Summary
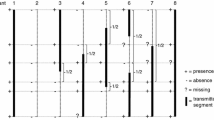
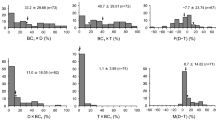
Isozyme analysis of Brassica napus cv ‘Topas’ and CGRC5006 as well as of Sinapis alba cv ‘Emergo’ revealed significant polymorphism between the two species for the isozymes, aconitate hydratase, glucose phosphate isomerase, and diaphorase. F1 hybrids between B. napus ‘5006’ and S. alba cv ‘Emergo’ were backcrossed to B. napus cv ‘Topas’, and the S1 progeny of the first two backcrosses were studied isozymically. At the backcross one level the frequency of S. alba or S. alba plus B. napus patterns observed ranged from 18% to 87% across the four lines studied. There were differences between lines for the frequency of S. alba patterns, which could have an impact on the efficiency of selection for subsequent backcrossing. By the backcross two generation in one of the two lines studied, GR86-24, the S. alba patterns for GPI and DIA had been lost, while in the other line, GR86-28, the S. alba pattern for ACO had been lost, resulting in lost opportunity for S. alba gene transfer. In a wide cross such as S. alba x B. napus, which requires an intensive effort to accomplish, the isozymes ACO, GPI, and DIA may serve as useful markers to ensure gene transfer between the two species has occurred. In addition, the identification of lines with divergent isozyme patterns from B. napus will provide the basis for establishing linkages between S. alba traits of interest and isozyme markers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bodnaryk RP, Lamb RJ (1991) Mechanisms of resistance to flea beetle, Phyllotreta cruciferae (Goeze), in mustard seedlings, Sinapis alba L. Can J Plant Sci: 71:13–20
Brun HJ, Plessis J, Renard M (1987) Resistance of some crucifers to Altemaria brassicae (Berk) Sacc. In: Regnault Y, Rimmer SG (eds) Proc Int Rapeseed Cong. Polska Agencja Interpress, Poznan, Poland, pp 1222–1227
Chen BY, Heneen WK, Simonsen V (1989) Genetics of isozyme loci in Brassica campestris L. and in the progeny of a trigenomic hybrid between B. napus L and B. campestris L. Genome 33:433–440
Chevre AM, This P, Eber F, Deschamps M, Renard M, Delseny M, Quiros CF (1991) Characterization of disomic addition lines Brassica napus-Brassica nigra by isozyme, fatty acid and RFLP markers. Theor Appl Genet 81:43–49
Chien YC, Kao KN, Wetter LR (1982) Chromosomal and isozyme studies of Nicotiana tabacum—Glycine max hybrid cell lines. Theor Appl Genet 62:301–304
Mizushima U (1980) Genome analysis in Brassica and allied genera. In: Tsunoda S, Hinata K, Gomez-Campo C (eds) Brassica crops and wild allies. Jpn Sci Soc Press, Tokyo, pp 89–106
Quiros CF, Ochoa O Douches DS (1988) Exploring the role of X=7 species in Brassica evolution; Hybridization with B. nigra and B. oleracea. J Hered 79:351–358
Ripley VL, Arnison PG (1990) Hybridization of Sinapis alba and Brassica napus L. via embryo rescue. Plant Breed 104:26–33
Schenk HR, Wolf G (1986) Characterization of somatic Brassica napus hybrids by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Plant Breed 97:72–74
Suarez JC, Graef GL, Fehr WR, Cianzo SR (1991) Association of isozyme genotypes with agronomic and seed composition traits in soybean. Euphytica 52:137–146
Tanksley D, Medina-Filho H, Rick CM (1981) The effect of isozyme selection on metric characters in an interspecific backcross of tomato — Basis of an early screening procedure. Theor Appl Genet 60:291–296
Thorpe ML, Duke LH, Beversdorf WD (1987) Procedures for the detection of isozymes of rapeseed (Brassica napus and B. campestris) by starch gel electrophoresis OAC. Tech Bull 887:1–65
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by H. F. Linskens
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ripley, V., Thorpe, M., Iler, S. et al. Isozyme analysis as a tool for introgression of Sinapis alba germ plasm into Brassica napus . Theoret. Appl. Genetics 84, 403–410 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00229500
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00229500