Summary
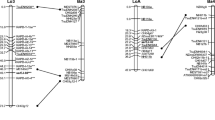
Using primarily cDNA restriction fragment length polymorphism markers (RFLPs) previously located to Brassica oleracea (cabbage, 2n=18) chromosomes, we initiated a comparative RFLP map in an F2 population of B. campestris (turnip x mock pak-choi, 2n=20). As with B. oleracea, the genome of B. campestris showed extensive gene duplication, and the majority of detected duplicated loci were unlinked. Only 6 of the 49 identified loci were represented as a single copy, and 3 of these 6 were clustered on a single linkage group showing a distorted segregation ratio. Comparison with B. Oleracea indicates this synteny is conserved between species. Two other linkage groups also appeared syntenic between B. oleracea and B. campestris. One single copy locus appears to have changed synteny between B. oleracea and B. campestris. These observations suggest that B. oleracea and B. campestris share a common ancestor, but that chromosome repatterning has occurred during or after speciation. Within B. campestris, 5 loci appeared duplicated in one parent or the other, and 2 of these were linked. Differentiation through subspecies-specific duplication or deletion events is suggested as one mechansim for the evolution of numerous morphotypes within each of these species.
Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
Attia T, Röbbelen G (1986) Cytogenetic relationship within cultivated Brassica analyzed in amphihaploids from the three diploid ancestors. Can J Genet Cytol 28:323–329
Bernatzsky R, Tanksley SD (1986) Majority of random cDNA clones correspond to single loci in the tomato genome. Mol Gen Genet 203:8–14
Bonierbale MW, Plaisted RL, Tanksley SD (1988) RFLP maps based on a common set of clones reveal modes of chromosomal evolution in potato and tomato. Genetics 120:1095–1103
Chiang, M. S., Crête, R. (1983) Transfer of resistance to race 2 of Plasmodiophora brassicae from Brassica napus to cabbage (B. oleracea ssp. capitata). V. The inheritance of resistance. Euphytica 32:479–483
Coulthart M, Denford KE (1982) Isozyme studies in Brassica. I. Electrophoretic techniques for leaf enzymes and comparison of B. napus, B. campestris, and B. oleracea using phosphoglucomutase. Can J Plant Sci 62:621–630
Crouch ML, Tenbarge KM, Simon AE, Ferl R (1983) cDNA clones from Brassica napus seed storage proteins: evidence from nucleotide sequence analysis that both subunits of napin are cleaved from a precursor polypeptide. J Mol Appl Genet 2:273–283
Feinberg AP, Vogelstein B (1983) A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction fragments to a high specific activity. Anal Biochem 132:6–13
Harada JJ, Baden CS, Comai L (1988) Spatially regulated genes expressed during seed germination and postgerminative development are activated during embryogeny. Mol Gen Genet 212:466–473
Hosaka K, Kianian SF, McGrath JM, Quiros CF (1990) Development and chromosome localization of genome-specific DNA markers of Brassica and the evolution of amphidiploids and n=9 diploid species. Genome 33:131–142
Helentjaris T, Weber D, Wrigth S (1988) Identification of the genomic locations of duplicate nucleotide sequences in maize by analysis of restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Genetics 118:353–363
Hulbert SH, Richter TE, Axtell JD, Bennetzen JL (1990) Genetic mapping and characterization of sorghum and related crops by means of maize DNA probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:4251–4255
Lander ES, Green P, Abrahamson J, Barlow A, Daly MJ, Lincoln SE, Newburg L (1987) MAPMAKER: an interactive computer package for constructing primary genetic linkage maps of experimental and natural populations. Genomics 1:174–181
Maniatis T, Fritsch EF, Sambrook J (1982) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y.
McGrath JM, Quiros CF (1990) Generation of alien chromosome addition lines from synthetic Brassica napus: morphology, cytology, fertility and chromosome transmission. Genome 33:374–383
McGrath JM, Quiros CF (1991) Inter-subspecies hybrids and their progeny in Brassica campestris L. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 116:349–355
McGrath JM, Quiros CF, Harada JJ, Landry BS (1990) Identification of Brassica oleracea monosomic alien chromosome addition lines with molecular markers reveals extensive gene duplication. Mol Gen Genet 223:198–204
Palmer JD (1988) Interspecific variation and multicircularity in Brassica mitochondrial DNA. Genetics 118:341–351
Palmer JD, Shields CR, Cohen DB, Orton TJ (1983) Chlorolast DNA evolution and the origin of amphidiploid Brassica species. Theor Appl Genet 65:181–189
Prakash S, Hinata K (1980) Taxonomy, cytogenetics and origin of crop Brassicas, a review, Opera Bot 55:1–57
Quiros CF, Ochoa O, Kianian S, Douches D (1987) Analysis of the Brassica oleracea genome by the generation of B. campestris-oleracea chromosome addition lines. Theor Appl Genet 74:758–766
Saghai-Maroof MA, Soliman KM, Jorgensen RA, Allard RW (1984) Ribosomal DNA spacer-length polymorphisms in barley: Mendelian inheritance, chromosomal location, and population dynamics. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:8014–8018
Slocum MK (1989) Analyzing the genomic structure of Brassica species and subspecies using RFLP analysis. In: Helentjaris T, Burr B (eds) Development and application of molecular markers to problems in plant genetics. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y. pp 73–80
Slocum MK, Figdore SS, Kennard WC, Suzuki JY, Osborn TC (1990) Linkage arrangement of restriction fragment length polymorphism loci in Brassica oleracea. Theor Appl Genet 80:57–64
Song K, Osborn TC, Williams PH (1990) Brassica taxonomy based on nuclear restriction fragment polymorphisms (RFLPs). 3. Genome relationships in Brassica and related genera and the origin of B. oleracea and B. rapa (syn. campestris). Theor Appl Genet 79:497–506
Suiter KA, Wendel JF, Case JS (1983) Linkage-1: a pascal computer program for the detection and analysis of genetic linkage. J Hered 74:203–204
Tanksley SD, Bernatzky R, Lapitan NL, Prince JP (1988) Conservation of gene repertoire but not gene order in pepper and tomato. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:6419–6423
Verma SC, Rees H (1974) Nuclear DNA and the evolution of allotetraploid Brassicae. Heredity 33:61–68
Yarnell SH (1956) Cytogenetics of the vegetable crops. II. Crucifers. Bot Rev 12:81–166
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by H. F. Linskens
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McGrath, J.M., Quiros, C.E. Inheritance of isozyme and RFLP markers in Brassica campestris and comparison with B. oleracea . Theoret. Appl. Genetics 82, 668–673 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00227309
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00227309