Abstract
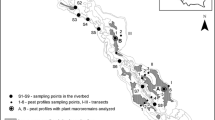
Vegetation composition and structure of 58 sites along gradients in the valley mire of Biebrza, Poland, are related to physical and chemical variables of groundwater and peat. The three most prominent hydrochemical processes in the valley are (a) dissolution of calcite; (b) dissolution of iron, manganese and aluminium; and (c) enrichment with nitrogen and potassium. Major factors determining these processes are vertical flow of the groundwater and river flooding.
Within the rheophilous zone of the mire, calcium-richness of the shallow groundwater and base-saturation of the peat are caused by upward seepage of groundwater originating from adjacent higher grounds. This groundwater movement keeps the larger part of the mire saturated with calcium.
Good correlations exist between hydrochemistry and vegetation patterns. Groundwater-fed sites support a characteristic rich fen vegetation (Caricetum limoso-diandrae) with a low biomass production. The flood-plain vegetation consists of highly-productive communities of Glycerietum maximae and Caricetum elatae. In a belt in the Upper Basin where neither flooding nor upward seepage occurs, succession, probably caused by intensified drainage, leads to a dwarf-shrub vegetation (Betuletum humilis; poor fen).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armstrong, W. and Boatman, D.J. 1967. Some field observations relating the growth of bog plants to conditions of soil aeration. J. Ecol., 55: 101–110.
Bellamy, D.J. and Rieley, J. 1967. Some ecological statistics of a ‘miniature bog’. Oikos, 18: 33–40.
Bolt, H. and Bruggenwert, M.G.M. 1978. Soil chemistry. A. Basic elements. Elsevier, Amsterdam.
Bos, C.B. and Fredeen, K.J. 1989. Concepts instrumentation and techniques in Inductively Coupled Plasma Atomic Emission Spectroscopy. Perkin-Elmer Cooperation, Norwalk.
Boumans, P.J.W.M. 1987. Inductively Coupled Plasma Emission Spectroscopy, part. 1. Wiley Interscience Publication, New York.
Byczkowski, A. and Kicinski, T. 1984. Surface waters in the Biebrza drainage basin. Polish Ecological Studies, 10: 271–299.
Clymo, R.S. 1978. A model of peat bog growth. In: Heal, O.W. and Perkins, D.F. (ed), Production ecology of British moors and montane grasslands. Ecological Studies 27. pp. 187–226. Springer Verlag, Berlin.
Eisen, C. and Anderson, M.P. 1979. The effect of urbanisation on groundwater quality, a case-study. Groundwater, 17: 456–462.
Garcke, A. 1972. Illustrierte Flora Deutschlands und angrenzende Gebiete. 23 Aufl. Paul Parey Verlag, Berlin, Hamburg.
Giller, K.E. and Wheeler, B.D. 1988. Acidification and succession in a flood-plain mire in the Norfolk Broadland, U.K. J. Ecol., 76: 849–866.
Gore, A.J.P. 1983. Mires: Swamp, bog, fen and moor. General Studies. Ecosystems of the World 4A. Elsevier, Amsterdam.
Grootjans, A.P., Van Diggelen, R., Wassen, M.J. and Wiersinga, W.A. 1988. The effects of drainage on groundwater quality and plant species distribution in stream valley meadows. Vegetatio, 75: 37–48.
Hem, J.D. 1985. Study and interpretation of the chemical characteristics of natural water. Water supply paper 2254. U.S. Geological survey, Alexandria.
Ingram, H.A.P. 1967. Problems of hydrology and plant distribution in mires. J. Ecol., 55: 711–724.
Institute of Meteorology and Water Management. 1978. Hydrographic subdivision of Poland. Wydawnictwa Komisji i Lacznosci, Warszawa.
Kemmers, R.H. 1986. Perspectives in modelling of processes in the root zone of spontaneous vegetation at wet and damp sites in relation to regional water management. In: Proceedings & Information, 34. Commissie Hydrologisch Onderzoek - Toegepast Natuurwetenschappelijk Onderzoek. pp. 91–116. The Hague.
Kossowska-Cezak, U. 1984. Climate of the Biebrza ice-marginal valley. Polish Ecological Studies, 10: 253–270.
Kulczynski, S. 1949. Peatbogs of Polesie. Memoires de l'academie polonaise des sciences et des lettres, Classe des sciences mathematiques et naturelles, Serie B, Sciences naturelles, Cracovie.
Liwski, L., Maciak, F., Okruszko, H., Churski, T., Gotkiewicz, J., Oswit, J., Pacowski, R., Szuniewicz, J. and Zurek, S. 1984. Characteristics of soil formation and soils and their evolution due to draining and different utilization. Polish Ecologial Studies, 12: 313–346.
Margadant, W.D. and During, H.J. 1982. Beknopte flora van de Nederlandse blad- en levermossen. Thieme, Zutphen.
Moore, P.D. and Bellamy, D.J. 1973. Peatlands. Elek Science, London.
Nielsen, D.R. and McDonald, J.G. 1978. Nitrogen in the environment. Acad. Press Inc., New York.
