Abstract
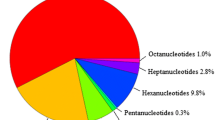
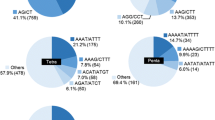
A size-fractionated library of Brassica napus L. (rapeseed), composed of 15000 clones, was screened for the presence of GA-, CA-, and GATA-simple-sequence repeats (SSRs). GA-SSRs were four- and five-fold more abundant than CA- and GATA-SSRs, respectively, and present at a frequency of approximately one SSR for every 100 kb of DNA. Following the sequencing of 124 positive clones, primer pairs were designed and evaluated for seven selected SSRs. Products were amplified in an array of individuals of B. napus, B. oleracea and B. rapa, demonstrating that the seven SSRs were conserved among species. Two SSRs were polymorphic. Among 11 accessions, the dinucleotide (GA)-repeat, B.n.9A, yielded 12 fragments, while the tetranucleotide-repeat (GATA), B.n.6A2, revealed two fragments. Automated, fluorescence-based detection of polyacrylamide gels has been employed to simultaneously increase throughput, reduce unit cost, improve analytical resolution, and expedite data acquisition of SSR analysis. Though initial financial investment and technical capabilities may prevent some from directly employing our documented approach, SSR analysis warrants further investigation as a tool in genetic studies for enhancing both the conservation and utilization of genetic resources.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akkaya MA, Bhagwat AA, Cregan PB (1992) Length polymorphisms of simple sequence repeat DNA in soybean. Genetics 132:1131–1139
Bell CJ, Ecker JR (1994) Assignment of thirty microsatellite loci to the linkage map of Arabidopsis. Genomics 19:137–144
Colosi JC, Schaal BA (1993) Tissue grinding with ball bearings and vortex mixer for DNA extraction. Nucleic Acids Res 21:1051–1052
Cooper, NC (ed) (1992) Los Alamos science. Los Alamos National Laboratory, Los Alamos, California
Condit R, Hubbell SP (1991) Abundance and sequence of 2-base repeat regions in tropical tree genomes. Genome 34:66–71
Cregan PB (1992) Simple-sequence repeat DNA length polymorphisms. Probe 2:18–22
Dumais MM, Nochumson S (1987) Small DNA fragment separation and M13 cloning directly in remelted NuSieve GTG agarose gels. BioTechniques 5:62–67
Economou EP, Bergen AW, Warren AC, Antonarakis SE (1990) The polydeoxyadenylate tract of Alu repetitive elements is polymorphic in the human genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:2951–2954
Fregeau CJ, Fourney RM (1993) DNA typing with fluorescently tagged short tandem repeats: a sensitive and accurate approach to human identification. BioTechniques 15:100–118
Kimpton CP, Gill P, Walton A, Urquhart A, Millican ES, Adams M (1993) Automated DNA profiling employing multiplex amplification of short tandem-repeat loci. PCR Methods Appl 3:13–22
Kowalski SP, Lan TH, Feldmann KA, Paterson AH (1994) Comparative mapping of Arabidopsis thaliana and Brassica oleracea chromosomes reveals islands of conserved organization. Genetics 138:499–510
Kresovich S, Williams JGK, McFerson JR, Routman EJ, Schaal BA (1992) Characterization of genetic identities and relationships of Brassica oleracea L. via a random polymorphic DNA assay. Theor Appl Genet 85:190–196
Kresovich S, Lamboy WF, Szewc-McFadden AK, McFerson JR, Forsline PL (1993) Molecular diagnostics and plant genetic resources conservation. AgBiotech News Info 5:555–558
Lagercrantz U, Ellegren H, Andersson L (1993) The abundance of various polymorphic microsatellite motifs differs between plants and vertebrates. Nucleic Acids Res 21:1111–1115
Mellersh C, Sampson J (1993) Simplifying detection of microsatellite length polymorphisms. BioTechniques 15:582–584
Morgante M, Olivieri AM (1993) PCR-amplified microsatellites as markers in plant genetics. Plant Jour 3:175–182
Poulsen GB, Kahl G, Weising K (1993) Abundance and polymorphism of simple repetitive DNA sequences in Brassica napus L. Theor Appl Genet 85:994–1000
Queller DC, Strassmann JE, Hughes CE (1993) Microsatellites and kinship. Trends Ecol Evol 8:285–288
Rafalski JA, Tingey SV (1993) Genetic diagnostics in plant breeding: RAPDs, microsatellites and machines. Trends Genet 9:275–279
Rafalski JA, Tingey SV, Williams JGK (1991) RAPD markers — a new technology for genetic mapping and plant breeding. AgBiotech News Info 3:645–648
Ragot M, Hoisington DA (1993) Molecular markers for plant breeding: comparisons of RFLP and RAPD genotyping costs. Theor Appl Genet 86:975–984
Rongwen J, Cregan PC, Akkaya MS, Bhagwat AA, Lavi U (1995) The use of simple sequence repeat DNA markers for soybean genotype identification. Theor Appl Genet 90:43–48
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual (2nd ed.) Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, New York
Saghai-Maroof, MA, Biyashev RM, Yang GP, Zhang Q, Allard RW (1994) Extraordinarily polymorphic microsatellite DNA in barley: species diversity, chromosomal locations, and population dynamics. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:5466–5470
Senior ML, Heun M (1993) Mapping maize microsatellites and polymerase chain reaction confirmation of the targeted repeats using a CT primer. Genome 36:884–889
Tanksley SD, Young ND, Paterson AH, Bonierbale MW (1989) RFLP mapping in plant breeding: new tools for an old science. BioTechniques 7:257–264
Thomas MR, Scott NS (1993) Microsatellite repeats in grapevine reveal DNA polymorphisms when analysed as sequence-tagged sites (STSs). Theor Appl Genet 86:985–990
Thomas MR, Matsumoto S, Cain P, Scott NS (1993) Repetitive DNA of grapevine: classes present and sequences suitable for cultivar identification. Theor Appl Genet 86:173–180
U N (1935) Genome analysis in Brassica with special reference to the experimental formation of B. napus and peculiar mode of fertilization. Jpn J Bot 7:389–452
Wang Z, Weber JL, Zhong G, Tanksley SD (1994) Survey of plant short tandem repeats. Theor Appl Genet 88:1–6
Weber JL, May PE (1989) Abundant class of human DNA polymorphisms which can be typed using the polymerase chain reaction. Am J Hum Genet 44:388–396
Ziegle JS, Su Y, Corcoran KP, Nie L, Mayrand PE, Hoff LB, McBride LJ, Kronick MN, Diehl SR (1992) Application of automated DNA sizing technology for genotyping microsatellite loci. Genomics 14:1026–1031
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by A. S. Kahler
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kresovich, S., Szewc-McFadden, A.K., Bliek, S.M. et al. Abundance and characterization of simple-sequence repeats (SSRs) isolated from a size-fractionated genomic library of Brassica napus L. (rapeseed). Theoret. Appl. Genetics 91, 206–211 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00220879
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00220879