res. 197, 69–77 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00233554
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00233554