Summary
Bombesin-like and gastrin-releasing peptide (GRP)-like immunoreactivities were localized in nerves of the guinea-pig small intestine and celiac ganglion with the use of antibodies raised against the synthetic peptides. The anti-bombesin serum (preincubated to avoid cross reactivity with substance P) and the anti-GRP serum revealed the same population of neurons. Preincubation of the antibombesin serum with bombesin abolished the immunoreactivity in nerves while absorption of the anti-GRP serum with either bombesin or the 14–27 C-terminal of GRP only reduced the immunoreactivity. The immunoreactivity was abolished by incubation with GRP 1–27.
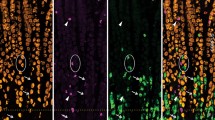
Immunoreactive nerves were found in the myenteric plexus, circular muscle, submucous plexus and in the celiac ganglion. Faintly reactive nerve cell bodies were found in the myenteric ganglia (3.2% of all neurons) but not in submucous ganglia. After all ascending and descending pathways in the myenteric plexus had been cut, reactive terminals disappeared in the myenteric plexus, circular muscle (including the deep muscular plexus) and the submucous plexus on the anal side. After the mesenteric nerves were cut no changes were observed in the intestinal wall but the reactive fibres in celiac ganglia disappeared. It is deduced that GRP/bombesin-immunoreactive nerve cell bodies in myenteric ganglia project from the myenteric plexus to other myenteric ganglia situated further anally (average length 12 mm), anally to the circular muscle (average length 9 mm), anally to submucous ganglia (average length 13 mm) and external to the intestine to the celiac ganglia.
It is concluded that the GRP/bombesin-reactive neurons in the intestinal wall represent a distinct population of enteric neurons likely to be involved in controlling motility and in the coordination of other intestinal functions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anastasi A, Erspamer V, Bucci M (1971) Isolation and structure of bombesin and alytesin, two analogous active peptides from the skin of the European amphibians Bombina and Alytes. Experientia 27:166–167
Bertaccini G (1982) Peptides: Candidate hormones. In: Bertaccini G (ed) Handbook of experimental pharmacology. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, p 85–135
Bertaccini G, Erspamer V, Melchiorri P, Sopranzi N (1974) Gastrin release by bombesin in the dog. Br J Pharmacol 52:219–225
Buffa R, Solvieva I, Fiocca R, Giorgino S, Rindi G, Solcia E, Mochizuchi T, Yanaihara C, Yanaihara N (1982) Localization of bombesin and GRP (gastrin releasing peptide) sequences in gut nerves of endocrine cells. Histochemistry 76:457–467
Costa M, Furness JB (1982) Neuronal peptides in the intestine. Br Med Bull 38:247–252
Costa M, Furness JB (1983) The origins, pathways and terminations of neurons with VIP-like immunoreactivity in the guineapig small intestine. Neuroscience 8:665–676
Costa M, Buffa R, Furness JB, Solcia E (1980a) Immunohistochemical localization of polypeptides in peripheral autonomic nerves using whole mount preparations. Histochemistry 65:157–165
Costa M, Cuello AC, Furness JB, Franco R (1980b) Distribution of enteric neurons showing immunoreactivity for substance P in the guinea-pig ileum. Neuroscience 5:323–331
Costa M, Furness JB, Llewellyn-Smith IJ, Davies B, Oliver J (1980c) An immunohistochemical study of the projections of somatostatin-containing neurons in the guinea-pig intestine. Neuroscience 5:841–852
Dalsgaard CJ, Hökfelt T, Schultzberg M, Lundberg JM, Terenius L, Dockray GJ, Cuello C, Goldstein M (1983) Origin of peptide-containing fibres in the inferior mesenteric ganglion of the guinea-pig: immunohistochemical studies with antisera to substance P, enkephalin, vasoactive intestinal polypeptide, cholecystokinin/gastrin and bombesin. Neuroscience (to be published)