Okruszko, H. 1973. Natural and agricultural characteristic of the Biebrza valley. Problems of reclamation and use of swampy flooded valleys. Zeszyty problemowe Postepow Nauk rolniczych 134: 173–199.
Oswit, J. 1973. The development of peatlands in the lower Biebrza valley versus water conditions. Roczniki Nauk rolniczych (Polish Agric. Ann.), Serie D, 143. Polska Akademia Nauk, Warszawa.
Pajnowska, H., Pozniak, R. and Wienclaw, E. 1984. Groundwater of the Biebrza valley. Polish Ecological Studies, 10: 301–311.
Palczynski, A. 1975. Das Urtal der Biebrza, Die geobotanische palaeophytosociologische und wirtschaftliche Probleme. Roczniki Nauk rolniczych (Polish Agric. Ann.), Serie D, 145. Polska Akademia Nauk, Warszawa.
Palczynski, A. 1984. Natural differentiation of plant communities in relation to hydrological conditions of the Biebrza valley. Polish Ecological Studies, 10: 347–385.
Palczynski, A. 1985. Succession trends in plant communities of the Biebrza valley. Polish Ecological Studies, 11: 5–20.
SAS 1985. User's guide: statistics, 5th edition. SAS Institute Incorporated. Gary, North Carolina.
Scheffer, F. and Schachtschnabel, P. 1982. Lehrbuch den Bodenkunde. Enke Verlag, Stuttgart.
Sjörs, H. 1950a. Regional studies in North Swedish mire vegetation. Botaniska Notiser, 103: 173–222.
Sjörs, H. 1950b. On the relation between vegetation and electrolytes in north Swedish mire waters. Oikos, 2: 241–258.
Soil Survey Staff. 1975. Soil taxonomy. Agricult. Handbook no. 436, Soil Cons. Series, U.S. Dept. of Agriculture, Washington D.C.
Stumm, W. and Morgan, J.J. 1981. Aquatic Chemistry. John Wiley & Sons Inc. New York.
Stuyfzand, P.J. 1989. An accurate, relatively simple calculation of the Saturation Index of calcite for fresh to salt water. J. Hydrol., 105: 95–107.
Succow, M. 1988. Landschaftökologische Moorkunde. Gebr. Borntraeger, Berlin, Stuttgart.
Succow, M. and Jeschke, L. 1986. Moore in der Landschaft. Urania Verlag, Leipzig.
Szczepanski, A., Krolikowska, J., Szajnowski, F. and Szczepanska, W. 1984. Preliminary estimation of productivity of peatlands in the lower part of the Biebrza River. Polish Ecological Studies, 10: 387–401.
Van der Maarel, E. 1979. Transformation of cover-abundance values in phytosociology and its effects on community similarity. Vegetatio, 39: 97–114.
Van Diggelen, R., Grootjans A.P., Kemmers, R.H., Kooijman A.M., Succow, M., De Vries., N.P.J. and Van Wirdum, G. 1991. Hydroecological analysis of the fen system Lieper Posse, eastern Germany. J. Veg. Sci., 2: 465–476.
Van Tongeren, O. 1986. FLEXCLUS, an interactive program for classification and tabulation of ecological data. Acta But. Neerl., 35: 137–142.
Wassen, M.J., Barendregt, A. and De Smidt, J.T. 1988. Groundwater flow as conditioning factor for fen ecosystems in the Kortenhoef area, the Netherlands. In: Ruzicka, M. Hrnciarova, T. and Miklos, L. (ed), Spatial and functional relationships in Landscape Ecology, pp. 103–110. Inst. of Exp. Biology and Ecology of the Centre of Biol.-Ecol. Sciences of the Slovak Acad. of Sc., Bratislava, CSSR.
Wassen, M.J., Barendregt, A., Bootsma, M.C. and Schot, P.P. 1989. Groundwater chemistry and vegetation of gradients from rich fen to poor fen in the Naardermeer (the Netherlands). Vegetatio, 79: 117–132.
Wassen, M.J. 1990. Water flow as a major landscape ecological factor in fen development. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Utrecht, the Netherlands.
Wassen, M.J., Barendregt, A., Palczynski, A., De Smidt, J.T. and De Mars, H. 1990. The relationship between fen vegetation gradients, groundwater flow and flooding in an undrained valley mire at Biebrza, Poland. J. Ecol., 78: 1106–1122.
Waughman, G.J. 1980. Chemical aspects of the ecology of some South German peatlands. J. Ecol., 68: 1025–1046.
Westhoff, V. and Den Held, A.J. 1969. Plantengemeenschappen in Nederland. Thieme, Zutphen.
Wheeler, B.D. 1980. Plant communities of rich-fen systems in England and Wales. II. Communities of calcareous mires. J. Ecol., 68: 405–420.
Witting, M. 1948. Forsatta Katjonbestammingen i Myrvatten. Svensk Botanisk Tidskrift, 42: 116–134.
Zurek, S. 1984. Relief, geologic structure and hydrography of the Biebrza ice-marginal valley. Polish Ecological Studies, 10: 239–251.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wassen, M.J., Barendregt, A., Palczynski, A. et al. Hydro-ecological analysis of the Biebrza mire (Poland). Wetlands Ecol Manage 2, 119–134 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00215319
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00215319