Abstract
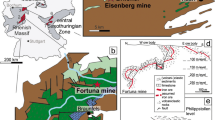
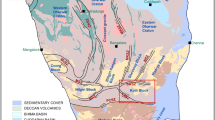
The Proterozoic metamorphic rocks of the Selwyn Range area in western Queensland contain a variety of styles of Au + Cu deposit including some (e.g. Selwyn mine and Osborne prospect) that are spatially associated with magnetite-rich ironstones. The area is characterized by extensive alkali-(chloride) metasomatism that occurred during the later stages of regional metamorphism. Existing experimental data indicate that hot saline fluids will dissolve and transport iron as they move through temperature/pressure gradients in the vicinity of the amphibolite-greenschist facies transition and predict that circulation cells will move iron and concentrate it in relatively cool, dilute and/or oxidized parts of such systems. New geological mapping coupled with geochemical data from the amphibolite facies zone of the Selwyn Range area suggest such processes occurred on a large scale and that large masses of Fe were mobilized, particularly in association with Na-metasomatism of biotite-bearing metasediments and high Fe-tholeiitic dolerites. Field and textural features of ironstones and other Fe-rich lithologies demonstrate that some of them at least formed by replacement of other rocks during metamorphism and deformation. Mineralization localized within such iron stones must itself be epigenetic.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amoco (1976) 1975 annual report, Squirrel Hills Project, Queensland Australia, Queensland Dept. Mines Open File Company Rpt. 5885
Appleby, A.-K., Williams, P.J. (1988) Epigenetic tourmalinite and arsenopyrite in the aureole of the Leinster batholith, SE Ireland. Mineral. Deposita 23:247–255
Beardsmore, T.J. (1993) The role of metamorphic fluids in the petrogenesis of Mount Dore style breccia-hosted Cu-Au mineralization in the eastern Mount Isa inlier, Queensland. Geol. Soc. Aust. Abstr. 35:54–55
Beardsmore, T.J., Newbery, S.P., Laing, W.P. (1988) The Maronan Supergroup: an inferred early volcanosedimentary rift sequence in the Mount Isa Inlier and its implications for ensialic rifting in the Middle Proterozoic of northwest Queensland. Precambrian Res. 40/41:487–507
BHP (1985) Six monthly report, Authority to Prospect 3740M Bustard Creek, Queensland Dept. Mines Open File Company Rpt. 14091
Blake, D.H. (1982) A review of the Corella Formation, Mount Isa Inlier, BMR Jour. Aust. Geol. Geophys. 7:113–118
Blake D.H. (1987) Geology of the Mount Isa Inlier and environs, Queensland and Northern Territory. Aust. Bureau Min. Res. Bull. 225
Blake, D.H., Jaques, A.L., Donchak, P.J.T. (1983) 1 ∶ 100 000 geological map commentary Selwyn Region Queensland. Aust. Bureau Min. Res., Canberra
Blake D.H., Bultitude, R.J., Donchak, P.J.T., Wyborn, L.A.I., Hone, I.G. (1984) Geology of the Duchess-Urandangi region Mount Isa Inlier, Queensland. Aust. Bureau Min. Res. Bull. 219
Chou, I-M., Eugster, H.P. (1977) Solubility of magnetite in super-critical chloride solutions. Am. J. Sci. 277:1296–1314
Davidson, G.J., Dixon, G.H. (1992) Two sulphur isotope provinces deduced from ores in the Mount Isa Eastern Succession, Australia. Mineral. Deposita 27:30–41
Davidson, G., Large, R., Kary, G., Osborne, R. (1989) The BIF- hosted Starra and Trough Tank Au-Cu mineralization: a new stratiform association from the Proterozoic eastern succession of Mt. Isa, Australia. Econ. Geol. Monogr. 6:135–150
De Jong, G. (1993) Syn- to late metamorphic Na metasomatism, southeast Mount Isa Inlier. Geol. Soc. Aust. Abstr. 35:58–59
Derrick, G.M., Wilson, I.H., Hill, R.M. (1976) Revision of stratigraphic nomenclature in the Precambrian of northwestern Queensland V. Soldiers Cap Group. Queensland Govt. Min. J. 77:600–604
Derrick, G.M., Wilson, I.H., Hill, R.M. (1977) Revision of stratigraphic nomenclature in the Precambrian of northwestern Queensland. VI. Mary Kathleen Group. Queensland Govt. Min. J. 78:15–23
Donchak, P.J.T., Blake, D.H., Noon, T.A., Jaques, A.L. (1983) 1∶100000 geological map commentary Kuridala Region Queensland. Aust. Bureau Min. Res., Canberra
Edwards, A.B., Baker, G. (1959) Scapolitization in the Cloncurry district of northwestern Queensland. J. Geol. Soc. Aust. 1:1–31
Eugster, H.P., Chou, I-M. (1979) A model for the deposition of Cornwall-type magnetite deposits. Econ. Geol. 74:763–774
Grant, J.A. (1986) The isocon diagram — a simple solution to Gresens' equation for metasomatic alteration. Econ. Geol. 81:1976–1982
Hemley, J.J., Cygan, G.L., D'Angelo, W.M. (1986) Effect of pressure on mineral solubilities under hydrothermal conditions. Geology 14:377–379
Hemley, J.J., Cygan, G.L., Fein, J.B., Robinson, G.R., D'Angelo, W.M. (1992) Hydrothermal ore-forming processes in the light of studies in rock-buffered systems. I. Iron-copper-zinc-lead sulfide solubility relations. Econ. Geol. 87:1–22
