Abstract
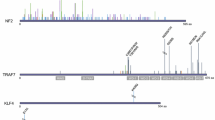
Meningiomas are benign tumors of the central nervous system. Although usually sporadic, they can occur in patients affected by the autosomal dominant syndrome, neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2). The NF2 gene has recently been isolated from chromosome 22. The presence of germline mutations in NF2 patients and the loss of heterozygosity (LOH) on 22q in NF2 tumors support the hypothesis that the NF2 gene acts as a tumor suppressor. Cytogenetic and LOH studies have suggested that the gene responsible for the development of meningiomas is located in the region of 22q in which the NF2 gene maps. The meningioma gene could therefore be the NF2 gene itself. Recently, somatic mutations of the NF2 gene have been identified in sporadic meningiomas, thus supporting the hypothesis that the NF2 gene is also important in meningioma pathogenesis. In this study, we analyzed sixty-one sporadic meningiomas for LOH of 22q and for mutations in the NF2 gene. LOH was detected in 36 of the 60 informative tumors. Single-strand conformational polymorphism analysis was used to identify nine mutations in five of the eight exons of the NF2 gene studied. The nine tumors with an altered NF2 gene also showed LOH for 22q markers. These results further support the hypothesis that mutations in the NF2 gene are a critical pathogenetic event in at least some meningiomas.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arakawa H, Hayashi N, Nagase H, Ogawa M, Nakamura Y (1994) Alternative splicing of the NF2 gene and its mutation analysis of breast and colorectal cancers. Hum Mol Genet 3:565–568
Bianchi AB, Hara T, Ramesh V, Gao J, Lein-Szanto AJP, Morin F, Menon AG, Trofatter JA, Gusella JF, Seizinger BR, Kley N (1994) Mutations in transcript isoforms of the neurofibromatosis 2 gene in multiple human tumour types. Nature Genet 6:185–192
Bourn D, Carter S, Mason S, Gareth D, Evans R, Strachan T (1994) Germline mutations in the neurofibromatosis type 2 tumour suppressor gene. Hum Mol Genet 3:813–816
Donghi R, Longoni A, Pilotti S, Michieli P, Della Porta G, Pierotti MA (1993) Gene p53 mutations are restricted to poorly differentiated and undifferentiated carcinomas of the thyroid gland. J Clin Inv 91:1753–1760
Dumanski JP, Carlbom E, Collins VP, Nordenskjold M (1987) Deletion mapping of a locus on human chromosome 22 involved in the oncogenesis of meningioma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:9275–9279
Dumanski JP, Rouleau GA, Nordenskjold M, Collins VP (1990) Molecular genetic analysis of chromosome 22 in 81 cases of meningioma. Cancer Res 50:5863–5867
Evans DGR, Huson SM, Donnai D, Neary W, Blair V, Teare D, Newton V, Strachan T, Ramsden R, Harris R (1992) A genetic study of type 2 neurofibromatosis in the United Kingdom. 1. Prevalence, mutation rate, fitness and confirmation of maternal transmission effect on severity. J Med Genet 29:841–846
Irving RM, Moffat DA, Hardy DG, Barton DE, Xuereb JH, Maher ER (1994) Somatic NF2 gene mutations in familial and non-familial vestibular schwannoma. Hum Mol Genet 3:347–350
Knudson AG Jr (1985) Hereditary cancer, oncogenes and antioncogenes. Cancer Res 45:1437–1443
Lekanne-Deprez RH, Groen NA, Biezen NA van, Hagemeijer A, Drunen E van, Koper JW, Avezaat CJJ, Bootsma D, Zwarthoff EC (1991) A t (4; 22) in a meningioma points to the localization of a putative tumor-suppressor gene. Am J Hum Genet 48:783–790
