Summary
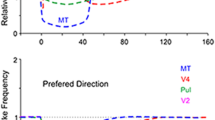
In immobilized pigmented rabbits anesthetized with N2O (70%) and halothane (2–4%), extracellular spikes were recorded from neurons in the nucleus reticularis tegmenti pontis (NRTP) and their responses to optokinetic stimulation (OKS) were examined. OKS was delivered using constant-velocity (0.1–4.0°/s) movements of a random dot pattern (60° × 60°) at 0°, 45°, 90° or 135° to the horizon. With OKS delivered to the contralateral eye (n=43), the preferred directions of NRTP cells were forward (F, n = 10), backward (B, n = 7), downward (D, n = 5), and the remaining cells showed no response (N, n = 21). With OKS delivered to the ipsilateral eye (n = 43), the preferred directions were F (n = 8), B (n = 8), upward (U, n = 2), D (n= 1) and N (n = 24). The majority of cells which responded to OKS (17/22 for contralateral, and 16/19 for ipsilateral OKS) preferred the horizontal orientation. The optimum velocity ranged from 0.2 to l°/s. The results suggest that the NRTP cells mainly transfer horizontal optikinetic signals to the flocculus and control horizontal optokinetic eye movements.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balaban CD (1983) A projection from nucleus reticularis tegmenti pontis of Bechterew to the medial vestibular nucleus in rabbits. Exp Brain Res 51: 304–309
Barthelemy J, Xerri C, Borel L, Lacour M (1988) Neuronal coding of linear motion in the vestibular nuclei of the alert cat. Exp Brain Res 70: 287–298
Cazin L, Precht W, Lannou J (1980a) Pathways mediating optokinetic responses of vestibular nucleus neurons in the rat. Pflügers Arch 384: 19–29
Cazin L, Precht W, Lannou J (1980b) Optokinetic responses of vestibular nucleus neurons in the rat. Pflügers Arch 384: 31–38
Cazin L, Precht W, Lannou J (1980c) Firing characteristics of neurons mediating optokinetic responses to rat's vestibular neurons. Pflügers Arch 386: 221–230
Cazin L, Magnin M, Lannou J (1982) Non-cerebellar visual afferents to the vestibular nuclei involving the prepositus hypoglossal complex: an autoradiographic study in the rat. Exp Brain Res 48: 309–313
Cazin L, Lannou J, Precht W (1984) An electrophysiological study of pathways mediating optokinetic responses to the vestibular nucleus in the rat. Exp Brain Res 54: 337–348
Crandall WF, Keller EL (1985) Visual and oculomotor signals in nucleus reticularis tegmenti pontis in alert monkey. J Neurophysiol 54: 1326–1345
Epema AH, Gerrits NM, Voogd J (1990) Secondary vestibulocerebellar projections to the flocculus and uvulonodular lobule of the rabbit: a study using HRP and double fluorescent tracer techniques. Exp Brain Res 80: 72–82
Graf W, Simpson JI, Leonard CS (1988) Spatial organization of visual messages of the rabbit's cerebellar flocculus. II. Complex and simple spike responses of Purkinje cells. J Neurophysiol 60: 2091–2121
Hess BJM, Blanks RHI, Lannou J, Precht W (1989) Effects of kainic acid lesions of the nucleus reticularis tegmenti pontis on fast and slow phases of vestibulo-ocular and optokinetic reflexes in the pigmented rat. Exp Brain Res 74: 63–79
Ito M (1984) The cerebellum and neural control. Raven Press, New York, pp 354–388
Ito M, Nisimaru N, Yamamoto M (1977) Specific patterns of neuronal connections involved in the control of the rabbit's vestibuloocular reflexes by the cerebellar flocculus. J Physiol (Lond) 265: 833–854
Ito M, Jastreboff PJ, Miyashita Y (1982a) Specific effects of unilateral lesions in the flocculus upon eye movements in albino rabbits. Exp Brain Res 45: 233–242
Ito M, Orlov I, Yamamoto M (1982b) Topographical representation of vestibuloocular reflexes in rabbit cerebellar flocculus. Neuroscience 7: 1657–1664
Kano M, Kusunoki M, Maekawa K (1987) Response properties of neurons in the nucleus prepositus hypoglossi and underlying reticular formation to optokinetic and vestibular stimuli. J Physiol Soc Jpn 48: 411
Kano M, Iino K, Maekawa K, Kano MS (1990a) Direction selectivity of cells in the nucleus reticularis tegmenti pontis projecting to the cerebellar flocculus to optokinetic stimulation in the pigmented rabbit. Jpn J Physiol 40 (Suppl): S202
