Summary
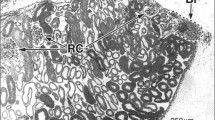
The ultrastructure of the renal corpuscle, the neck segment, the proximal tubule and the intermediate segment of the kidney of a South American caecilian, Typhlonectes compressicaudus (Amphibia, Gymnophiona) was examined by means of transmission electron microscopy (TEM), scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and freezefracture technique. The glomerular filter apparatus consists of the podocyte epithelium, a distinct basement membrane, a subendothelial space and the capillary endothelium. Emanating from the podocyte cell body, several long primary processes encircle neighboring capillaries. The short slender foot processes originating from the primary processes interdigitate with those from other primary processes, thereby forming the meandering filtration slit. Thick bundles of microfilaments are found in the primary processes, but absent in the foot processes. The basement membrane consists of a lamina rara externa and a rather thin lamina densa (50 nm thickness). The wide subendothelial space contains abundant microfibrils, a few collagen fibrils and many thin processes of mesangial cells. The endothelium is flat and fenestrated (compared to mammals displaying relatively few fenestrations); some of the fenestrations are bridged by a diaphragm. The glomerular mesangium is made up of the mesangial cells and a prominent mesangial matrix containing microfibrils and collagen fibrils. The cells of the neck and intermediate segments display numerous cilia with their microtubules arranged in the typical 9+2 pattern. The basal bodies of the cilia are attached to thick filaments with a clear crossbanding pattern of 65 nm periodicity. The proximal tubule is composed of cells typical for this segment (PT cells) and light cells lacking a brush border (bald-headed cells). The PT cells measure 10–25 μm in height and 15–30 μm in width and do not interdigitate at their lateral borders with each other. Their basolateral cell membrane is amplified by many folds projecting into lateral intercellular spaces and into basal recesses. The brush border is scarce and composed of loosely arranged short microvilli.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altland PD, Hathaway WE (1974) Erythrocyte and hemoglobin values: vertebrates. In: Altman PL, Dittmer DS (eds) Biology data book, 2nd ed, vol 3, Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology, Bethesda, pp 1849–1953
Bargmann W (1934) Untersuchungen über Histologie und Histophysiologie der Fischniere. I. Dipnoer: Lepidosiren paradoxa. Z Zellforsch 21:388–411
Bargmann W, Hehn Gv (1971) Über das Nephron der Elasmobranchier. Z Zellforsch 114:1–21
Brenner BM, Dworkin LD, Ichikawa I (1986) Glomerular ultrafiltration. In: Brenner BM, Rector FC (eds) The kidney, 3rd ed, vol l, WB Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 124–144
Chase SW (1923) The mesonephros and urogenital ducts of Necturus maculosus, Rafinesque. J Morphol 37:457–531
Conel JLR (1917) The urogenital system of myxinoids. J Morphol 29:75–163
Dantzler WH (1985) Comparative aspects of renal function. In: Seidin DW, Giebisch G (eds) The kidney: physiology and pathophysiology. Raven Press, New York, pp 333–364
Davis LE, Schmidt-Nielsen B (1967) Ultrastructure of the crocodile kidney (Crocodylus acutus) with special reference to electrolyte and fluid transport. J Morphol 121:255–276
Davis LE, Schmidt-Nielsen B, Stolte H (1976) Anatomy and ultrastructure of the excretory system of the lizard, Sceloporus cyanogenys. J Morphol 149:279–326
Dworkin LD, Brenner BM (1985) Biophysical basis of glomerular filtration. In: Seldin DW, Giebisch G (eds) The kidney: physiology and pathophysiology. Raven Press, New York, pp 397–426
Freytag GE (1970) Schwanzlurche und Blindwühlen. In: Freytag GE, Grzimek B, Kühn O, Thenius E (eds) Grzimeks Tierleben, vol 5: Lurche, Kindler, Zürich, pp 313–358
Gaupp E (1904) A Ecker's und R Wiedersheim's Anatomie des Frosches. 3. Abt: Lehre von den Eingeweiden, dem Integument und den Sinnesorganen. 2. Aufl, Friedrich Vieweg und Sohn, Braunschweig
Heath-Eves MJ, McMillan DB (1974) The morphology of the kidney of the Atlantic hagfish, Myxine glutinosa (L). Am J Anat 139:309–334
Himmelhoch SR, Karnovsky MJ (1961) Oxidative and hydrolytic enzymes in the nephron of Necturus maculosus. Histochemical, biochemical, and electron microscopical studies. J Biophys Biochem Cytol 9:893–908
Kaissling B, Kriz W (1979) Structural analysis of the rabbit kidney. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol 56:1–123
