Summary
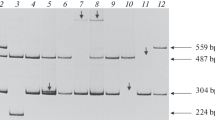
Despite marked genetic heterogeneity in families with hemophilic patients, transition mutations in CG dinucleotides occur frequently. Of 71 CG dinucleotides in the factor VIII cDNA, a C-to-T transition in 12 would lead to a new Stop codon (CGA to TGA). Using restriction enzyme digestion of 11 amplified DNA fragments, seven point mutations were localized among 60 patients with severe hemophilia A. Five were detected as loss of a natural or introduced TaqI site at codons -5, 583, 1941, 2116, and 2209 and were confirmed as CGA (Arg) to TGA (Stop) nonsense mutations by DNA sequencing. A novel C-to-T nonsense mutation was detected as loss of the RsaI site at codon 1966 and confirmed by sequence in two unrelated individuals. Two partial gene deletions were detected as selective failure to amplify exon 1 and exons 15–22, respectively. In an additional (61st) patient who was subsequently found to have mild (instead of severe) hemophilia, digests suggested a mutation in codon 1696. Upon sequencing, this codon contained a novel missense mutation, a C-to-G transversion changing CGA (Arg 1696) to GGA (Gly). In four families with women available for testing, carrier status was rapidly determined by direct screening for the point mutation. In two of three with sporadic occurrences, the mother was a carrier as were two of four sisters. In the other family, the mother and a sister were homozygous for the TaqI cleavage site in their amplified exon 24 fragment, indicating a de novo C-to-T transition in codon 2209 in the patient's factor VIII gene. This final patient's sister was a noncarrier even though by linkage analysis she inherited the same factor VIII gene as her brother.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antonarakis SE, Waber PG, Kittur SD, Patel AS, Kazazian HH, Mellis MA, Counts RB, Stamatoyannopoulos G, Bowie EJW, Fass DN, Pittman DD, Wozney JM, Toole JJ (1985) Hemophilia A: detection of molecular defects and of carriers by DNA analysis. N Engl J Med 313:842–848
Arai M, Inaba H, Higuchi M, Antonarakis SE, Kazazian HH, Fujimaki M, Hover LW (1989) Direct characterization of factor VIII in plasma: detection of a mutation altering a thrombin cleavage site (arginine-372→histidine) Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:4277–4281
Casula L, Murru S, Pecorara M, Ristaldi MS, Restagno G, Manucuso G, Morfini M, De Biasi R, Baudo F, Carbonara A, Mori PG, Pirastu M (1990) Recurrent mutations and three novel rearrangements in the factor VIII gene of hemophilia A patients of Italian descent. Blood 75:662–670
Chen S-H, Yoshitake S, Chance PF, Bray GL, Thompson AR, Scott CR, Kurachi K (1985) An intragenic deletion of the factor IX gene in a family with hemophilia B. J Clin Invest 76:2161–2164
Chen S-H, Thompson AR, Zhang M, Scott CR (1989) Three point mutations in the factor IX genes of five hemophilia B patients: identification strategy using localization by altered epitopes in their hemophilic proteins. J Clin Invest 84:113–118
Chen S-H, Zhang M, Lovrien EW, Scott CR, Thompson AR (1991) CG dinucleotide transitions in the factor IX gene account for about half of the point mutations in hemophilia B patients. Hum Genet 87:177–182
Diamond CA, Kogan SA, Gitschier J (1991) Mutations causing hemophilia A. Thromb Haemost 65:727
Eaton DL, Vehar GA (1986) Factor VIII structure and proteolytic processing. Prog Hemost Thromb 8:47–70
Foster PA, Fulcher CA, Houghten RA, Zimmerman TS (1988) An immunogenic region within residues Val1670-Glu1684 of the factor VIII light chain induces antibodies which inhibit binding of factor VIII to von Willebrand factor. J Biol Chem 263:5230–5234
