Abstract
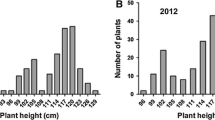
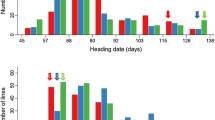
‘Lemont’ and ‘Teqing’ are both semidwarf rice varieties that differ in heading date by only 6 days. However, when ‘Lemont’ and ‘Teqing’ are crossed there is transgressive segregation for both heading date (HD) and plant height (PH). By testing 2418 F4 lines with 113 well-distributed RFLP markers, we identified and mapped chromosomal regions that were largely responsible for this transgressive segregation. QHd3a, a QTL from ‘Lemont’ that gives 8 days earlier heading, was identified on chromosome 3 approximately 3 cM from the marker RG348. Another QTL with a large effect, QHd8a, which gives 7 days earlier heading, was identified on chromosome 8 of ‘Teqing’ between RG20 and RG1034. Along with a QTL, QHd9a with a phenotypic effect of 3.5 days, these genomic regions collectively explain 76.5% of the observed phenotypic variance in heading date. Four QTLs which altered plant height from 4 to 7 cm were also mapped; these collectively explain 48.8% of the observed phenotypic variation in plant height. None of the QTLs for plant height mapped to chromosome 1, the location of the semidwarf gene sd-1. All three of the HD loci mapped to approximately the same genomic locations as PH QTLs, and in all cases, there was a reduction in height of approximately 1 cm for every day of earlier heading. The correspondence between the HD and some of the PH loci suggests that genes at these chromosome locations may have pleiotropic effects on both HD and PH. The observed heterosis in the F1 plants for HD can be largely explained by the dominance for earliness of the identified HD loci and distribution of earlier heading alleles in the parents. However, overdominance observed at one of the PH QTL may, at least in part, be responsible for the observed heterosis in PH.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bollich CN, Webb BD, Marchetti MA, Scott J (1985) Registration of ‘Lemont’ rice. Crop Sci 25:883–885
Bollich CN, Webb BD, Marchetti MA, Scott J (1990) Registration of ‘Gulfmont’ rice. Crop Sci 30:1159–1160
Bollich CN, Webb BD, Marchetti MA, Scott J (1991) Registration of ‘Maybelle’ rice. Crop Sci 31:1090
Causse MA, Fulton TM, Cho YG, Ahn SN, Chunwongse J, Wu KS, Xiao JH, Yu ZH, Ronald PC, Harrington SE, Second G, McCouch S, Tanksley SD (1994) Saturated molecular map of the rice genome based on an interspecific backcross population. Genetics: 1251–1274
Chang TT, Li CC (1984) Semidwarfing genes in rice germplasm collection. Rice Genet Newsl 1:93–94
Foster KW, Rutger JN (1978) Inheritance of semidwarfism in rice, Oryza sativa L. Genetics 88:559–574
Haley CS, Knott SA (1992) A simple regression method for mapping quantitative trait loci in line crosses using flanking markers. Heredity 69:315–324
Hargrove TR, Cabanilla VL, Coffman WR (1988) Twenty years of rice breeding: the role of semidwarf varieties in rice breeding for Asian farmers and the effects of cytoplasmic diversity. BioScience 38:675–681
Khush GS, Kinoshita T (1991) Rice karyotype, marker genes, and linkage groups In: Khush GS, Toenniessen GH (eds), Rice Biotechnology. CAB Int, Walling-ford, UK, pp 83–107
Kikuchi F, Ikehashi H (1984) Semidwarfing genes of high-yielding rice varieties in Japan. Rice Genet Newsl 1:93
Kinoshita T, Takahashi M (1991) The one hundredth report of genetical studies on rice plant — Linkage studies and future prospects. J Fac Agric Hokkaido Univ 65:1–61
Kosambi, DD (1944) The estimation of map distances from recombination values. Ann Eugen 12:172–175
Lander ES, Botstein D (1989) Mapping Mendelian factors underlying quantitative traits using RFLP linkase maps. Genetics 121:185–199
Li ZK, Pinson SRM, Marchetti MA, Stansel JS, Park WD (1995) Characterization of quantitative trait loci (QTLs) in cultivated rice contributing to field resistance to sheath blight (Rhizoctonia solani). Theor Appl Genet 91:382–388
Lincoln SE, Daly MJ, Lander ES (1990) Constructing genetic linkage maps with MAPMAKER: a tutorial and reference manual. Whitehead Inst for Biomed Res Tech Rep, Cambridge, Mass. 2nd edn.
Lincoln SE, Daly MJ, Lander ES (1992) Mapping genes controlling quantitative traits with MAPMAKER/QTL 1.1. Whitehead Ins Tech Rep, Cambridge, Mass. 2nd edn.
McCouch SR, Kochert G, Yu ZH, Wang ZY, Khush GS, Coffman WR (1988) Molecular mappins of rice chromosomes. Theor Appl Genet 76:815–829
McCouch SR, Tanksley SD (1991) Development and use of restriction fragment length polymorphism in rice breeding and genetics. In: Khush GS, Toenniessen GH (eds) Rice Biotechnology CAB Int. Wallingford, UK, pp 83–107
Nakazaki JM, Sato YI, Yamagata H (1986) Effect of an earliness gene Ef-1 on culm length and internode elongation. Rice Genet Newsl 3:76
Paterson AH, Lander ES, Hewitt JD, Peterson S, Lincoln SE, Tanksley SD (1988) Resolution of quantitative traits into Mendelian factors by using a complete linkage map of restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Nature 335:721–726
Rutger JN (1984) Induced semidwarf mutants in rice. Rice Genet Newsl 1:92
Rutger JN, Bollich CN (1989) The use of introduced germplasm in rice improvement. In: Shands HL, Weisner LE (eds) Crop Sci Soc Amer Special Publ No 7. Crop Sci Soc Am Madison, pp 1–13
SAS Institute (1987) SAS/STAT guide for personal computers, version 6. SAS Institute, Cary, N.C.
Stuber CW, Edwards MD, Wendel JF (1987) Molecular marker-facilitated investigations of quantitative trait loci in maize. II. Factors influencing yield and its components traits. Crop Sci 27:239–248
Tai TH, Tanksley SD (1990) A rapid and inexpensive method for isolation of total DNA from dehydrated plant tissue. Plant Mol Biol Rep 8:297–303
Tsai KH (1986) Genes controlling heading time found in a tropical Japonica variety. Rice Genet Newsl 3:70–71
Wallace DH, Zobel RW, Yourstone KS (1993) A whole-system reconsideration of paradigms about photoperiod and temperature control of crop yield. Theor Appl Genet 86:17–26
Wang GL, Mackill DJ, Bonman JM, McCouch SR, Nelson RJ (1993) RFLP mapping of genes conferring complete and partial resistance in a rice cultivar with durable resistance to blast. In: Jacobs T, Parlevliet JE (eds) Durability of disease resistance. (Current Plant Science and Biotechnology in Agriculture, Vol 18), Kluwer Academic Publ, Dordrecht, the Netherlands, pp 219–225
Zamir D, Tadmor Y (1987) Unequal segregation of nuclear genes in plants. Bot Gaz 147:135–358
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by G. E. Hart
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Z., Pinson, S.R.M., Stansel, J.W. et al. Identification of quantitative trait loci (QTLs) for heading date and plant height in cultivated rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theoret. Appl. Genetics 91, 374–381 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00220902
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00220902