Summary
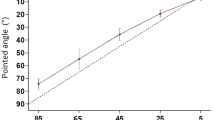
The responses of non-cutaneous receptors in the human hand to normal digit movements were studied using single afferent recordings from the radial nerve. Eight joint-related afferents had thresholds of 50 mN or less. All responded to passive flexion movements within the physiological range of joint rotation and showed predominantly static response sensitivity; none increased its discharge during passive extension. However, only two of these eight afferents showed the same response pattern during active movements; three discharged only during the extension phase whereas the other three discharged both during extension and flexion. No highthreshold, joint-related mechanoreceptive afferents were encountered in a population of 148 afferents recorded from the cutaneous portion of the radial nerve indicating a scarcity of such afferents on the dorsal aspect of finger joints. Seven high-threshold, subcutaneous mechanoreceptive units not related to joints had thresholds for indentations of 50 mN or more and lacked responses to finger movements. Low-threshold mechanoreceptive afferents related to joints in the human hand may thus provide kinematic information in the physiological midrange of both passive and active movements. Joint position cannot, however, be derived unambiguously from their discharge since the receptor responses may be dramatically altered by muscle activity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boyd IA (1954) The histological structure of the receptors in the knee joint of the cat correlated with their physiological response. J Physiol (London) 123:476–488
Boyd IA, Roberts TDM (1953) Proprioceptive discharges from stretch-receptors in the knee-joint of the cat. J Physiol (London) 122:38–58
Burgess PR, Clark FJ (1969) Characteristics of knee joint receptors in the cat. J Physiol (London) 203:317–335
Burke DA, Gandevia SC, Macefield G (1988) Responses to passive movement of receptors in joint, skin and muscle of the human hand. J Physiol (London) 402:347–361
Clark FJ, Burgess PR (1975) Slowly adapting receptors in cat knee joint: can they signal joint angle? J Neurophysiol 38:1448–1463
Clark FJ, Grigg P, Chapin JW (1989) The contribution of articular receptors to proprioception with the fingers in humans. J Neurophysiol 61:186–193
Craske B (1977) Perception of impossible limb positions induced by tendon vibration. Science 196:71–73
Cross MJ, McCloskey DI (1973) Position sense following surgical removal of joints in man. Brain Res 55:443–445
Edin BB, Bäckström PA, Bäckström LO (1988) Single unit retrieval in microneurography: a microprocessor-based device controlled by an operator. J Neurosci Methods 24:137–144
Ferrell WR, Gandevia SC, McCloskey DI (1987) The role of joint receptors in human kinaesthesia when intramuscular receptors cannot contribute. J Physiol (London) 386:63–71
Goodwin GM, McCloskey DI, Matthews PBC (1972) The persistence of appreciable kinesthesia after paralysing joint afferents but preserving muscle afferents. Brain Res 37:326–3229
Grigg P, Fingerman GA, Riley LH (1973) Joint position sense after total hip replacement. J Bone J Surg 55A:1016–1025
Grigg P, Greenspan BJ (1977) Response of primate joint afferent neurons to mechanical stimulation of the knee joint. J Neurophysiol 40:1–8
Houk JA, Henneman EL (1967) Responses of Golgi tendon organs to active contractions of the soleus muscle of the cat. J Neurophysiol 30:466–481
Hulliger M, Nordh E, Thelin A-E, Vallbo ÅB (1979) The response of afferent fibres from the glabrous skin of the hand during voluntary finger movements in man. J Physiol (London) 291:233–249
Jansen JKS, Rudjord T (1964) On the silent period and Golgi tendon organs of the soleus muscle of the cat. Acta Physiol Scand 62:364–379
Kelso JAS, Holt KG, Flatt AE (1980) The role of proprioception in the perception and control of human movement: toward a theoretical reassessment. Percept Psychophys 28:45–52
McCloskey DI (1978) Kinesthetic sensibility. Physiol Rev 58:763–820
Mclntyre AK, Proske U, Tracey DJ (1978) Afferent fibers from muscle receptors in the posterior nerve of the cat's knee joint. Brain Res 61:119–131
Millar JU (1973) Joint afferent fibres responding to muscle stretch, vibration and contraction. Brain Res 63:380–383
Proske U, Schaible H-G, Schmidt RF (1988) Joint receptors and kinaesthesia. Exp Brain Res 72:219–224
Romanes GJ (1981) Joints. In: Romanes GJ (ed) Cunningham's textbook of anatomy. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 240–242
Schaible H-G, Schmidt RF (1983) Responses of fine medial articular nerve afferents to passive movements of knee joint. J Neurophysiol 49:1118–1126
Skoglund S (1956) Anatomical and physiological evidence of knee joint innervation in the cat. Acta Physiol Scand [Suppl] 124
Torebjörk HE, Vallbo ÅV, Ochoa JL (1987) Intraneural microstimulation in man: its relation to specificity of tactile sensations. Brain 110:1509–1529
Vallbo ÅB, Hagbarth K-E (1968) Activity from skin mechanoreceptors recorded percutaneously in awake human subjects. Exp Neurol 21:270–289
Zimny ML (1988) Mechanoreceptors in articular tissues. Am J Anat 182:16–32
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Edin, B.B. Finger joint movement sensitivity of non-cutaneous mechanoreceptor afferents in the human radial nerve. Exp Brain Res 82, 417–422 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00231261
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00231261