Summary
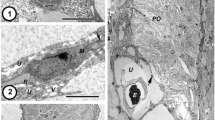
The lateral oviduct and calyx of nulliparous Aedes aegypti on a sucrose diet are both flattened sacs, lacking a well defined lumen. Both are formed of an inner epithelial and an outer muscular layer, each one cell thick. The lateral oviduct is surrounded by a circular muscle sheath which is continuous with the ovarian sheath. Each ovariolar sheath is continuous with the outer layer of the calyx. The structure of both the lateral oviduct and the calyx is greatly modified after the initial blood meal. A distinct lumen develops; there is an extensive development of the outer muscular layers, and the inner epithelial layers become invaginated forming deep crypts lined with extensive microvilli. The follicular stem, which joins the primary follicle to the calyx in each ovariole, is not hollow and does not mark the opening into the calyx through which the mature egg can pass. The eggs gain access to the oviductal system after the calyx extends around the follicular epithelium of the primary follicle, when breaks appear in the calyx wall opposed to the follicular epithelium, until the mature eggs, eventually lie in a highly distended thin-walled sac of calyx from which they have direct and easy access to the lateral oviduct. After oviposition, this sac contracts to occupy once more a compact axial position in the ovary. Remnants of the follicular epithelium, containing many lysosomes are attached to the calyx at this time.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akster, H.A., Smit, W.A.: The structure of the terminal filament, the ovariole sheath and the oviduct musculature of the Colorado beetle, (Leptinotarsa decemlineata Say, 1824). Bijdr. de Dierk. 46, 136–150 (1977)
Anderson, W.A., Spielman, A.: Permeability of the ovarian follicle of Aedes aegypti mosquitoes. J. Cell Biol. 50, 201–221 (1971)
Bertram, D.S.: The ovary and ovarioles of mosquitoes. Annex in W.H.O. Monograph Ser. No. 47, 195–210 (1962)
Christophers, S.R.: Aedes aegypti, the yellow fever mosquito: Life history, bionomics and structure, pp. 671. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press 1960
Curtin, T.J., Jones, J.C.: The mechanism of ovulation and oviposition in Aedes aegypti. Ann. ent. Soc. Amer. 54, 298–313 (1961)
Detinova, T.S.: Age grouping methods in Diptera of medical importance; with special reference to some vectors of malaria. W.H.O. Monograph Ser. No. 47 (1962)
Giglioli, M.E.C.: Some illustrations showing the morphology of the female reproductive organs of A. gambiae melas and the structure of follicular dilatations in some anophelines. Trans, roy. Soc. trop. Med. Hyg. 58, 5 (1964a)
Giglioli, M.E.C.: The female reproductive system of Anopheles gambiae melas. Riv. Malariol. 43, 265–275 (1964b)
Hagedorn, H.H.: The control of vitellogenesis in the mosquito, Aedes aegypti. Amer. Zool. 14, 1207–1217 (1974)
Hagedorn, H.H., O'Connor, J.D., Fuchs, M.S., Sage, B., Schlaeger, D.A., Bohm, M.K.: The ovary as a source of α-ecdysone in the adult mosquito. Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.) 72, 3255–3259 (1975)
Imms, A.O.: A general textbook of entomology, pp. 886 London: Methuen (1977)
Lea, A.O.: Regulation of egg maturation in the mosquito by the neurosecretory system: the role of the corpora cardiacum. Gen. comp. Endocr., Suppl. 3, 602–608 (1972)
Roth, T.F., Porter, K.R.: Yolk protein uptake in the oocyte of the mosquito Aedes aegypti L. J. Cell Biol. 20, 313–332 (1964)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lehane, M.J., Laurence, B.R. Development of the calyx and lateral oviduct during oogenesis in Aedes aegypti . Cell Tissue Res. 193, 125–137 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00221606
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00221606