Kano MS, Kano M, Maekawa K (1990b) Receptive field organization of climbing fiber afferents responding to optokinetic stimulation in the cerebellar nodulus and flocculus of the pigmented rabbit. Exp Brain Res 82: 499–512
Kano M, Kano MS, Maekawa K (1991) Optokinetic responses of simple spikes of Purkinje cells in the cerebellar flocculus and nodulus of the pigmented rabbit. Exp Brain Res: in press
Kato I, Harada K, Nakamura T, Sato Y, Kawasaki T (1982) Role of the nucleus reticularis tegmenti pontis on visually induced eye movements. Exp Neurol 78: 503–516
Kawaguchi Y (1985) Two groups of secondary vestibular neurons mediating horizontal canal signals, probably to the ipsilateral medial rectus muscle, under inhibitory influences from the cerebellar flocculus in rabbits. Neurosci Res 2: 434–446
Kitai ST, Kocsis JD, Kiyohara T (1976) Electrophysiological properties of nucleus reticularis tegmenti pontis cells: antidromic and synaptic activation. Exp Brain Res 24: 295–309
Kusunoki M, Kano M, Kano MS, Maekawa K (1990) Nature of optokinetic response and zonal organization of climbing fiber afferents in the vestibulocerebellum of the pigmented rabbit. I. The flocculus. Exp Brain Res 80: 225–237
Lannou J, Cazin L, Precht W, Le Taillanter M (1984) Responses of prepositus hypoglossi neurons to optokinetic and vestibular stimulations in the rat. Brain Res 301: 39–45
Le Taillanter M, Lannou J (1988) Responses of nucleus reticularis tegmenti pontis neurons to vestibular stimulation in the rat. Exp Brain Res 69: 417–423
Maekawa K, Kimura M (1981) Electrophysiological study of the nucleus of the optic tract that transfers optic signals to the nucleus reticularis tegmenti pontis — the visual mossy fiber pathway to the cerebellar flocculus. Brain Res 211: 456–462
Maekawa K, Takeda T (1978) Origin of the mossy fiber projection to the cerebellar flocculus from the optic nerves in rabbits. In: Ito M, Tsukahara N, Kubota K, Yagi K (eds) Integrative control functions of the brain, Vol 1. Kodansha, Tokyo; Elsevier, North-Holland, pp 93–95
Maekawa K, Takeda T, Kimura M (1981) Neural activity of nucleus reticularis tegmenti pontis — the origin of visual mossy fiber afferents to the cerebellar flocculus of rabbits. Brain Res 210: 17–30
Maekawa K, Takeda T, Kimura M (1984) Responses of the nucleus of the optic tract neurons projecting to the nucleus reticularis tegmenti pontis upon optokinetic stimulation in the rabbit. Neurosci Res 2: 1–25
McCrea RA, Baker R, Delgado-Garcia J (1979) Afferent and efferent organization of the prepositus hypoglossi nucleus. Prog Brain Res 50: 653–665
Miyashita Y, Nagao S (1984) Analysis of signal content of Purkinje cell responses to optokinetic stimuli in the rabbit cerebellar flocculus by selective lesions of brainstem pathways. Neurosci Res 1: 223–241
Miyashita Y, Ito M, Jastreboff PJ, Maekawa K, Nagao S (1980) Effect upon eye movements of rabbits induced by severance of mossy fiber visual pathway to the cerebellar flocculus. Brain Res 198: 210–215
Nagao S (1983) Effects of vestibulocerebellar lesions upon dynamic characteristics and adaptation of vestibulo-ocular and optokinetic responses in pigmented rabbits. Exp Brain Res 53: 36–46
Sato Y, Kawasaki T, Ikarashi K (1983) Afferent projections from the brainstem to the three floccular zones in cats. II. Mossy fiber projections. Brain Res 272: 37–48
Torigoe Y, Blanks RHI, Precht W (1986) Anatomical studies on the nucleus reticularis tegmenti pontis in the pigmented rat. II. Subcortical afferents demonstrated by the retrograde transport of horseradish peroxidase. J Comp Neurol 243: 88–105
Yamamoto M (1979) Topographical representation in rabbit cerebellar flocculus for various afferent inputs from the brainstem investigated by means of retrograde axonal transport of horseradish peroxidase. Neurosci Lett 12: 29–34
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kano, M., Iino, K., Maekawa, K. et al. Optokinetic response of cells in the nucleus reticularis tegmenti pontis of the pigmented rabbit. Exp Brain Res 87, 239–244 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00231840
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00231840