Abstract
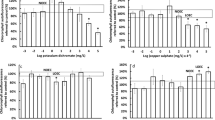
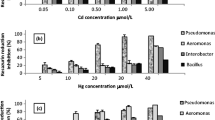
Heavy metal toxicity was studied by assaying six microbiological toxicity tests, both in solution and wastewater. Pseudomonas fluorescens and baker's yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) were used; growth and respirometric determinations were performed. In addition, the Microtox® test was employed as a reference method. The Microtox® test is the most sensitive assay for detecting toxicity of zinc, copper, and mercury but not for cadmium, chromium, and nickel. Wastewater increases the sensitivity threshold (EC20) and EC50 values of the metals in most of the assays, which is correlated to the presence of organic and inorganic compounds that can reduce the bioavailability of the metals, leading to a general loss of sensitivity.
All the above-mentioned assays are potentially useful in the detection of chemical toxicity of metals. However, each test shows different sensitivies to each metal, which is related to different sensitivities of the organisms used in the assays, as well as to other factors. Therefore, it would be advisable to use a battery of tests for biological evaluation of metal toxicity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babich H, Stotzky G (1979) Differential toxicities of mercury to bacteria and bacteriophages in sea and in lake water. Can J Microbiol 25(11):1252–1257
—, — (1986) Environmental factors that affect the utility of microbial assays for the toxicity and mutagenicity of chemical pollutants. In: Bitton G, Dutka BJ (eds) Toxicity testing using microorganisms. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, Vol II, pp 10–41
Beauvien A, Jolicoeur C (1984) The toxicity of various heavy metals salts, alcohols and surfactants to microorganisms in a biodegradation process: A flow microcalorimetry investigation. In: Liu D, Dutka BJ (eds) Toxicity screening procedures using bacterial systems. Marcel Dekker Inc, NY pp 261–281
Berkowitz D (1979) Potential uses of bacteria in toxicology. Vet Hum Toxicol 21:422–426.
Bitton G (1983) Bacterial and biochemical tests for assessing chemical toxicity in the aquatic environment: A review. CRC Crit Rev Environ Control 13(1):51–67
Bitton G, Koopman B, Wang H (1984) Baker's yeast assay procedure for testing heavy metal toxicity. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 32:80–84
Bitton G, Dutka BJ (1986) Introduction and review of microbial and biochemical toxicity screening procedures. In: Bitton G, Dutka BJ (eds) Toxicity testing using microorganisms. Vol 1, CRC Press, Boca Ratón, FL, pp 1–8
Coleman WE, Qureshi AA (1985) Microtox® and Spirillum volutans tests for assessing toxicity of environmental samples. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 35:443–451
Dutka BJ, Kwan KK (1981) Comparison of three microbial toxicity screening tests with the Microtox test. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 27:753–757
Dutka BJ, Nyholm N, Petersen J (1983) Comparison of several microbiological toxicity screening tests. Water Res 17:1363–1368
Dutka BJ, Kwan KK (1984) Studies on a synthetic activated sludge toxicity screening procedure with comparison to three microbial toxicity tests. In: Liu D, Dutka BJ (eds) Toxicity screening procedures using bacterial systems. Marcel Dekker Inc, NY, pp 125–138
Dutton RJ (1983) Use of a tetrazolium salt (INT) for enumeration of active bacteria and toxicity testing in aquatic environments. M.S. Thesis, University of Florida, Gainesville
Dutton RJ, Bitton G, Koopman B (1986) Rapid test for toxicity in wastewater systems. Toxic Assess 1(2):147–158
Gadd GM, Griffiths AJ (1978) Microorganisms and heavy metal toxicity. Microb Ecol 4:303–317.
Greene JC, Miller WE, Debacon MK, Long MA, Bartels CL (1985) A comparison of three microbial assay procedures for measuring toxicity of chemical residues. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 14:659–667
Lampinen J, Korpela M, Saviranta P, Kroneld R, Karp M (1990) Use of Escherichia coli cloned with genes encoding bacterial luciferase for evaluation of chemical toxicity. Toxic Assess 5:337–350
McFeters GA, Bond PJ, Olson SB, Tchan YT (1983) A comparison of microbial bioassays for the detection of aquatic toxicants. Water Res 17:1757–1762
Paran JH, Sharma S, Qureshi AA (1990) A rapid and simple toxicity assay based on growth rate inhibition of Pseudomonas fluorescens. Toxic Assess 5:351–365
Pérez-García A, Codina JC, Cazorla F, de Vicente A (1993) Rapid respirometric toxicity test: sensitivity to metals. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 50:703–708
Qureshi AA, Coleman RN, Paran JH (1984) Evaluation and refinement of the Microtox® test for use in toxicity screening. In: Liu D, Dutka BJ (eds) Toxicity screening procedures using bacterial systems. Marcel Dekker Inc, NY, p 1
Slabert JL (1986a) An improved bacterial agar technique for the evaluation of water toxicity. Abstract of the 1st Joint Congress of the South African Biochemical Society, the South African Genetics Society, and the South African Society for Microbiology, Wits, p 57
— (1986b) Improved bacterial growth test for rapid water toxicity screening. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 37:565–569
Vives-Rego J, Vaqué D, Martinez J (1986) Effect of heavy metals and surfactants on glucose metabolism, thymidine incorporation and exoproteolytic activity. Water Res 20:1411–1415.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Codina, J.C., Pérez-García, A., Romero, P. et al. A comparison of microbial bioassays for the detection of metal toxicity. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 25, 250–254 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00212137
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00212137