Dockray GJ, Vaillant C, Walsh JH (1979) The neuronal origin of bombesin-like immunoreactivity in the rat gastrointestinal tract. Neuroscience 4:1561–1568
Erspamer V (1980) Peptides of the amphibian skin active on the gut. II Bombesin-like peptides, isolation structure and basic functions. In: Glass J (ed) Gastrointestinal hormones. Raven Press, New York, p 343–361
Erspamer V, Erspamer GF, Inselvini M, Negri L (1972) Occurrence of bombesin and alytesin in extracts of the skin of three European discoglossid frogs and pharmacological actions of bombesin on extravascular smooth muscle. Br J Pharmacol 45:333–348
Furness JB, Costa M (1975) The use of glyoxylic acid for the fluorescence histochemical demonstration of peripheral stores of noradrenaline and 5-hydroxytryptamine in whole mounts. Histochemistry 41:335–352
Furness JB, Costa M (1982a) Identification of gastrointestinal neurotransmitters. In: Bertaccini G (ed) Handbook of experimental pharmacology. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, p 383–460
Furness JB, Costa M (1982b) Neurons with 5-hydroxytryptaminelike immunoreactivity in the enteric nervous system: Their projections in the guinea-pig small intestine. Neuroscience 7:341–349
Furness JB, Costa M, Franco R, Llewellyn-Smith IJ (1980) Neuronal peptides in the intestine: Distribution and possible functions. In: Costa M, Trabucchi M (eds) Neural peptides and neuronal communication. Raven Press, New York, p 601–617
Furness JB, Costa M, Emson PC, Håkanson R, Moghimzadeh E, Sundler F, Taylor IL, Chance RE (1983) Distribution, pathways and reactions to drug treatment of nerves with neuropeptide Y- and pancreatic polypeptide-like immunoreactivity in the guinea-pig digestive tract. Cell Tissue Res (submitted)
Hutchison JB, Dimaline R, Dockray GJ (1981) Neuropeptides in the gut: Quantification and characterization of cholecystokinin octapeptide bombesin- and vasoactive intestinal polypeptidelike immunoreactivities in the myenteric plexus of the guineapig small intestine. Peptides 2:23–30
McDonald TJ, Nilsson G, Vagne M, Ghatei M, Bloom SR, Mutt V (1978) A gastrin releasing peptide from the porcine nonantral gastric tissue. Gut 19:767–774
McDonald TJ, Jörnvall H, Nilsson G, Vagne M, Ghatei M, Brown SR, Mutt V (1979) Characterization of gastrin releasing peptide from porcine non-antral gastric tissue. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 90:227–233
Moody TW, Pert CB (1979) Bombesin-like peptides in rat brain: quantitation and biochemical characterization. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 90:7–14
Schultzberg M (1983) Bombesin-like immunoreactivity in sympathetic ganglia. Neuroscience 8:363–374
Szurszewski JH (1977) Towards a new view of prevertebral ganglion. In: Brooks FP, Evers PW (eds) Nerves and the gut. Slack, New Jersey, pp 244–258
Walsh JH, Wong HC, Dockray GJ (1979) Bombesin-like peptides in mammals. Fed Proc 38:2315–2319
Walsh JH, Reeve JR, Vigna SR (1981) Distribution and molecular forms of mammalian bombesin. In: Bloom S, Polak J (eds) Gut hormones. Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh, London, Melbourne, pp 413–424
Wilson AJ, Furness JB, Costa M (1981) The fine structure of the submucous plexus of the guinea-pig ileum. I. The ganglia, neurons, Schwann cells and neuropil. J Neurocytol 10:759–784
Yanaihara N, Yanaihara C, Mochizuki T, Iwahara K, Fujita T, Iwanaga T (1981) Immunoreactive GRP. Peptides 2:185–191
Zetler G (1980) Antagonism of the gut-contracting effects of bombesin and neurotensin by opioid peptides, morphine, atropine or tetrodotoxin. Pharmacology 21:348–354
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Costa, M., Furness, J.B., Yanaihara, N. et al. Distribution and projections of neurons with immunoreactivity for both gastrin-releasing peptide and bombesin in the guinea-pig small intestine. Cell Tissue Res. 235, 285–293 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00217852
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00217852