Summary
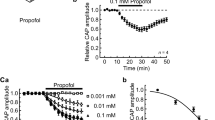
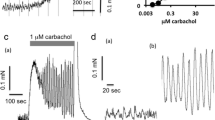
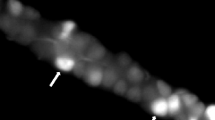
Maximal amylase release occurred with 10-5 M carbachol and slightly greater than half maximal response occurred with 3×10-7 M carbachol in dispersed pancreatic acini. The preparation released more than 45% of its initial amylase content after 60 min of maximal carbachol stimulation. Electron microscopy revealed depletion of zymogen granules and the presence of secretory material in the ductules after carbachol stimulation. At 37° C, maximal binding of methyl scopolamine occurred in about 45 min with 3×10-10 M 3H-methyl scopolamine. The dissociation constant for 3H-methyl scopolamine was 6.8×10-10 M and saturation occurred at 109 pm/g protein. The I.C. 50 for 3H-methyl scopolamine inhibition of carbachol-induced amylase secretion was 7 × 10-10 M.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amsterdam A, Jamieson JD (1974) Studies on dispersed pancreatic exocrine cells. 1. Dissociation technique and morphologic characteristics of separated cells. J Cell Biol 63:1037–1056
Amsterdam A, Jamieson JD (1974a) Studies on dispersed pancreatic exocrine cells. 2. Functional characteristics of separated cells. J Cell Biol 63:1057–1073
Bennett HD, Luft JH (1959) s-Collidine as a basis for buffering fixatives. J Biophys Biochem Cytol 6:113–114
Christophe J, De Neef P, Deschodt-Lackman M, Robberecht P (1978) The interaction of caerulein with the rat pancreas. 2. Specific binding of (3H) caerulein on dispersed acinar cells. Eur J Biochem 91:31–38
Fields JZ, Roeske WR, Morkin E, Yamamura HI (1978) Cardiac muscarinic cholinergic receptors. Biochemical identification and characterization. J Biol Chem 253:3251–3258
Gardner JD, Jackson MJ (1977) Regulation of amylase release from pancreatic acinar cells. J Physiol (Lond) 270:439–454
Harms DR, Camfield RN (1966) An automated iodometric method for the determination of amylase. Am J Med Technol 32:34–37
Hayat MA (1970) Principles and techniques of electron microscopy: Biological applications, Vol 1. Van Nostrand Reinhold Company, New York, pp 274 and 343
Jensen RT, Moody T, Pert C, Rivier SE, Gardner JD (1978) Interaction of bombesin and litorin with specific membrane receptors on pancreatic acinar cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 75:6139–6143
Kloog Y, Sokolovsky M (1978) Muscarinic binding to mouse brain receptor sites. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 81:710–717
Korman LY, Gardner JD (1979) Functionally distinct modes of action of CCK and cholinergic agents on pancreatic acinar cells. Gastroenterology 76:1175
Larose L, Lanoe J, Morisset J, Goeffrion L, Dumont Y, Lord A, Poirier GG (1979) Rat pancreatic muscarinic cholinergic receptors. In: Bonfils S, Fromagoet P, Rosseling G (eds) Hormone receptors in digestion and nutrition. Biomedical Press, Elsevier/North-Holland, pp 229–238
Larose L, Dumont Y, Asselin J, Morisset J, Poirier GG (1981) Muscarinic receptors of the rat pancreatic acini. 3H QNB binding and amylase secretion. Eur J Pharm (In Press)
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Meldolesi J, Castiglioni G, Parma R, Nassivera N, De Camilli P (1979) Ca++-dependent disassembly and reassembly of occluding junctions in guinea pig pancreatic acinar cells. Effect of drugs. J Cell Biol 79:156–172
Morisset J, Ng KH, Poirier GG (1977) Comparative inhibitory effects of 3-quinuclidinyl benzilate (QNB) and atropine on amylase release from rat pancreas. Br J Pharmacol 61:97–100
Morisset J, Ng KH, Poirier GG (1979) Pancreatic muscarinic receptors. Muscarinic receptors of the pancreas: A correlation between displacement of (3H)-quinuclidinyl benzilate binding and amylase secretion. Pharmacology 18:263–270
Oliver C (1981) Isolation and maintenance of differentiated exocrine gland acinar cells in vitro. In vitro (In Press)
Palade GE (1952) A study of fixation for electron microscopy. J Exp Med 95:285–298
Peikin SR, Rottman AJ, Batzri S, Gardner JD (1978) Kinetics of amylase release by dispersed acini prepared from guinea pig pancreas. Am J Physiol 235:E743–749
Reynolds ES (1963) The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol 17:208–212
Robberecht P, Deschodt-Lackman M, Morgat JL, Christophe J (1978) The interaction of caerulein with the rat pancreas. 3. Structural requirements for in vitro binding of caerulein-like peptides and its relationship to increased calcium outflux, adenylate cyclase activation,and secretion. Eur J Biochem 91:39–48
Sabatini DD, Bensch K, Barrnett RJ (1963) Cytochemistry and electron microscopy. The preservation of cellular ultrastructure and enzymatic activity by aldehyde fixation. J Cell Biol 17:19–58
Schultz GS, Gunther GR, Hull BE, Alicea HA, Gorelick FS, Sarras Jr MP, Jamieson JD (1981) Guinea pig pancreatic acini prepared with purified collagenase. Exp Cell Res 130:49–62
Spurr AR (1969) A low-viscosity expopy resin embedding medium for electron microscopy. J Ultrastruct Res 26:31–43
Williams JA (1978) The effect of ionophore A23187 on amylase release, cellular integrity and ultrastructure of mouse pancreatic acini. Cell Tissue Res 186:287–295
Williams JA (1980) Multiple effects of Na+ removal on pancreatic secretion. Cell Tissue Res 210:295–303
Williams JA, Korc M, Dormer RL (1978) Action of secretagogues on a new preparation of functionally intact, isolated pancreatic acini. Am J Physiol 235:E517–524
Yamamura HI, Snyder SH (1974) Muscarinic cholinergic receptor binding in the longitudinal muscle of the guinea pig ileum with (3H)-quinuclidinyl benzilate. Mol Pharmacol 10:861–867
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by NIH Biomedical Research Support Grant 5-501-RR-05700-10 and a Grant from the Upjohn Company
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Appert, H.E., Chiu, T.H., Budd, G.C. et al. 3H-methyl scopolamine binding to dispersed pancreatic acini. Cell Tissue Res. 220, 673–684 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00210454
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00210454