Abstract
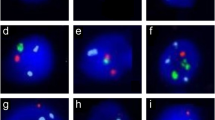
Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) with single-color chromosome-specific probes was used to study the rates of disomy for chromosome 1, 16, X, and Y in sperm of fertile and infertile subjects. Diploidy rates were studied using a two-color cocktail of probes for chromosomes 17 and 18 in the same sperm samples. Two-color methodology was not available at the outset of the study. A total of 450,580 spermatozoa were studied from 21 subjects (9 fertile, 12 infertile). Significant differences were observed in the disomy rates between chromosomes with the highest frequency observed for chromosome 16 (0.17%) and the lowest for the Y chromosome (0.10%). No differences were observed between fertile and infertile subjects for either diploidy or disomy. Total disomy rates for chromosomes 1, 16, X and Y ranged from 0.34% to 0.84% among infertile subjects, and 0.32% to 0.61% among fertile subjects. Our data suggest that generalized aneuploidy in sperm is not a major contributor to unexplained infertility.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brandiff B, Gordon L, Ashworth L, Watchmaker G, Carrano A, Wyrobek A (1984) Chromosomal abnormalities in human sperm: comparisons among four healthy men. Hum Genet 66:193–201
Carothers AD, Beatty RA (1975) The recognition and incidence of haploid and polyploid spermatozoa in man, rabbit, and mouse. J Reprod Fertil 44:487–500
Chaudhuri JP, Yanagimachi R (1984) An improved method to visualize human sperm chromosomes using zona-free hamster eggs. Gamete Res 10:233–239
Coonen E, Pieters MHEC, Dumoulin JCM, Meyer H, Evers JLH, Ramaekers FCS, Feraedis JPM (1991) Nonisotopic in situ hybridization as a method for nondisjunction studies in human spermatozoa. Mol Reprod Dev 28:18–22
Guttenbach M, Schmid M (1990) Determination of Y chromosome aneuploidy in human sperm nuclei by nonradioactive in situ hybridization. Am J Hum Genet 46:553–558
Guttenbach M, Schmid M (1991) Non-isotopic detection of chromosome 1 in human sperm meiosis and demonstration of disomic sperm nuclei. Hum Genet 87:261–265
Han TL, Webb GC, Flaherty SP, Correll A, Matthews CD, Ford JH (1992) Detection of chromosome 17- and X-bearing human spermatozoa using fluorescence in sitz hybridization. Mol Reprod Dev 33:189–194
Hassold TJ, Jacobs PA (1984) Trisomy in man. Annu Rev Genet 18:69–97
Hassold TJ, Chen N, Funkhouser J, Jooss T, Manuel B, Matsuura K, Matsuyama A, Wilson C, Yamane JA, Jacobs PA (1980) A cytogenetic study of 1000 spontaneous abortions. Ann Hum Genet 44:151–164
Holmes JM, Martin RH (1993) Aneuploidy detection in human sperm nuclei using fluorescence in situ hybridization. Hum Genet 91:20–24
Joseph AM, Gosden JR, Chandley AC (1984) Estimation of aneuploidy levels in human spermatozoa using chromosome-specific probes and in situ hybridization. Hum Genet 66:234–238
Kajii T, Ferrier A, Niikawa N, Takahara H, Ohama K, Avirachan S (1980) Anatomic and chromosomal anomalies in 639 spontaneous abortuses. Hum Genet 55:87–98
Kamiguchi Y, Mikamo K (1986) An improved efficient method for analyzing human sperm chromosomes using zona-free hamster ova. Am J Hum Genet 38:724–740
Kruger TF, Acosta AA, Simmons KF, Swanson RJ, Matta JF, Oehninger S (1988) Predictive value of abnormal sperm morphology in in vitro fertilization. Fertil Steril 49:112–117
Luciani JM, Guicaoua MR, Delefontaine D, North MO, Gabriel-Robez O, Rumpler Y (1987) Pachytene analysis in a 17;21 reciprocal translocation carrier: role of the acrocentric chromosomes in male sterility. Hum Genet 77:246–250
Martin RH (1983) A detailed method for obtaining preparations of human sperm chromosomes. Cytogenet Cell Genet 35:253–256
Martin RH, Rademaker A (1987) The relationship between sperm chromosomal abnormalities and sperm morphology in humans. Mutat Res 207:159–164
Martin RH, Rademaker A (1990) The frequency of aneuploidy among individual chromosomes in 6821 human sperm chromosomes complements. Cytogenet Cell Genet 53:103–107
Martin RH, Ko E, Rademaker A (1991) Distribution of aneuploidy in human gametes: comparison between human sperm and oocytes. Am J Med Genet 39:321–331
Pieters MHEC, Geraedts JPM, Meyer H, Dumoulin JCM, Evers JLH, Jongbloed RJE, Nederlof MP, Flier S van der (1990) Human gametes and zygotes studies by nonradioactive in situ hybridization. Cytogenet Cell Genet 53:15–19
Plachot M, Grouchy J de, Junca A-M, Turleau C, Couillin P, Cohen J, Salat-Baroux J (1987) From oocyte to embryo: a model, deduced from in vitro fertilization, for natural selection against chromosome abnormalities. Ann Genet 30:22–32
Robbins WA, Segraves R, Pinkel D, Wyrobek A (1993) Detection of aneuploid human sperm by fluorescence in situ hybridization: evidence for a donor difference in frequency of sperm disomic for chromosomes 1 and Y. Am J Hum Genet 52:799–807
Rosenbusch B, Sterzik K (1991) Sperm chromosomes and habitual abortion. Fertil Steril 56:370–372
Rosenmann A, Wharman J, Richler C, Voss R, Persitz A, Goldman B (1985) Meiotic association between XY chromosomes and unpaired autosomal elements as a cause of human male sterility. Cytogenet Cell Genet 39:19–29
Rudak E, Jacobs PA, Yanagimachi R (1978) Direct analysis of the chromosome constitution of human spermatozoa. Nature 274:911–913
Schroder J, Lydecker K, Chapelle A de la (1971) Meiosis and spermatogenesis in G-trisomic males. Hum Genet 13:15–24
Watt JL, Templeton AA, Messinis I, Bell L, Cunningham P, Duncan RO (1987) Trisomy 1 in eight cell human pre-embryo. J Med Genet 24:60–64
World Health Organization (1987) WHO Laboratory Manual for the examination of human semen and semen-cervical mucus nteraction, 2nd edn. Cambridge University Press, NewYork Sydney, pp 3–10
Wyrobek AJ, Ahlborn T, Balhorn R, Stanker L, Pinkel D (1990) Fluorescence in situ hybridization to Y chromosomes in decondensed human sperm nuclei. Mol Reprod Dev 27:200–208
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miharu, N., Best, R.G. & Young, S.R. Numerical chromosome abnormalities in spermatozoa of fertile and infertile men detected by fluorescence in situ hybridization. Hum Genet 93, 502–506 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00202812
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00202812