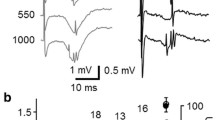
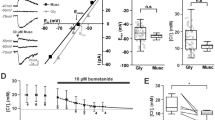
Abstract
In the in vitro hippocampal slice, novel interactions of a β-adrenergic agonist (l-isoproterenol) and neuropeptide (cholecystokinin 8-S) differentially produce long-lasting modifications in the dentate gyrus. When co-applied, a low concentration of l-isoproterenol (50–75 nM) and cholecystokinin 8-S (1.0 μM) produce long-lasting depression of evoked action potentials (i.e., population spikes). In contrast, the same concentration of l-isoproterenol followed by a 30-min wash with artificial cerebrospinal fluid and application of cholecystokinin 8-S produces long-lasting potentiation of evoked action potentials. In neither condition are there corresponding modifications of excitatory post-synaptic potentials. These results indicate that l-isoproterenol and cholecystokinin 8-S temporally interact to differentially produce depression or potentiation of granule cell activation. In contrast to long-lasting modifications produced by continuous application of 1.0 μM l-isoproterenol, in which both evoked action potentials and excitatory post-synaptic potentials are affected, the present novel paradigm may modify an extra-synaptic locus.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson P, Holmqvist B, Voorhoeve PE (1966) Entorhinal activation of dentate granule cells. Acta Physiol Scand 66:448–460
Axelrod J (1971) Noradrenalin: fate and control of its biosynthesis. Science 173:598–606
Burgard EC and Sarvey JM (1991) Long-lasting potentiatyion and epileptiform activity produced by GABAB receptor activation in the dentate gyrus of the rat hippocampal slice. J Neurosci 11:1198–1209
Dahl D (1988) Central administration of cholecystokinin potentiates evoked potential amplitude in the hippocampal dentate gyrus. Neuropept 11:147–151
Dahl D, LeCompte BB (1994) Cholecystokinin and response modifications in hippocampal field CA1. Psychobiology (in press)
Dahl D, Li J, Anderson, J (1993) The sign of long-lasting EAP modification in the dentate gyrus is predicted by the sequence of ISO-CCK 8-S application. Soc Neurosci Abstr 19:547.19
Dahl D, Sarvey JM (1990) β-adrenergic agonist-induced longlasting synaptic modifications inhippocampal dentate gyrus require activation of NMDA receptors, but not electrical activation of afferents. Brain Res 526:347–350
Fekete M, Lengyel A, Hegedus B, Penke B, Zarandy M, Toth G, Telegdy G (1984) Further analysis of cholecystokinin octapeptides on avoidance behavior in rats. Eur J Pharm 98:79–91
Gustafsson B, Wigstrom H (1986) Hippocampal long-lasting potentiation produced by pairing single volleys and brief conditioning tetani evoked in separate afferents. J Neurosci 6:1575–1582
Handelmann GE, Meyer DK, Bienfeld MC, Oertel WH (1981) CCK-containing terminals in the hippocampus are derived from intrinsic neurons: an immunochemical radioimmunological study. Brain Res 224:180–184
Harrison NL (1990) On the presynaptic action of baclofen on inhibitory synapses between cultured rat hippocampal neurons. J Physiol 422:433–446
Hopkins WF, Johnston D (1984) Frequency-dependent noradrenergic facilitation of long-term potentiation in hippocampus. Science 226:350–352
Inroini IB, McGaugh JL (1986) Epinephrine modulates long-term retention of an aversely motivated discrimination. Behav Neural Biol 45:358–365
Jones BE, Yang TZ (1985) The efferent projections from the reticular formation and the locus coeruleus studied by anterograde and retrograde axonal transport. J Comp Neurol 242:56–92
Lisman J (1989) A mechanism for Hebb and anti-Hebb processes underlying learning and memory. Proc Natl Acad Sci 86:9574–9578
Matthies H, Reymann KG (1993) Protein kinase A inhibitors prevent the maintenance of hippocampal long-term potentiation. NeuroRep 4:712–714
McNaughton BL, Douglas RM, Goddard GV (1978) Synaptic enhancement in the fascia dentata: cooperativity among coactive afferents. Brain Res 157:277–293
Northrup JK (1989) Regulation of cyclic nucleotides In: Siegel G, Agranoff B, Albers RW, Molinoff P (eds) Basic Neurochemistry, 4th edn. Raven Press, New York
Pan J-T, Kow L-M, Pfaff DW (1988) Modulatory actions of LHRH on preoptic neurons in brain slices. Neuroscience 2:107–117
Rich-Bennett ER, Dahl D, LeCompte BB (1993) Modulation of paired-pulse activation in the hippocampal dentate gyms by cholecystokinin, baclofen, and bicuculine. Neuropept 24:263–270
Segal M (1976) Interactions of ACTH and norepinephrine on the activity of rat hippocampal cells. Neuropharmacology 15:329–333
Slack JR, Pockett S (1991) Cyclic AMP-induced long-term potentiation in synaptic efficacy in CA1 region of rat hippocampus. Neurosci Lett 13:69–72
Staubli U, Thibault O, DiLorenzo M, Lynch G (1989) Antagonism of NMDA receptors impairs acquisition but not retention of olfactory memory. Behav Neurosci 103:54–60
Studler JM, Reibaud M, Herve D, Blanc G, Glowinski J, Tassin JP (1986) Opposite effects of sulfated cholecystokinin on DA-sensitive adenylate cyclase in two areas of the rat nucleus accumbens. Eur J Pharm 126:125–128
Sunayashiki-Kusuzaki K, Lester DS, Schreurs BG, Alkon D (1993) Associative learning potentiates protein kinase C activation in synaptosomes of the rabbit hippocampus. Proc Natl Acad Sci 90:4286–4289
Teyler TJ, DiScenna P (1984) Long-term potentiation as a candidate mnemonic device. Brain Res Rev. 7:15–28
Schwartzkroin P, Wester K (1975) Long-lasting facilitation of synaptic potential following tetanization in the rat in vitro hippocampal slice. Brain Res 89:107–119
Wigstrom H, Gustafsson B (1985) Facilitation of hippocampal long-term potentiation by GABA antagonists. Acta Physiol Scand 125:159–172
Winson J, Dahl D (1985) Action of norepinephrine in the dentate gyrus. II. Iontophoretic studies. Exp Brain Res 59:497–506
Zilles K (1991) Receptors in the human nervous system. Academic Press, New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dahl, D., Li, J. Long-lasting potentiation and depression by novel isoproterenol and cholecystokinin 8-S interactions in the dentate gyrus. Exp Brain Res 100, 155–159 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00227288
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00227288