Kanwar YS (1984) Biology of disease. Biophysiology of glomerular filtration and proteinuria. Lab Invest 51:7–21
Lacy ER, Reale E (1986) The elasmobranch kidney. II. Sequence and structure of the nephrons. Anat Embryol 173:163–186
Linss W, Geyer G (1964) Über die elektronenmikroskopische Struktur der Nierentubuli von Rana esculenta. Anat Anz 115:281–296
Maunsbach AB (1973) Ultrastructure of the proximal tubule. In: Orloff J, Berliner RW (eds) Handbook of physiology, section 8: Renal physiology, American Physiological Society Washington DC, pp 31–79
Maunsbach AB, Boulpaep EL (1983) Paracellular shunt ultrastructure and changes in fluid transport in Necturus proximal tubule. Kidney Int 24:610–619
Maunsbach AB, Boulpaep EL (1984) Quantitative ultrastructure and functional correlates in proximal tubule of Ambysloma and Necturus. Am J Physiol 246:F710-F724
Moodie GEE (1978) Observations on the life history of the caecilian Typhlonectes compressicaudus (Dumeril and Bibron) in the Amazon basin. Can J Zool 56:1005–1008
Pak Poy RKF (1958) Electron microscopy of the piscine (Carassius auratus) renal glomerulus. Aust J Exp Biol 36:191–210
Renkin EM, Gilmore JP (1973) Glomerular filtration. In: Orloff J, Berliner RW (eds) Handbook of physiology, section 8: Renal physiology, American Physiological Society, Washington DC, pp 185–248
Romer AS, Parsons TS (1985) The vertebrate body. 6th ed, Saunders, Philadelphia
Sakai T (1985) The structure of the kidney from the freshwater teleost Carassius auratus. Anat Embryol 171:31–39
Sakai T, Kawahara K (1983) The structure of the kidney of Japanese newts, Triturus (Cynops pyrrhogaster). Anat Embryol 166:31–52
Sakai T, Kriz W (1987) The structural relationship between mesangial cells and basement membrane of the renal glomerulus. Anat Embryol 176:373–386
Sakai T, Billo R, Kriz W (1986) The structural organization of the kidney of Typhlonectes compressicaudus (Amphibia, Gymnophiona). Anat Embryol 174:243–252
Sarasin P, Sarasin F (1887–1890) Ergebnisse naturwissenschaftlicher Forschungen auf Ceylon in den Jahren 1884–1886. II. Zur Entwicklungsgeschichte über Anatomie des Ceylonischen Bilindwühle Ichthyophis glutinosus. LCW Kreidels, Wiesbaden
Shea SM, Morrison AB (1975) A stereological study of the glomerular filter in the rat. J Cell Biol 67:436–443
Stanton B, Biemesderfer D, Stetson D, Kashgarian M, Giebisch G (1984) Cellular ultrastructure of Amphiuma distal nephron: effects of exposure of potassium. Am J Physiol 247:C204-C216
Taugner R, Schiller A, Ntokalou-Knittel S (1982) Cells and intercellular contacts in glomeruli and tubules of the frog kidney. Cell Tissue Res 226:589–608
Tsujii T, Naito I, Ukita S, Ono T, Seno S (1984a) The anionic barrier system in the mesonephric renal glomerulus of the arctic lamprey, Entosphenus japonicus (Martens) (Cyclostomi). Cell Tissue Res 235:491–496
Tsujii T, Naito I, Ukita S, Ono T, Seno S (1984b) The anionic barrier system in the mesonephric renal glomerulus of the brown hagfish, Paramyxine atami Dean (Cyclostomi). Anat Rec 208:337–347
Unsicker K, Krisch B (1975) Kontraktile Filamente im Nephron. Dtsch Med Wschr 100:116–119
Wake MH (1969) Kidney morphology in terrestrial and aquatic caecilians. Anat Rec 163:331
Wake MH (1970) Evolutionary morphology of the caecilian urogenital system. II. The kidneys and urogenital ducts. Acta Anat 75:321–358
Welsch U, Storch V (1973) Elektronenmikroskopische Beobachtungen am Nephron adulter Gymnophionen (Ichthyophis kohtaoensis Taylor). Zool Jb Anat 90:311–322
Wendelaar Bonga SE, Veenhuia M (1974) The membranes of the basal labyrinth in the kidney cells of the stickleback, Gasterosteus aculeatus, studied in ultrathin sections and freeze etch replicas. J Cell Sci 14:587–609
Yamada E (1960) Collagen fibrils within the renal glomerulus. J Biophys Biochem Cytol 7:407–409
Youson JH, McMillan DB (1970a) The opisthonephric kidney of the sea lamprey of the great lakes, Petromyzon marinus L. I. The renal corpuscle. Am J Anat 127:207–232
Youson JH, McMillan DB (1970b) The opisthonephric kidney of the sea lamprey of the great lakes, Petromyzon marinus L. II. Neck and proximal segments of the tubular nephron. Am J Anat 127:233–258
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Research fellow of the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sakai, T., Billo, R., Nobiling, R. et al. Ultrastructure of the kidney of a South American caecilian, Typhlonectes compressicaudus (Amphibia, Gymnophiona). Cell Tissue Res. 252, 589–600 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00216646
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00216646