Pulst SM, Rouleau GA, Marineau C, Fain P, Sieb JP (1993) Familial meningioma is not allelic to neurofibromatosis type 2. Neurology 43:2096–2098
Rouleau GA, Wertelecki W, Haines JL, Hobbs WJ, Trofatter JA, Seizinger BR, Martuza RL, Superneau DW, Conneally PM, Gusella JF (1987) Genetic linkage of bilateral acoustic neurofibromatosis to a DNA marker on chromosome 22. Nature 329:246–248
Rouleau GA, Seizinger BR, Wertelecki W, Haines JL, Superneau DW, Martuza RL, Gusella JF (1990) Flanking markers bracket the neurofibromatosis type 2 gene on chromosome 22. Am J Hum Genet 46:323–328
Rouleau GA, Merel P, Lutchman M, Sanson M, Zuchman J, Marineau C, Hoang-Xuan K, Demczuk S, Desmaze C, Plougastel B, Pulst SM, Lenoir G, Bijlsma E, Fashold R, Dumanski J, Jong P de, Parry D, Roswell E, Aurias A, Delattre O, Thomas G (1993) Alteration in a new gene encoding a putative membrane-organizing protein causes neuro-fibromatosis type 2. Nature 363:515–521
Russel DS, Rubinstein LJ (1989) Pathology of tumours of the nervous system, 5th edn. Arnold, London, pp 449–532
Ruttledge MH, Narod SA, Dumanski JP, Parry DM, Eldridge R, Wertelecki W, Parboosingh J, Faucher M-C, Lenoir GM, Collins VP, Nordenskjold M, Rouleau GA (1993) Presymptomatic diagnosis for neurofibromatosis 2 with chromosome 22 markers. Neurology 43:1753–1760
Ruttledge MH, Sarrazin J, Rangaratnam S, Phelan CM, Twist E, Merel P, Delattre O, Thomas G, Nordenskjold M, Collins VP, Dumanski JP, Rouleau GA (1994) Evidence for the complete inactivation of the NF2 gene in the majority of sporadic meningiomas. Nature Genet 6:180–184
Sainz J, Huynh DP, Figueroa K, Ragge NK, Baser ME, Pulst S-M (1994) Mutations of the neurofibromatosis type 2 gene and lack of the gene product in vestibular schwannomas. Hum Mol Genet 3:885–891
Schneider G, Lutz S, Henn W, Zang KD, Blin N (1992) Search for putative suppressor genes in meningioma: significance of chromosome 22. Hum Genet 88:579–582
Seizinger BR, Martuza RL, Gusella JF (1986) Loss of genes on chromosome 22 in tumorigenesis of human acoustic neuroma. Nature 322:644–647
Seizinger BR, De La Monte S, Atkins SL, Gusella JF, Martuza RL (1987) Molecular genetic approach to human meningioma: loss of genes on chromosome 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:5419–5423
Sieb JP, Pulst S-M, Buch A (1992) Familial CNS tumors. J Neurol 239:343–344
Trofatter JA, MacCollin MM, Rutter JL, Murrel JR, Duyao MP, Parry DM, Eldridge R, Kley N, Menon AG, Pulaski K, Haase VH, Ambrose CM, Munroe D, Bove C, Haines JL, Martuza RL, MacDonald ME, Seizinger BR, Short MP, Buckler AJ, Gusella JF (1993) A novel moesin-, ezrin-, radixin-like gene is a candidate for the neurofibromatosis 2 tumor suppressor. Cell 72:791–800
Twist EC, Ruttledge MH, Rousseau M, Sanson M, Papi L, Merel P, Delattre O, Thomas G, Rouleau GA (1994) The neurofibromatosis type 2 gene is inactivated in schwannomas. Hum Mol Genet 3:147–151
Wolff RK, Frazer KA, Jackler RK, Lanser MJ, Pitts LH, Cox DR (1992) Analysis of chromosome 22 deletions in neurofibromatosis type 2 — related tumors. Am J Hum Genet 51:478–485
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Papi, L., De Vitis, L.R., Vitelli, F. et al. Somatic mutations in the neurofibromatosis type 2 gene in sporadic meningiomas. Hum Genet 95, 347–351 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00225206
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00225206