Gitschier J, Wood WI, Goralka TM, Wion KL, Chen EY, Eaton DH, Vehar GA, Capon DJ, Lawn RM (1984) Characterization of the human factor VIII gene. Nature 312:326–330
Haliassos A, Chomel JC, Tesson L, Baudis M, Kruh J, Kaplan JC, Kitzis A (1989) Modification of enzymatically amplified DNA for the detection of point mutations. Nucleic Acids Res 17:3606
Higuchi M, Wong C, Kochhan L, Olek K, Aronis S, Kasper CK, Kazazian HH, Antonarakis SE (1990) Characterization of mutations in the factor VIII gene by direct sequencing of amplified genomic DNA. Genomics 6:65–71
Kane WH, Davie EW (1988) Blood coagulation factors V and VIII: structural and functional similarities and their relationship to hemorrhagic and thrombotic disorders. Blood 71:539–555
Kogan S, Gitschier J (1990) Mutations and a polymorphism in the factor VIII gene discovered by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:2092–2096
Kogan SC, Doherty M, Gitschier J (1987) An improved method for prenatal diagnosis of genetic diseases by analysis of amplified DNA sequences. N Engl J Med 317:985–990
Nafa K, Meriane F, Reghis A, Benabadji M, Demenais F, Guilloud-Bataille M, Sultan Y, Kaplan JC, Delpech M (1990) Investigation of factor VIII:C gene restriction fragment length polymorphisms and search for deletions in hemophiliac subjects in Algeria. Hum Genet 84:401–405
Pattinson JK, Millar DS, McVey JH, Grundy CB, Wieland K, Mibashan RS, Martinowitz U, Tan-Un K, Vidaud M, Goossens M, Sampietro M, Mannucci PM, Krawczak M, Reiss J, Zoll B, Whitmore D, Bowcock S, Wensley R, Ajani A, Mitchell V, Rizza C, Maia R, Winter P, Mayne EE, Schwartz M, Green PJ, Kakkar VV, Tuddenham EGD, Cooper DN (1990) The molecular genetic analysis of hemophilia A: a directed search strategy for the detection of point mutations in the human factor VIII gene. Blood 76:2242–2248
Saiki RK, Gelfand DHS, Stoffel S, Scharf SJ, Higuchi R, Horn GT, Mullis KB, Erlich HA (1988) Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with thermostable DNA polymerase. Science 239:487–491
Sanger F, Nicklen S, Coulson AR (1977) DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74:5463–5467
Thompson AR (1991) Molecular biology of the hemophilias. Prog Hemost Thromb 10:175–214
Thompson AR, Counts RB (1976) Removal of heparin and protamine from plasma. J Lab Clin Med 88:922–929
Traystman MD, Higuchi M, Kasper CK, Antonarakis SE, Kazazian HH (1990) Use of denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis to detect mutations in factor VIII. Genomics 6:293–301
Wion KL, Tuddenham EGD, Lawn RM (1986) A new polymorphism in the factor VIII gene for prenatal diagnosis of hemophilia A. Nucleic Acids Res 14:4535–4542
Wood WI, Capon DJ, Simonsen CC, Eaton DL, Gitschier J, Keyt B, Seeburg PH, Smith DH, Hollingshead P, Wion KL, DeIwart E, Tuddenham EGD, Vehar GA, Lawn RM (1984) Expression of active human factor VIII from recombinant DNA lones. Nature 312:330–337
Youssoufian H, Kazazian HH, Phillips DG, Aronis S, Tsiftis G, Brown VA, Antonarakis SE (1986) Recurrent mutations in haemophilia A give evidence for CpG mutation hotspots. Nature 324:380–382
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
These results have already been published in part in abstract form: Reiner AP, Thompson AR (1990) Circulation Research 82:304
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reiner, A.P., Thompson, A.R. Screening for nonsense mutations in patients with severe hemophilia A can provide rapid, direct carrier detection. Hum Genet 89, 88–94 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00207049
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00207049