Abstract
Norway lobsters, Nephrops norvegicus were exposed for 18 days to combinations of cadmium, copper and zinc at three sublethal concentrations (1, 5, 25 μg/L for Cd and Cu, and 8, 40 and 200 μg/L for Zn). Male animals were exposed to all three concentrations, while female animals were studied only in one (highest) concentration of the metals. Activities of Na,K-ATPase and both oligomycin-sensitive and insensitive Mg-ATPase were investigated in relation to metal exposure. A group of male Nephrops of different size groups from a single location in the Clyde Sea was also sampled to investigate the relationship between size and ATPase activity.
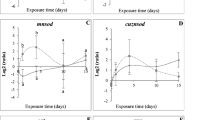
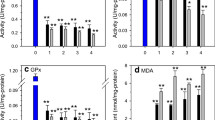
Cadmium concentrations increased significantly with increases in exposure concentrations in both male and female animals, whereas copper and zinc increased significantly only in the highest treatment in males. There was no significant difference in concentrations of the metals in control male and female animals, whereas males accumulated significantly higher levels of copper and zinc in the highest concentrations of the metals. Control males showed higher activity of Na,K-ATPase than control females. Na,K-ATPase activity was significantly inhibited in male animals exposed to metals whereas in female animals there was only a significant inhibition in total Mg-ATPase activity. Na,K-ATPase activity had a negative relationship with copper in males, while in treated females this ATPase had positive relationship with zinc and copper. There were negative relationships between the activities of Na,K-ATPase and oligomycin sensitive Mg-ATPase with carapace length of the animals.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdullah MI, Royle LG (1974) A study of dissolved and particulate trace elements in the Bristol Channel. J Mar Biol Assoc UK 54:581
Atkinson A, Gatemby AO, Lowe AG (1973) The determination of inorganic orthophosphate in biological systems. Biochem Biophys Acta 320:195–204
Balls PW, Topping G (1987) The influence of inputs to the Firth of Firth on the concentrations of trace metals in coastal waters. Environ Pollut 45:159–172
Bloom H, Aylin GM (1977) Heavy metals in the Derwent Estuary. Environ Geol 2:3
Bouquegneau JM (1976) ATPase activity in mercury intoxicated eels. Specialia Experientia 13(7):941–943
Boyer PD, Chance B, Ernster L, Mitchell P, Racker E, Slater EC (1977) Oxidative phophorylation and photophosphorylation. Ann Rev Biochem 46:955–1026
Bradford M (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–251
Bryan GW, Langston WJ, Hummerstone LG, Burt GR (1985) A guide to the assessment of heavy metal contamination in estuaries using biological indicators. Mar Biol Assoc UK Occasional Publication No. 4
Canli M (1993) Field and laboratory studies on heavy metal uptake and tissue distribution, ATPase activity and metallothionein in tissues of the Norway lobster Nephrops norvegicus (L.). PhD Thesis, University of Glasgow, UK
Canli M, Furness RW (1993a) Heavy metals in tissues of the Norway lobster, Nephrops norvegicus: Effects of sex, size and season. Chemistry Ecology 8:19–32
Canli M, Furness RW (1993b) Toxicity of heavy metals dissolved in seawater and influences of sex and size on metal accumulation and tissue distribution in the Norway lobster, Nephrops norvegicus. Mar Environ Res 36(4):217–236
Dehn PF, Haya K, Aiken DE (1985) Adenylate energy charge, arginine phosphate and ATPase activity in juvenile Homarus americanus during the moult cycle. Comp Biochem Physiol 81B(3):629–633
Desaiah D, Cutkomp LK, Yap HH, Koch RB (1972) Inhibition of oligomycin-sensitive magnesium Adenosine Triphosphatase activity in fish by polychlorinated biphenyls. Biochem Pharmacol 21:857–865
Eisler R, Hennekey RJ (1977) Acute toxicities of Cd2+, Cr6+, Hg2+, Ni2+, and Zn2+ to estuaries macrofauna. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 6:315–323
Harris RR, Bayliss D (1988) Gill (Na+ + K+)-ATPase in decapod crustaceans: Distribution and characterizations in relation to Na+ regulation. Comp Biochem Physiol 90A(2):303–308
Haya K, Waidwood BA, Johston DW (1983) Adanylate energy charge and ATPase activity of lobster (Homarus americanus) during sublethal exposure to zinc. Aquatic Toxicol 3:115–126
Holliday CW (1985) Salinity-induced changes in gill Na,K-ATPase activity in the mud fiddler crab, Uca pugnax. J Exp Zool 233:199–208
Horiuchi S (1977) Characterization of gill Na,K-ATPase in the freshwater crayfish, Procambarus clarkii (Girard). Comp Biochem Physiol 56B:135–138
