Summary
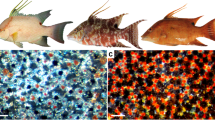
The chromatophore unit concept is applicable to the variety of chromatophore associations in the coho salmon, Oncorhynchus kisutch. Individual pigment cells of three general types—melanophores, xanthophores, and iridophores—vary structurally according to skin location, age, and physiological state. In growing fish, melanophores have a bimodal size distribution; in adults, they have a normal size distribution. Both melanophores and xanthophores are dendritic cells which respond to potassium and sodium ions by respectively aggregating and dispersing pigment granules. The third cell, the iridophore, is characterized by reflecting platelets of birefringent crystals of guanine of hypoxanthine and has at least two distinct shapes. In the upper dermis of the dark-colored skin, globular iridophores are encompassed by the dendritic arms of subjacent melanophores. In relation to this melanophoreiridopbore unit, the xanthophores appear to be randomly distributed and to afford an effective filter by virtue of their quantity and shape as well as their pigment granules. In deeper locations in the dermis, particularly below the stratum compactum in the shiny ventral skin, layers of dendritic iridophores are only partially shielded by the few melanophores and thus represent the nadir of chromatophore unit organization in the salmon.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander, N. J., Fahrenbach, W. H.: The dermal chromatophores of Anolis carolinensis (Reptilia, Iguanidae). Amer. J. Anat. 126, 41–56 (1969)
Bagnara, J. T.: Hypophyseal control of guanophores in anuran larvae. J. exp. Zool. 137, 265–284 (1958)
Bagnara, J. T.: Stimulation of melanophores and guanophores by melanophore-stimulating hormone peptides. Gen. comp. Endocr. 4, 290–294 (1964 a)
Bagnara, J. T.: Independent actions of pineal and hypophysis in the regulation of chromatophores of anuran larvae. Gen. comp. Endocr. 4, 299–303 (1964 b)
Bagnara, J. T.: Cytology and cytophysiology of non-melanophore pigment cells. Int. Rev. Cytol. 20, 173–205 (1966)
Bagnara, J. T., Ferris, W.: Interrelationships of vertebrate chromatophores. In: Biology of normal and abnormal melanocytes (eds. T. Kawamura, T. B. Fitzpatrick, M. Seiji), p. 57–76. Tokyo: Univ. Tokyo Press 1971
Bagnara, J. T., Hadley, M. E.: Chromatophores and color change. 202 pp. Engelwood Cliffs: Prentice-Hall, Inc. 1973
Bagnara, J. T., Taylor, J. D., Hadley, M. E.: The dermal chromatophore unit. J. Cell Biol. 38, 67–79 (1968)
Denton, E. J., Land, M. F.: Mechanism of reflection in silvery layers of fish and cephalopoda. Proc. roy. Soc. 178, 43–61 (1971)
Denton, E. J., Saunders, R. L.: On the organization of silvery layers in the skin of the Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) during smoltification and on the regeneration of these layers under abnormal lighting conditions. J. Marine Biol. Assoc. U.K. 52, 889–898 (1972 a)
Denton, E. J., Saunders, R. L.: Osmotic properties of the epithelial layers covering scales of herring (Clupea harengus) and Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). J. Marine Biol. Assoc. U.K. 52, 899–902 (1972 b)
Fessler, J. L., Wagner, H. H.: Some morphological and biochemical changes in steelhead trout during the parr-smolt transformation. J. Fish. Res. Bd. Can. 26, 2823–2841 (1969)
Fujii, R.: Correlation between fine structure and activity in fish melanophore. In: Structure and control of the melanocyte (eds., G. Della Porta, O. Mühlbock) p. 114–123. BerlinHeidelberg-New York: Springer 1966
Fujii, R.: Chromatophores and pigments. In: Fish physiology (eds. W. S. Hoar, D.J. Randall) III, p. 307–354. New York-London: Academic Press 1969
Fries, E. F. B.: Iridescent white reflecting chromatophores (antaugophores, iridoleucophores) in certain teleost fishes, particularly in Bathygobius. J. Morph. 103, 203–254 (1958)
