Summary
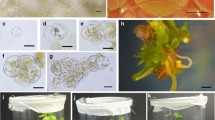
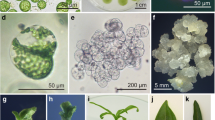
Regenerants from a 30-month-old haploid and a 10-month-old diploid tissue culture were cross-pollinated to generate a synthetic genotype (HE/89) with improved competence for maintenance of totipotency in various cultured expiants. The HE/89 zygotic embryos developed friable, embryogenic cultures in the commonly used MS-and N6-based media without the addition of L-proline. By optimalization and changing the culture conditions, we were able to regulate the maintenance of the earlier, more synchronous (Type II) and the later, asynchronous (Type I) in vitro embryogenesis, as well as the shift between different ontogenic stages. Within 70 days after the inoculation of immature embryos a relatively homogeneous, early-embryogenic suspension culture usable for protoplast isolation was established from the initially surface-grown cultures. Using modified solutions for protoplast isolation and culture, viable protoplasts were reproducibly obtained from which plants were regenerated via defined ontogenic steps. Despite the long in vitro history of the parental genotypes, 60–70% of the more than 500 plants derived from the HE/89 protoplasts set seeds following self or sib-pollination.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amstrong CL, Green CE (1984) Establishment and maintenance of friable, embryogenic maize callus and the involvement of L-proline. Planta 164:207–214
Cai Q, Kuo C, Quian Y, Jiong R, Zhon Y (1988) Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from protoplast of maize (Zea mays L.) In: Puite KJ, Dons JJM, Huising HJ, Kool AJ, Koornneef M, Krens FA (eds) Progress in plant protoplast research. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, p 120
Chourey PS, Zurawski DB (1981) Callus formation from protoplasts of a maize cell culture. Theor Appl Genet 59:341–344
Chu CC, Wang CC, Sun CS, Hsu C, Yin KC, Chu CY, Bi FY (1975) Establishment of an efficient medium for anther culture of rice through comparative experiments on the nitrogen sources. Sci Sin 18:659–668
Green CE (1982) Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from the friable callus of Zea mays. In: Proc 5th Int Congr Plant Tiss Cell Cult. Fujiwara, Tokyo, pp 107–108
Green CE, Phillips RL (1975) Plant regeneration from tissue cultures of maize. Crop Sci 15:417–421
Hanne G, Lörz H (1988) Release of phytotoxic factors from cell walls during protoplast isolation. Plant Physiol 132:345–350
Hodges TK, Kamo KK, Becwar MR, Schroll S (1985) Regeneration of maize. In: Zaitlin M, Day P, Hollander A (eds.) Biotechnology in plant science. Academic Press, New York, pp 15–33
Imbrie-Milligan CW, Hodges TK (1986) Microcallus formation from maize protoplasts prepared from embryogenic callus. Planta 168:395–401
Kamo KK, Chang KL, Lymm ME, Hodges TK (1987) Embryogenic callus formation from maize protoplasts. Planta 172:245–251
Kao KN, Michayluk MR (1975) Nutrient requirements for growth of Vicia hajastana cells and protoplasts at very low population density in liquid media. Planta 126:105–110
Kuang VD, Shamina ZB, Butenko RG (1983) Use of nurse tissue culture to obtain clones from cultured cells and protoplasts of corn. Fiziol Rast 30:803–812
Lowe K, Taylor DB, Ryan P, Paterson KE (1985) Plant regeneration via organogenesis and embryogenesis in the maize inbred line B73. Plant Sci 41:125–132
Ludwig SR, Somers DA, Petersen WL, Pohlman RF, Zarowits MA, Gengenbach BG, Messing J (1985) High frequency callus formation from maize protoplasts. Theor Appl Genet 71:344–350
Lupotto E (1986) In vitro culture of isolated somatic embryos of maize (Zea mays L.). Madica 31:193–201
Mórocz S, Dudits D, Németh J (1986) Two approaches to rendering Zea mays L. applicable to tissue culture manipulations. In: Somers DA, Gegenbach BG, Biesboer DD, Hackett WP, Green CE (eds) VI. International Congress on Plant Tissue and Cell Culture, Minneapolis MN, University of Minneosta, p 190
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Potrykus I, Harms CT, Lörz H (1979) Callus formation from cell culture protoplasts of corn (Zea mays, L.). Theor Appl Genet 54:209–214
Prioli LM, Söndahl MR (1989) Plant regeneration and recovery of fertile plants from protoplasts of maize (Zea mays L.). Bio/Technol 7:589–594
Rhodes CA, Lowe KS, Ruby KL (1988) Plant regeneration from protoplasts isolated from embryogenic maize cell cultures. Bio/Technol 6:56–60
Saleem M, Cutler AS (1986) Stabilizing corn leaf protoplasts with n-propyl gullate. J Plant Physiol 128:479–484
Shilito RD, Carswell GK, Johnson CM, DiMaio JJ, Harms CT (1989) Regeneration of fertile plants from protoplasts of elite inbred maize. Bio/Technol 7:581–587
Somers DA, Birnberg PR, Petersen WL, Brenner ML (1987) The effect of conditioned medium on colony formation from “Black Mexican Sweet” corn Protoplasts. Plant Sci 53:249–256
Tomes DT, Smith OS (1985) The effect of parental genotype on initiation of embryogenic callus from elite maize (Zea mays L.) germ-plasm. Theor Appl Genet 70:505–509
Vasil V, Vasil IK (1987) Formation of callus and somatic embryos from protoplasts of a commercial hybrid of maize (Zea mays L.). Theor Appl Genet 73:793–798
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by G. Melchers
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mórocz, S., Donn, G., Nérneth, J. et al. An improved system to obtain fertile regenerants via maize protoplasts isolated from a highly embryogenic suspension culture. Theoret. Appl. Genetics 80, 721–726 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00224183
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00224183