Abstract
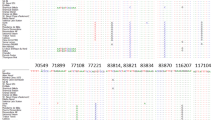
The genetic variability of seven Phaseolus taxa has been evaluated on the basis of molecular data and the results have used to clarify the phyletic relationships between several taxa of the P. coccineus L. complex. Chloroplast DNA (cpDNA) from 33 populations was digested with six restriction endonucleases, revealing some polymorphisms that made it possible to divide most of the taxa into two main groups: the subspecies of P. coccineus on the one hand, and P. vulgaris L., P. polyanthus Greenman and P. costaricensis (Freytag and Debouck) on the other hand. P. polyanthus is closer to P. vulgaris than the other taxa of the second group and should be considered as a separate species. The position of the wild species P. costaricensis is intermediate between P. coccineus and P. polyanthus. P. glabellus shows sufficient polymorphisms at the cpDNA level to be recognized as a separate species, as previously suggested from total seed-protein electrophoretic studies. These results favour the hypothesis of a common phylogeny for P. vulgaris, P. polyanthus, P. costaricensis and P. coccineus from a single wild ancestor. Although cpDNA is generally known to be uniform at the intraspecific level, some additional polymorphisms were also detected within P. vulgaris, P. polyanthus and P. coccineus. Further studies are required to understand the significance of the latter.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baudoin JP, Marechal R (1991) Wide crosses and taxonomy of pulse crops, with special emphasis on Phaseolus and Vigna. In: Ng NP, Perrino P, Attere F, Zedan H (eds) Proceedings of an African plant genetic resources Workshop, International Institute of Tropical Agriculture (Nigeria), 17–20 October 1988, pp 287–302
Baudoin JP, Camarena Mayta F, Schmit V (1992) Contribution à une meilleure connaissance de la position phylétique de la légumineuse alimentaire Phaseolus polyanthus Greenm. Bull Rech Agron Gembloux 27:167–198
Buckner B, Hyde BB (1985) Chloroplast DNA variation between the common cultivated potato (Solarium tuberosum ssp. tuberosum) and several South American relatives. Theor Appl Genet 71:527–531
Camarena F, Baudoin JP (1987) Obtention des premiers hybrides interspécifiques entre Phaseolus vulgaris et Phaseolus polyanthus avec le cytoplasme de cette dernière forme. Bull Rech Agron Gembloux 22:43–55
Dally AM, Second G (1990) Chloroplast DNA diversity in wild and cultivated species of rice (Genus Oryza section Oryza). Cladistic mutation and genetic-distance analysis. Theor Appl Genet 80:209–222
Debouck DG (1986) Phaseolus germplasm collection in the Huasteca and surrounding regions, Mexico. Trip Report, Centro Internacional de Agricultura Tropical (CIAT), Cali, Colombia
Debouck DG (1991). Systematics and morphology. In: van Schoonhoven A, Voysest O (eds) Common beans: research for crop improvement. Commonwealth Agricultural Bureaux International, Wallingford, United Kingdom, pp 55–118
Debouck DG, Araya VR, Ocampo S, Gonzalez UWG (1989) Collecting Phaseolus in Costa Rica. FAO/IBPGR P1 Genet Res Newslett 78/79:44–46
Delgado SA (1985) Systematics of the genus Phaseolus (Leguminosae) in North and Central America. PhD thesis, University of Texas, Austin
Delgado SA (1988) Variation, taxonomy, domestication and germplasm potentialities in Phaseolus coccineus. In: Gepts P (ed) Genetic resources of Phaseolus beans. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht (The Netherlands), pp 441–463
Doebley J, Renfroe W, Blanton A (1987) Restriction site variation in the Zea Chloroplast genome. Genetics 117:139–147
Gawel NJ, Jarret RL (1991) Chloroplast DNA restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLPs) in Musa species. Theor Appl Genet 81:783–786
Gepts P (1988) A middle American and an Andean common bean gene pool. In: Gepts P (ed) Genetic resources of Phaseolus beans. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht (The Netherlands), pp 375–390
Hosaka K, Ogihara Y, Matsubayashi M, Tsunewaki (1984) Phylogenetic relationship between the tuberous Solanum species as revealed by restriction endonucleases analysis of Chloroplast DNA. Jpn J Genet 59:349–369
Hosaka K (1986) Who is the mother of the potato? Restriction endonuclease analysis of chloroplast DNA of cultivated potatoes. Theor Appl Genet 72:606–618
Hosaka K, Hanneman RE, Jr (1988) The origin of the cultivated tetraploid potato based on chloroplast DNA. Theor Appl Genet 76:172–176
Hucl P, Scoles GJ (1985) Interspecific hybridization in the common bean: a review. HortScience 20:352–357
Jonhson SC (1967) Hierarchic clustering schemes. Psychometrika 32:241–254
Khairallah MM, Adams MW, Sears BB (1990) Mitochondrial DNA polymorphisms of Malawian bean lines: further evidence for two major gene pools. Theor Appl Genet 80:753–761
Khairallah MM, Sears BB, Adams MW (1992) Mitochondrial restriction fragment length polymorphisms in wild Phaseolus vulgaris L.: insights on the domestication of the common bean. Theor Appl Genet 84:915–922