Jowett PE, Rhead MM (1978) In vitro changes in the activity of ATPases in the gills of Carcinus maenas exposed to various concentrations of PP'-DDT. Environ Pollut 17:1–16
Jowett PE, Rhead MM, Bayne BL (1981) In vivo changes in the activity of ATPases and haemolymph ions of Carcinus maenas exposed to PP'-DDT and reduced salinities. Comp Biochem Physiol 69C:399–402
Krishnaja AD, Rege MS, Joshi AG (1987) Toxic effects of certain heavy metals (Hg, Cd, Pb, As and Se) on the intertidal crab Scylla serrata. Mar Environ Res 21:109–119
Kuhnert PM, Kuhnert BR (1976) The effect of in vivo chromium exposure on Na/K-and Mg-ATPase activity in several tissues of the rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri). Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 15: No.4:383–390
Lauren DJ, McDonald DG (1987) Acclimation to copper by rainbow trout, Salmo gairdneri: Biochemistry. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 44:105–111
McLusky DS (1989) The estuarine ecosystem. 2nd edition, 215 pp. Blackie, Glasgow
Neufeld GJ, Holliday CW, Pritchard JB (1980) Salinity adaptation of gill Na,K-ATPase in the blue crab, Callinectes sapidus. J Exp Zool 211:215–224
Nolting RF (1986) Copper, zinc, cadmium, nickel, iron and manganese in the Southern Bight of the North Sea. Mar Pollut Bull 17(3):113–117
Peerzada N, Ryan P (1987) Determination of Pb, Zn, Cu and Cd in Darwin Harbour. Mar Pollut Bull 18(8):458–461
Pequeux A, Marchal A, Wanson S, Gilles R (1984) Kinetic characteristics and specific activity of gill (Na+ + K+)ATPase in the euryhaline chinese crab, Eriocheir sinensis during salinity acclimation. Marine Biol Lett 5:35–45
Proverbio T, Zanders IP, Marin R, Rodriguez JM, Proverbio F (1990) Effects of Na+ and/or K+ on the Mg+2 dependent ATPase activities in shrimp (Macrobrachium amazonium) gill homogenates. Comp Biochem Physiol 97B(2):383–390
Rainbow PS, White SL (1989) Comparative strategies of heavy metal accumulation by crustacea: Zinc, copper and cadmium in a decapod, an amphipod and a barnacle. Hydrobiologia 174:245–262
Schmidt-Nielsen K (1990) Animal physiology, adaptation and environment. 4th edition, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 602 pp
Siebers D, Leweck K, Markus H, Winkler A (1982) Sodium regulation in the shore crab Carcinus maenas as related to ambient salinity. Marine Biology 69:37–43
Stagg RM, Shuttleworth TJ (1982) The effects of copper on ionic regulation by the gill of the seawater adapted flounder (Platichthys flesus L.). J Comp Physiol 149:83–90
Stern S, Borut A, Cohen D (1984) Characterization of Na-K ATPase from the gill of the freshwater prawn Macrobrachium rosenbergii (De Man). Comp Biochem Physiol 79B(1):47–50
Torreblanca A, Del Ramo J, Arnav JA, Diaz-Mayans J (1989) Cadmium, mercury and lead effects on gill tissue of freshwater crayfish Procambarus clarkii (Girard). Biological Trace Element Research 21:343–347
Torreblanca A, Del Ramo J, Diaz-Mayans J (1989) Gill ATPase activity in Procambarus clarkii as an indicator of heavy metal pollution. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 42:829–834
Towle DW (1981) Role of Na,K-ATPase in ionic regulation by marine animals. Marine Biology Letters 2:107–122
Trausch G, Forget MC, Devos P (1989) Bioamines-stimulated phosphorylation and (Na+,K+)-ATPase in the gills of the chinese crab, Eriocheir sinensis. Comp Biochem Physiol 94B(3):487–492
Tucker RK (1979) Effects of in vivo cadmium exposure on ATPase in the gill of the lobster Homarus americanus. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 23:33–35
Tucker RK, Matte A (1980) In vitro effects of cadmium and lead on ATPases in the gill of the rock crab, Cancer irroratus. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 24:847–852
Verma SR, Jain M, Tonk IP (1983) In vivo effects of mercuric chloride on tissue ATPases of Notopterus notopterus. Toxicol Lett 16:305–309
Wanson SA, Pequeux AJR, Roer RD (1984) Na+ regulation and (Na+ + K+)ATPase activity in the euryahaline fiddler crab Uca minax (Le Conte). Comp Biochem Physiol 79A(4):673–678
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Canli, M., Stagg, R.M. The effects of In Vivo exposure to cadmium, copper and zinc on the activities of gill ATPases in the Norway lobster, Nephrops norvegicus . Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 31, 494–501 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00212433
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00212433