Summary
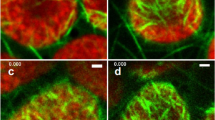
Immunofluorescence studies of bovine chromaffin cells in culture with specific antibodies against dopamine-gb-hydroxylase gave a distinct punctate pattern of labelling, reflecting the distribution of chromaffin granules. There was strong staining of cell extensions and growth cones. Linear arrays of fluorescent dots were observed, suggesting an association of granules with a filamentous cytoskeleton. Labelling of neuritic processes was periodic, perhaps indicative of a packaging of secretory granules.
Chromaffin cells stained strongly with specific anti-actin antisera. Fine filament bundles were observed, and also diffuse staining, some punctate labelling and staining of the plasma membrane or sub-membranous cytoplasm. Growth cones and non-terminal cytoplasmic varicosities contained significant amounts of actin. Colchicine (5×10-5M) caused retraction of neuritic extensions and formation of lateral growth cones. Cytochalasin (10μg/ml) caused ballooning of terminal growth cones and non-terminal cytoplasmic varicosities. Phalloidin (10-4M) stimulated microspike formation. The results are discussed in terms of the role of the cytoskeleton in growth cone formation, cell-substratum contacts and the transport of chromaffin granules.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abercrombie M (1980) The crawling movement of metazoan cells. Proc R Soc Lond B 207:129–147
Aunis DA, Miras-Portugal MT (1976) Isolation of dopamine-β-hydroxylase. In: Bittiger H, Schebli HO (eds) Concanavalin A as a tool. Wiley, London, pp 349–354
Aunis D, Miras-Portugal MT, Mandel P (1975) Bovine adrenal medullary dopamine-β-hiydroxylase: studies on the interaction with concanavalin A. J Neurochem 24:425–431
Aunis D, Bouclier M, Pescheloche M, Mandel P (1977) Properties of membrane bound dopamine-β-hydroxylase in chromaffin granules from bovine adrenal medulla. J Neurochem 29:439–447
Aunis D, Hesketh JE, Devilliers G (1980a) Immunohistological and immunocytochemical localization of myosin, chromogranin A and dopamine-β-hydroxylase in nerve cells in culture and in adrenal glands. J Neurocytol 9:255–274
Aunis D, Guerold B, Bader MF, Ciesielski-Treska J (1980b) Immunocytochemical and biochemical demonstration of contractile proteins in chromaffin cells in culture. Neuroscience 5:2261–2277
Babitch JA, Gage FH, Valdes JJ (1979) Effects of phalloidin on K+ dependant, Ca++ independant neurotransmitter efflux and Ca dependant neurotransmitter release. Life Sci 24:117–124
Bray D (1973) Branching patterns of individual sympathetic neurones in culture. J Cell Biol 56:702–712
Bray D (1977) Actin and myosin in neurones: a first review. Biochimie 59:1–6
Bray D, Thomas C, Shaw G (1979) Growth cone formation in cultures of sensory neurones. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 75:5226–9
Bunge MB (1973) Fine structure of nerve fibres and growth cones of isolated sympathetic neurones in culture. J Cell Biol 56:713–735
Douglas WW (1975) Secretomotor control of adrenal medullary secretion: synaptic membrane and ionic events in stimulus-secretion coupling. In: Blaschko H, Sayers G, Smith AD (eds) Handbook of Physiology. Endocrinology 6:367–388
Englert DF (1980) An optical study of isolated rat adrenal chromaffin cells. Exp Cell Res 125:369–376
Fuller GM, Brinkley BK, Boughter JM (1975) Immunofluorescence of mitotic spindles by using monospecific antibody against bovine brain tubulin. Science 187:948–951
Hesketh JE, Aunis D, Devilliers G, Mandel P (1978) Biochemical and morphological studies of bovine adrenal medullary myosin. Biol Cell 33:199–208
Kuczmarski ER, Rosenbaum JL (1979) Studies on the organization and localization of actin and myosin in neurones. J Cell Biol 80:356–371
Lazarides E (1976) Actin, α-actinin and tropomyosin interaction in the structural organization of actin filaments in non-muscle cells. J Cell Biol 68:202–219
Lazarides E, Weber K (1974) Actin antibody: the specific visualization of actin filaments in non-muscle cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 71:2268–2272
Lazarides E, Hubbard BD (1976) Immunological characterization of the subunit of the 100Å filaments from muscle cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 73:4334–4338
Poisner AM, Cooke P (1975) Microtubules and the adrenal medulla. Ann NY Acad Sci 253:653–669
Smith AD, Winkler H (1967) A simple method for the isolation of adrenal chromaffin granules on a large scale. Biochem J 103:480–2
Spooner BS (1978) In Cytochalasins: Biochemical and cell biological aspects. Tanenbaum SW (ed). North Holland
Trifaro JM (1977) Contractile proteins in tissues originating from the neural crest. Neurosci 3:1–24
Unsicker U, Krisch B, Otten U, Thoenen H (1978) Nerve growth factor-induced fiber outgrowth from isolated rat adrenal chromaffin cells: impairment by glucocorticoids. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 75:3498–3502
Unsicker U, Griesser G-H, Lindmar R, Loffelholz K, Wolf U (1980) Establishment, characterization and fibre outgrowth of isolated bovine adrenal medullary cells in long-term cultures. Neuroscience 5:1445–1460
Wehland J, Osborn M, Weber K (1977) Phalloidin-induced actin polymerization in the cytoplasm of cultured cells interferes with cell locomotion and growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74:5613–7
Winkler H (1976) The composition of adrenal chromaffin granules: an assessment of controversial results. Neuroscience 1:65–80
Winkler H (1977) The biogenesis of adrenal chromaffin granules. Neuroscience 2:657–683
Yamada KM, Spooner BS, Wessels NK (1971) Ultrastructure and function of growth cones and axons of cultured nerve cells. J Cell Biol 49:614–635
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hesketh, J.E., Ciesielski-Treska, J. & Aunis, D. A phase-contrast and immunofluorescence study of adrenal medullary chromaffin cells in culture: Neurite formation, actin and chromaffin granule distribution. Cell Tissue Res. 218, 331–343 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00210348
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00210348