Hitzman, M.W., Oreskes, N., Einaudi, M.T. (1992) Geological characteristics and tectonic setting of Proterozoic iron oxide (Cu-U- Au-REE) deposits. Precambrian Res. 58:241–287
Jaques, A.L., Blake, D.H., Donchak, P.J.T. (1982) Regional metamorphism in the Selwyn Range area, northwest Queensland. BMR J. Aust. Geol. Geophys. 7:181–196
Kary, G.L., Harley, R.A. (1990) Selwyn gold-copper deposits. In: Hughes, F.E., (ed.) Geology of the mineral deposits of Australia and Papua New Guinea. Australas. Inst. Min. Metal., Parkville, Victoria, pp. 955–960
Laing, W.P. (1991) Base metal + gold mineralization styles in the Cloncurry Terrane, Mount Isa Inlier. James Cook Univ. Econ. Geol. Res. Unit Contrib. 38:77–88
Long, K.R., Kelly, W.C., Ohle, E.L., Lohmann, K.C. (1986) Ground preparation and zinc mineralization in bedded and breccia ores of the Monte Cristo mine, North Arkansas. Econ. Geol. 81:809–830
McLean, G., Benjamin, P. (1993) The geology and development of the Mount Elliot copper-gold deposit. Aust. Inst. Geoscientists Bull. 13:47–54
McPhail, D.C. (1993) The behaviour of iron in high temperature chloride brines. Geol. Soc. Aust. Abstr. 34:50–51
Nisbet, B.W., Devlin, S.P., Joyce, P.J. (1983) Geology and suggested genesis of cobalt-tungsten mineralization at Mount Cobalt, northwestern Queensland. Proc. Aust. Inst. Mining Metall. 287:9–17
Oliver, N.H., Wall, V.J. (1987) Metamorphic plumbing system in Pfoterozoic calc-silicates, Queensland, Australia. Geology 15:793–796
Oliver, N.H.S., Valenta, R.K., Wall, V.J. (1990) The effect of heterogeneous stress and strain on metamorphic fluid flow, Mary Kathleen, Australia, and a model for large-scale fluid circulation. J. Metamorphic Geol. 8:311–331
Oreskes, N., Einaudi, M. (1990) Origin of rare earth element-enriched hematite breccias at the Olympic Dam Cu-U-Au-Ag deposit, Roxby Downs, South Australia. Econ. Geol. 85:1–28
Page, R.W. (1983) Timing of superposed volcanism in the Proterozoic Mount Isa Inlier, Australia. Precambrian Res. 21:223–245
Page, R.W. (1993) Geological constraints given by U-Pb zircon geochronology in the Mount Isa inlier. Aust. Inst. Geoscientists Bull. 13:13–15
Rankin, A.H., Ramsey, M.H., Coles, B., Vanglangvelde, F., Thomas, C.R. (1992) The composition of hypersaline iron-rich granitic fluids based on laser-ICP and synchrotron XRF microprobe analysis of individual inclusions in topaz, Mole Granite, Eastern Australia. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 56:67–79
Rattenbury, M. (1992) Stratigraphic and structural controls on ironstone mineralization in the Tennant Creek goldfield, Northern Territory, Australia. Aust. J. Earth Sci. 39:591–602
Ryburn, R.J., Grimes, K.G., et al. (1988) Cloncurry (1∶100 000 Scale map.) Aust. Bureau Min. Res., Canberra
Spear, F.S., Cheney, J.T. (1989) A petrogenetic grid for pelitic schists in the system SiO2-Al2O3-FeO-MgO-K2O-H2O. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 101 149–164
Switzer, C.K., Laing, W.P., Rubenach, M.J. (1988) The Proterozoic Starra Au + Cu deposit-syntectonic mineralization in a folded early regional zone of décollement. Geol. Soc. Aust. Abstr. Ser. 23:212–214
Vaughan, J.P., Stanton, R.L. (1986) Sedimentary and metamorphic factors in the development of the Pegmont stratiform Pb-Zn deposit, Queensland. Inst. Min. Metall. Trans. Sec. B. 95:B94–121
Wedekind, M.R., Large, R.R., Williams, B.T. (1989) Controls on high grade gold mineralization at Tennant Creek, Northern Territory, Australia. Econ. Geol. Monogr. 6:168–179
White, S. (1989) Structural controls on, and the origin and timing of ironstone and mineralization at Starra, northwest Queensland. Unpubl. Hons thesis, James Cook University of North Queensland
Williams, P.J., De Jong, G., Verran, T. (1993) Evolution of Na-K-Fe-Si metasomatism and mineralization associated with the Cloncurry Fault, SE Mount Isa Inlier: a comparison with Kiruna-Olympic Dam type systems. Geol. Soc. Aust. Abstr. 35:56–57
Williams, P.J., Phillips, G.N. (1992) Cloncurry mapping project 1990: geology of the Selwyn Range (McKinlay River and Maramungee Creek areas). James Cook Univ., Econ. Geol. Res. Unit, Contrib. 40
Wilson, I.H. (1983) Discussion of a review of the Corella Formation, Mount Isa Inlier, Queensland. BMR J. Aust. Geol. Geophys. 8:161–163
Wood, B.J., Walther, J.V. (1986) Fluid flow during metamorphism and its implications for fluid-rock ratios. In: Walther, J.V., Wood, B.J. (eds.) Fluid-rock interactions during metamorphism. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp. 89–108
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Williams, P.J. Iron mobility during synmetamorphic alteration in the Selwyn Range area, NW Queensland: implications for the origin of ironstone-hosted Au-Cu deposits. Mineral. Deposita 29, 250–260 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00206868
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00206868