Gorbman, A.: Thyroid function and its control in fishes. In: Fish physiology (eds. W.S. Hoar, D. J. Randall) II, p. 241–274. New York-London: Academic Press 1969
Hadley, M. E., Goldman, J. M.: The physiological regulation of the amphibian iridophore. In: Pigmentation (ed. V. Riley) p. 225–245. New York: Appleton-Century-Crofts 1972
Harris, J. D., Hunt, S.: The fine structure of iridophores in the skin of the Atlantic salmon, (Salmo salar L.). Tissue and Cell 5, 479–488 (1973)
Hawkes, J. W.: The structure of fish skin. I. General organization. Cell Tiss. Res. 149, 147–158 (1974)
Hoar, W. S.: The endocrine regulation of migratory behaviour in anadromous teleosts. Proc. XVI Int. Congr. Zool. 3, 14–20 (1963)
Hogben, L. T., Slome, D.: The pigmentary effector system. VI. The dual character of endocrine coordination in amphibian colour change. Proc. roy. Soc. 108, 10–53 (1931)
Kamei-Takeuchi, I., Hama, R.: Structural change of pterinosome (pteridine pigment granule) during the xanthophore differentiation of Oryzias fish. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 34, 452–463 (1971)
Kawaguti, S.: Electron microscopy on iridophores from fish and amphibians. Zool. Mag. 76, 281–287 (1967)
Kawaguti, S., Takeuchi, T.: Electron microscopy on guanophores of the medaka, Oryzias latipes. Biol. J. Okayama Univ. 14, 55–65 (1968)
Land, M. F.: The physics and biology of animal reflectors. Progr. Biophys. molec. Biol. 24, 75–106 (1972)
Lueken, W., Kaeser, U.: The role of melanoblasts in melanophore patterns polymorphism of Xiphophorus (Pisces, Poeciliidae). Experientia (Basel) 28, 1340–1341 (1972)
Mackay, G. R., Mead, M. L.: A simple dichromatic stain for plastic embedded tissues. Proc. 28th EMSA Meeting, p. 296–297 (1970)
Matsumoto, J.: Studies on the fine structure and cytochemical properties of erythrophores in swordtail, Xiphophorus helleri, with special reference to their pigment granules (pterinosomes). J. Cell Biol. 27, 493–504 (1965)
Pickford, G. E., Kosto, B.: Hormonal induction of melanogenesis in hypophysectomized killifish (Fundulus heteroclitus). Endocrinology 61, 177–196 (1957)
Sage, M.: Control of prolactin release and its role in color change in the teleost Gillichthys mirabilis. J. exp. Zool. 173, 121–128 (1970)
Sage, M., Bern, H. A.: Assay of prolactin in vertebrate pituitaries by its dispersion of xanthophore pigment in the teleost Gillichthys mirabilis. J. exp. Zool. 180, 169–174 (1972)
Taylor, J. D., Hadley, M. E.: Chromatophores and color change in the lizard, Anolis carolinensis. Z. Zellforsch. 104, 282–294 (1970)
Vanstone, W. E., Markert, J. R.: Some morphological and biochemical changes in coho salmon, Oncorhynchus kisutch, during parr-smolt transformation. J. Fish. Res. Bd. Can. 25, 2403–2418 (1968)
Wikswo, M. A., Novales, R. R.: Effect of colchicine on microtubules in the melanophores of Fundulus heteroclitus. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 41, 189–201 (1972)
Yasutomi, M., Hama, T.: Structural changes of drosopterinosomes (red pigment granules) during the erythrophore differentiation of the frog, Rana japonica, with reference to other pigment-containing organelles. Z. Zellforsch. 137, 331–343 (1973)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Publication No. 713 from the Oregon Regional Primate Research Center. Supported by postdoctoral training fellowship 5-T01-AM05512-08 from the National Institutes of Health.
The author wishes to thank Messrs. W. Parente and R. Wahl of National Marine Fisheries Service, Portland, Oregon, for their kind assistance in obtaining the fish and to Mr. N. Roman for excellent technical help with the paraffin sections.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hawkes, J.W. The structure of fish skin. Cell Tissue Res. 149, 159–172 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00222271
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00222271