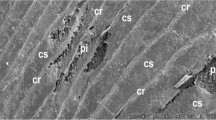
Summary
The spicule primordium is formed in an intercellular cavity within a group of sclerocytes. This cavity contains organic material which ensheaths the growing spicule but does not appear to determine the nature of the mineral morph (magnesian calcite) or the crystallographic orientation of the spicule. The tip of each growing spicule ray is seated in a ‘dense cup’ in the cytoplasm of the sclerocyte concerned. Both ends of monaxons are initially inserted each into a dense cup. As rays elongate the sclerocyte membrane around the tip becomes invaginated and forms a system of ‘converging spaces’ that possibly indicate high secretory activity in that region. Spicule growth involves the displacement and expansion of the organic sheath by the enlarging spicule. Fully formed spicules which are exposed to the mesohyl become surrounded by collagen fibrils. However, these fibrils are in no way concerned with the process of mineral deposition and are never found within the spicule calcite.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banks, E., Chianelli, R., Pintchovsky, F.: The growth of some alkaline earth orthophosphates in gelatine gels. J. Cryst. Growth. 18, 185–190 (1973)
Berner, R.A.: The role of magnesium in the crystal growth of calcite and aragonite from sea water. Geochim. cosmochim. Acta 39, 489–504 (1975)
Bischoff, J.L.: Kinetics of calcite nucleation: magnesium ion inhibition and ionic strength catalysis. J. geophys. Res. 73, 3315–3322 (1968)
Borojević, R., Fry, W.G., Jones, W.C., Lévi, C., Rasmont, R., Sarà, M., Vacelet, J.: Mise au point actuelle de la terminologie des Éponges. Bull. Mus. Hist. nat. (Paris) 39, 1224–1235 (1968)
Burton, M.: A revision of the classification of the calcareous sponges. London: British Museum (Nat. Hist.) 1963
Ebner, V. von: Über den feineren Bau der Skelettheile der Kalkschwämme nebst Bemerkung über Kalkskelete überhaupt. S.-B. Akad. Wiss. Wien, Abt. 1, 95, 55–149 (1887)
Folk, R.L.: The natural history of crystalline calcium carbonate: effect of magnesium content and salinity. J. sedim. Petrol. 44, 40–53 (1974)
Glover, E.D., Sippel, R.F.: Synthesis of magnesium calcites. Geochim. cosmochim. Acta 31, 603–614 (1967)
Henisch, H.K.: Crystal growth in gels. Pennsylvania State University Press 1970
Jones, W.C.: The orientation of the optic axis of spicules of Leucosolenia complicata. Quart. J. micr. Sci. 95, 33–48 (1954a)
Jones, W.C.: Spicule form in Leucosolenia complicata Quart. J. micr. Sci. 95, 191–203 (1954b)
Jones, W.C.: Crystalline properties of spicules of Leucosolenia complicata. Quart. J. micr. Sci. 96, 129–149 (1955 a)
Jones, W.C.: The sheath of spicules of Leucosolenia complicata. Quart. J. micr. Sci. 96, 411–421 (1955 b)
Jones, W.C.: Sheath and axial filament of calcareous sponge spicules. Nature (Lond.) 214, 365–368 (1967)
Jones, W.C.: The composition, development, form and orientation of calcareous sponge spicules. Symp. zool. Soc. Lond. 25, 91–123 (1970)
Jones, W.C.: Spicule formation and corrosion in recently metamorphosed Sycon ciliatum. In: Fourth European Marine Biology Symposium (D.J. Crisp, ed.). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press 1971
Jones, W.C., Jenkins, D.A.: Calcareous sponge spicules: a study of magnesian calcites. Calcif. Tiss. Res. 4, 314–329 (1970)
Khaimov-Mal'kov, V.I.: The question of the growth of crystals in porous media. Sov. Phys. (cryst.) 3, 487–493 (1958)
Kirov, G.K., Vesselinov, I., Cherneva, Z.: Conditions of formation of calcite crystals of tabular and acute rhombohedral habits. Krist. & Tech. 7, 497–509 (1972)
Kitano, Y., Hood, D.W.: The influence of organic material on the polymorphic crystallization of calcium carbonate. Geochim. cosmochim. Acta 29, 29–41 (1965)
Kitano, Y., Kanamori, N.: Synthesis of magnesian calcite at low temperatures and pressures. Geochem. J. (Jap.) 1, 1–10 (1966)
Kitano, Y., Kanamori, N., Tokuyama, A.: Effects of organic matter on solubilities and crystal form of carbonates. Amer. Zool. 9, 681–688 (1969)
Ledger, P.W.: Types of collagen fibres in the calcareous sponges Sycon and Leucandra. Tissue and Cell 6, 385–389 (1974)
Ledger, P.W.: Septate junctions in the calcareous sponge Sycon ciliatum. Tissue and Cell 7, 13–18 (1975)
Ledger, P.W.: Aspects of the secretion and structure of calcareous sponge spicules. Thesis, University of Wales (1976)
Lippmann, F.: Sedimentary carbonate minerals. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1973
Minchin, E.A.: Materials for a monograph of the ascons. I. On the origin and growth of the triradiate and quadriradiate spicules in the family Clathrinidae. Quart. J. micr. Sci. 40, 469–588 (1898)
Minchin, E.A.: Materials for a monograph of the ascons. II. The formation of spicules in the genus Leucosolenia, with some notes on the histology of the sponges. Quart. J. micr. Sci. 52, 301–335 (1908)
Simkiss, K.: Variation in the crystalline form of calcium carbonate precipitated from artificial sea water. Nature (Lond.) 201, 492–493 (1964)
Towe, K.M., Malone, P.G.: Precipitation of metastable carbonate phases from sea water. Nature (Lond.) 226, 348 (1970)
Travis, D.F.: The comparative ultrastructure and organization of five calcified tissues. In: Biological calcification: cellular and molecular aspects (H. Schraer, ed.). New York: Appleton-CenturyCrofts 1970
Woodland, W.: Studies on spicule formation. I. The development and structure of the spicules in Sycons: with remarks on the conformation, modes of disposition and evolution of spicules in calcareous sponges generally. Quart. J. micr. Sci. 49, 231–282 (1905)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ledger, P.W., Jones, W.C. Spicule formation in the calcareous sponge Sycon ciliatum . Cell Tissue Res. 181, 553–567 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00221776
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00221776