Kung SD, Zhu ZS, Chen GF (1982) Nicotiana chloroplast genome. III. Chloroplast DNA evolution. Theor Appl Genet 61:73–79
Le Marchand G, Maréchal R (1977) Chromosome pairing in interspecific hybrids reveals the value of pollen morphology for deducing phylogenic affinities in the genus Phaseolus. In: Interspecific hybridization in plant breeding. Proc 8th Congress Eucarpia, Madrid, pp 355–337
Llaca V, Gepts P (1991) Studies on Phaseolus inter and intraspecific evolution using cpDNA as a molecular marker. Annu Rep Bean Improv Coop 34:145–146
Londoño NR, Gathee JW, Sanders JH (1981) Bean production trends in Africa 1966–1979. In: Proceedings Regional Workshop on Potential for Fields Beans in Eastern Africa, Lilongwe, Malawi, 1980. Centro Internacional de Agricultura Tropical, Cali, Colombia, pp 19–29
Maniatis T, Fritsch EF, Sambrook J (1982) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, New York
Maréchal R, Masherpa JM, Stainier F (1978) Etude taxonomique d'un groupe complexe d'espèces des genres Phaseolus et Vigna (Papilionaceae) sur la base de données morphologiques et polliniques traitées par l'analyse informatique. Boissiera 28:1–273
Masoud SA, Jonhson LB, Sorensen EL (1990) High transmission of paternal plastid DNA in Alfalfa plants demonstrated by restriction fragment polymorphism analysis. Theor Appl Genet 79:49–55
Metzlaff M, Borner T, Hagemann R (1981) Variations of chloroplast DNAs in the genus Pelargonium and their biparental inheritance. Theor Appl Genet 60:37–41
Milligan BG (1991) Chloroplast DNA diversity within Land among populations of Trifolium pratense. Curr Genet 19:411–416
Palmer JD (1987) Chloroplast DNA evolution and biosystematic uses of chloroplast DNA variation. Am Nat 130 (Suppl):6–29
Palmer JD, Zamir D (1982) Chloroplast DNA evolution and phylogenetic relationships in Lycopersicon. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 79:5006–5010
Piñero D, Eguiarte L (1988) The origin and biosystematic status of Phaseolus coccineus ssp. polyanthus:electrophoretic evidence. Euphytica 37:199–203
Piper CV (1926) Studies in American Phaseolinae. Contr US Nat Herb 22:663–701
Schmit V (1992) Etude de Phaseolus polyanthus Greenman et autres taxons du complexe Phaseolus coccineus L. Thèse de doctorat, Faculté des Sciences Agronomiques, Gembloux
Schmit V, Baudoin JP (1987) Multiplication et évaluation de Phaseolus coccineus L. et Phaseolus polyanthus Greenman, deux espèces intéressantes pour l'amélioration de la productivité des légumineuses vivrières. Bull Rech Agron Gembloux 22:235–253
Schmit V, Debouck DG (1990) P. glabellus Piper, a noteworthy variant of the P. coccineus complex? Annu Rep Bean Improv Coop 33:124–125
Schmit V, Debouck DG (1991) Observations on the origin of Phaseolus polyanthus Greenman. Econ Bot 45:345–364
Schmit V, Baudoin JP, Wathelet B (1991) Considerations about the taxonomical position of various taxa of the P. coccineus complex on basis of seeds protein electrophoresis and experimental hybridizations. Annu Rep Bean Improv Coop 34:87–88
Schuman CM, Hancock JF (1989) Paternal inheritance of plastids in Medicago sativa. Theor Appl Genet 78:863–866
Smartt J (1973) The possible status of P. coccineus L. ssp. darwinianus Hdz X and Miranda C as a distinct species and cultigen of the genus Phaseolus. Euphytica 22:424–426
Smartt J (1979) Interspecific hybridization in the grain legumes — a review. Econ Bot 33:329–337
Sneath PHA, Sokal RR (1973) Numerical taxonomy. W. F. Freeman and Company, San Francisco
Soltis DE, Soltis PS, Milligan BG (1992) Intraspecific chloroplast DNA variation: systematic and phylogenetic implications. In: Soltis PS, Soltis DE, Doyle JJ (eds) Molecular Systematics of Plants. Chapman and Hall, New York, pp 117–150
Soreng RJ (1990) Chloroplast DNA phylogenetics and biogeography in a reticulating group: study in Poa (Poaceae). Am J Bot 77:1383–1400
Sprecher SL (1988) Allozyme differentiation between gene pools in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.), with special reference to Malawian germplasm. PhD thesis, Michigan State University, EAst Lansing, Michigan, USA
Sullivan JG, Freytag G (1986) Predicting interspecific compatibilities in beans (Phaseolus) by seed protein electrophoresis. Euphytica 35:201–209
Thimothy DH, Levings CS, III, Pring DR, Conde MF, Kermicle JL (1979) Organelle DNA variation and systematic relationships in the genus Zea: Teosinte. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76:4220–4224
Voyset O (1983) Variedades de frijol en America Latina y su origen. Centro Internacional de Agricultura Tropical, Cali, Colombia
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by R. Hagemann
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schmit, V., du Jardin, P., Baudoin, J.P. et al. Use of chloroplast DNA polymorphisms for the phylogenetic study of seven Phaseolus taxa including P. vulgaris and P. coccineus . Theoret. Appl. Genetics 87, 506–516 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00215097
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00215097