Abstract
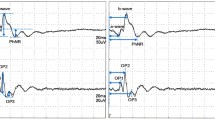
The direct current electroretinogram (DC-ERG) of 15 unilaterally vitrectomized albino rabbits was studied during continuous intraocular irrigation with a recently developed solution (‘PHS’) produced by Pharmacia Ophthalmics. The mean amplitudes of the b- and c-waves were somewhat lower than corresponding values of previously investigated reference subjects, but not statistically different. In 11 of the 15 rabbits PHS was then replaced by the commonly used balanced salt solution (BSS). The fluids were subsequently repeatedly alternated (PHS, BSS, PHS, BSS, PHS). During irrigation with BSS the average amplitude of the b-wave was reduced to 87% (p < 0.02) and that of the c-wave to 63% (p < 0.001) of the levels obtained during perfusion with PHS. In two rabbits the ERG was studied about one month after vitrectomy, where PHS-irrigation was used both during surgery and for 30 min after its completion. No marked differences were observed between the treated and the untreated eyes as to the b- and c-wave amplitudes at stable stages of the recording. Thus, judged by the ERG, retinal and pigment epithelial functions were influenced unfavorably by BSS, whereas they seemed to be well preserved with PHS. From this point of view PHS appears to be an excellent irrigation solution for vitreoretinal surgery that ought to be clinically tested.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bornschein H and Zwiauer A (1952) Das Elektroretinogramm des Kaninchens bei experimenteller Erhöhung des intraokularen Druckes. Albrecht von Graefes Arch Ophthalmol 152:527–531
Christiansen JM, Kollarits CR, Fukui H, Fishman ML, Michels RG and Mikuni I (1976) Intraocular irrigating solutions and lens clarity. Am J Ophthalmol 82:594–597
Cutler RWP, Young JN and Urion DK (1983) Factors influencing the vitreous potassium concentration in the rat. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 24:631–636
Dick E and Miller RF (1978) Light-evoked potassium activity in mudpuppy retina: its relationship to the b-wave of the electroretinogram. Brain Res 154:388–394
Edelhauser HF, Van Horn DL, Hyndiuk RA and Schultz RO (1975) Intraocular irrigating solutions. Their effect on the corneal endothelium. Arch Ophthalmol 93:648–657
Edelhauser HF, Van Horn DL, Schultz RO and Hyndiuk RA (1976) Comparative toxicity of intraocular irrigating solutions on the corneal endothelium. Am J Ophthalmol 81:473–481
Faber DS (1969) Analysis of the slow transretinal potentials in response to light. Ph.D. Thesis. State University of New York at Buffalo
Graham MV (1983) Safe intraocular medication and irrigation. Trans Ophthalmol Soc UK 103:600–604
Hagins WA and Yoshikami S (1974) A role for Ca2+ in excitation of retinal rods and cones. Exp Eye Res 18:299–305
Honda Y, Podos SM and Becker B (1973) The effect of diphenyl hydantoine on the electroretinogram of rabbits. II. Effects of hypoxia and potassium. Invest Ophthalmol 12:573–578
Kato S and Negishi K (1978) Effects of variations in the perfusate on the ERG and discharge of ganglion cells in carp retina. Exp Eye Res 26:363–376
Marmor MF (1979) Retinal detachment from hyperosmotic intravitreal injection. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 18:1237–1244
McEnerney JK, Peyman GA and Janevicius RV (1978) A new irrigating solution for intraocular surgery: TC Earle solution. Ophthalmic Surg 9:66–72
Miller RF and Dowling JE (1970) Intracellular responses of the Müller (glial) cells of mudpuppy retina: their relation to b-wave of the electroretinogram. J Neurophysiol 33:323–341
Miller SS and Steinberg RH (1977) Passive ionic properties of frog retinal pigment epithelium. J Membr Biol 36:337–372
Negi A, Honda Y and Kawano S (1982) Importance of bicarbonate ion in the vitreous space. Arch Ophthalmol 100:1839–1843
Newman EA (1979) B-wave currents in the frog retina. Vision Res 19:227–234
Newman EA (1980) Current source-density analysis of the b-wave of frog retina. J Neurophysiol 43:1355–1366
Nilsson SEG and Skoog K-O (1975) Covariation of the simultaneously recorded c-wave and standing potential of the human eye. Acta Ophthalmol. (Copenh) 53:721–730
Oakley B II (1977) Potassium and the photoreceptor-dependent pigment epithelial hyperpolarization. J Gen Physiol 70:405–425
Oakley B II and Green DG (1976) Correlation of light-induced changes in retinal extracellular potassium concentration with c-wave of the electroretinogram. J Neurophysiol 39:1117–1133
Oakley B II, Miller SS and Steinberg RH (1978) Effect of intracellular potassium upon the electrogenic pump of frog retinal pigment epithelium. J Membr Biol 44:281–307
Oakley B II, Steinberg RH, Miller SS and Nilsson SEG (1977) The in vitro frog pigment epithelial hyperpolarization in response to light. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 16:771–774
Shimazaki H and Oakley B II (1985) Effects of cesium upon Müller cell membrane responses, [K+]0, and the electroretinogram. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 26 (ARVO Suppl) 112
Skoog K-O (1974) The c-wave of the human d.c. registered ERG. III. Effects of ethyl alchol on the c-wave. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh) 52:913–923
Steinberg RH, Oakley B II and Niemeyer G (1980) Light-evoked changes in [K+]0 in retina of intact cat eye. J Neurophysiol 44:897–921
Textorius O, Welinder E and Nilsson SEG (1985) Combined effects of DL-α-aminoadipic acid and either sodium iodate, ethyl alcohol or light stimulation on the ERG c-wave and on the standing potential of albino rabbit eyes. Docum Ophthalmol 60:393–400
Weekers J-F and Dethinne M (1978) Effets de différentes solutions d'irrigation intraoculaires sur l'endothélium de la cornée humaine. J Fr Ophthalmol 11:643–648
Winkler BS (1972) The electroretinogram of the isolated rat retina. Vision Res 12:1183–1198
Winkler BS, Simson V and Benner J (1977) Importance of bicarbonate in retinal function. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 16:766–768
Witkovsky P, Dudek FE and Ripps H (1975) Slow PIII component of the carp electroretinogram. J Gen Physiol 65:119–134
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Textorius, O., Nilsson, S.E.G. & Andersson, BE. Effects of intraocular perfusion with two alternating irrigation solutions on the simultaneously recorded electroretinogram of albino rabbits. Doc Ophthalmol 63, 349–358 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00220226
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00220226