Summary
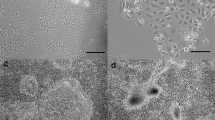
This study traced the origin of cells observed in human breast secretion samples obtained during lactation and describes the appearance of these cells following prolonged maintenance in vitro. Human milk contains a large number of single vacuolated foam cells and a small proportion of non-vacuolated epithelial cells in clusters. Foam cells are identified by their large size, the polarity of their cytoplasmic organelles, the variation in number and size of lipid vacuoles and the condensed chromatin of their eccentrically located nucleus. Both cell types originate by exfoliation from the mammary gland. This was established by comparing the structural characteristics of cells isolated from milk with those of the cuboidal cell linings of ducts and alveoli in lactating mammary tissue. Relatively pure populations of foam cells could be established from early lactation samples (3–7 days post/partum) while non-vacuolated epithelial cell clusters were more frequently cultured from late lactation specimens (1–10 days postweaning). Foam cells did not divide and lost cytoplasmic organization during prolonged culture. In contrast, non-vacuolated epithelium in clusters proliferated to form colonies of polygonal cells. These results, which imply that foam cells are an active form of the non-vacuolated mammary cells in clusters, call attention to one system for the study of the complex hormonal interactions necessary to induce and maintain lactation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Buehring, G.C.: Culture of human mammary epithelial cell: Keeping abreast with a new method. J. nat. Cancer Inst. 49, 1433–1434 (1972)
Ceriani, R.L., Contesso, G.P., Nataf, B.M.: Hormone requirement for growth and differentiation of human mammary gland in organ culture. Cancer Res. 32, 2190–2196 (1972)
Flaxman, B.A., Van Scott, E.J.: Growth of normal human mammary gland epithelium in vitro. Cancer Res. 32, 2407–24012 (1972)
Flaxman, B.A.: In vitro studies of the normal human mammary gland. J. invest. Derm. 63, 48–57 (1974)
Furmanski, P., Longley, C., Fouchey, D., Rich, R., Rich, M.A.: Normal human mammary cells in culture: Evidence for oncornairus-like particles. J. nat. Cancer Inst. 52, 975–977 (1974)
Holmquist, D.G., Papanicolaou, G.N.: The exfoliate cytology of the mammary gland during pregnancy and lactation. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 63, 1422–1435 (1956)
Papanicolaou, G.N.: Smears. Science 95, 438–439 (1942)
Papanicolaou, G.N., Bader, G.M., Holmquist, D.G., Falls, E.A.: Cytologic evaluation of breast secretions. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 63, 1409–1421 (1956)
Papanicolaou, G.N., Holmquist, D.G., Bader, G.M., Falk. E.A.: Exfoliate cytology of the human mammary gland and its value in the diagnosis of cancer and other diseases of the breast. Cancer (Philad.) 2, 377–409 (1958)
Russo, J., Furmanski, P., Rich, M.A.: An ultrastructural study of normal human mammary epithelial cells in culture. Amer. J. Ant. 142, 221–231
Stockdale, F.E., Juergens, W.G., Topper, Y.J.: A histological and biochemical study of hormone-dependent differentiation of mammary gland tissue in vitro. Develop. Biol. 13, 266–281 (1966)
Spurr, A.R.: A low-viscosity epoxy resin embedding medium for electron microscopy. J. Ultrastruct. 36, 21–46(1969)
Tobon, H., Salazar, H.: Ultrastructure of the human mammary gland. II. Postpartum lactogenesis. J. clin. Endocr. 40, 834–844 (1975)
Venable, J.H., Coggeshall, R.: A simplified lead citrate stain for use in electron microscopy. J. Cell Biol. 25, 402–408 (1965)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported in part by NCI contract NO 1-CB-33898
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gaffney, E.V., Polanowski, F.P., Blackburn, S.E. et al. Origin, concentration and structural features of human mammary gland cells cultured from breast secretions. Cell Tissue Res. 172, 269–279 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00226031
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00226031