Abstract
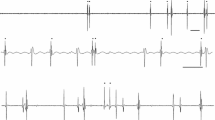
This study investigated the morphology of action potentials and the frequency of occurrence of the various waveforms encountered when using microneurography to record single-unit muscle afferent activity in humans. With 75% of the afferents recorded in this study (55 of 73 afferents), action potentials had a doublepeaked morphology. For action potentials with an initial, positive double peaked morphology, the relevant afferent conducts impulses past the microelectrode, with the second peak representing current fluctuations at the node of Ranvier proximal to the electrode. Accordingly, in the majority of recordings, the afferent is capable of conducting impulses to the spinal cord. The mean interpeak interval for these double-peaked units was 168 μs (range 90–310 μs). This represents marked prolongation of conduction time across the impaled internode. When the interpeak interval was relatively short (90–120 μs), the double peaked morphology could be recognized only if the low pass filter was high (≥10 kHz). The probability of recording a double peaked unit was the same whether the recording was acquired early or late in a 3-h experiment. Conduction block developed in 6 of 73 single units during the recordings. These findings indicate that the majority of isolated single afferents and, indeed, the majority of afferents within the relevant fascicle are capable of transmitting impulses across the recording site, even though conduction across the impaled internode is slow. Conduction block due to direct injury or pressure is relatively uncommon.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bischoff A, Thomas PK (1975) Microscopic anatomy of myelinated nerve fibers. In: Dyck PJ, Thomas PK, Lambert EH (eds) Peripheral neuropathy, vol 1. Saunders, Philadelphia
Brink EE, Mackel RG (1993) Time course of action potentials recorded from single human afferents. Brain 116:415–432
Burke D (1981) The activity of human muscle spindle endings in normal motor behavior. Int Rev Neurophysiol 25:91–126
Burke D, Aniss AM, Gandevia SC (1987) In-parallel and in-series behavior of human muscle spindle endings. J Neurophysiol 58:417–426
Calancie BM, Stein RB (1988) Microneurography for the recording and selective stimulation of afferents: an assessment. Muscle Nerve 11:638–644
David G, Barrett JN, Barrett EF (1993) Activation of internodal potassium conductance in rat myelinated axons. J Physiol (Lond) 472:177–202
Edin BB, Bäckström PA, Bäckström LO (1988) Single unit retrieval in microneurography: a microprocessor based device controlled by an operator. J Neurosci Methods 24:137–144
Katz B (1939) Electric excitation of nerve. Oxford University Press, London
Lafontaine S, Rasminsky M, Saida T, Sumner AJ (1982) Conduction block in rat myelinated fibres following acute exposure to anti-galactocerebroside serum. J Physiol (Lond) 323:287–306
Macefield G, Gandevia SC, Burke D (1990) Perceptual responses to microstimulation of single afferents innervating joints, muscles and skin of the human. J Physiol (Lond) 429:113–129
McKeon B, Burke D (1980) Identification of muscle spindle afferents during in vivo recordings in man. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 48:606–608
Rasminsky M, Sears TA (1972) Internodal conduction in undissected demyelinated nerve fibres. J Physiol (Lond) 227:323–350
Rice ASC, McMahon SB, Wall PD (1993) The electrophysiological consequences of electrode impalement of peripheral nerves in the rat. Brain Res 631:221–226
Tasaki I (1952) Properties of myelinated fibres in frog sciatic nerve and in spinal cord as examined with microelectrodes. Jap J Physiol 3:73–94
Torebjörk HE, Hallin RG, Hongell A, Hagbarth K-E (1970) Single unit potentials with complex waveform seen in microelectrode recordings from the human median nerve. Brain Res 24:443–450
Torebjörk HE, Vallbo ÂB, Ochoa JL (1987) Intraneural microstimulation in man. Its relation to specificity of tactile sensations. Brain 110:1509–1529
Vallbo ÂB (1970) Slowly adapting muscle receptors in man. Acta Physiol Scand 78:315–333
Vallbo ÂB (1972) Single unit recording from human peripheral nerves: muscle receptor discharge in resting muscles and during voluntary contractions. In: Somjen GG (ed) Neurophysiology studied in man. Excerpta Medica, Amsterdam
Vallbo ÂB (1976) Prediction of propagation block on the basis of impulse shape in single unit recordings from human nerves. Acta Physiol Scand 97:66–74
Vallbo ÂB, Hagbarth K-E (1968) Activity from skin mechanoreceptors recorded percutaneously in awake human subjects. Exp Neurol 21:270–289
Vallbo ÂB, Hagbarth K-E, Torebjörk HE, Wallin B (1979) Somatosensory, proprioceptive, and sympathetic activity in human peripheral nerves. Physiol Rev 59:919–957
Wall PD, McMahon SB (1985) Microneurography and its relation to perceived sensation. A critical review. Pain 21:209–229
Woodbury JW (1952) Direct membrane resting and action potentials from single myelinated nerve fibres. Cell Comp Physiol 39:323–339
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Inglis, J.T., Leeper, J.B., Burke, D. et al. Morphology of action potentials recorded from human nerves using microneurography. Exp Brain Res 110, 308–314 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00228561
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00228561