Abstract
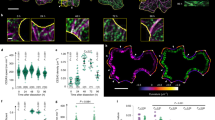
The arrangement of cortical microtubules (MTs) in differentiating tracheids of Abies sachalinensis Masters was examined by confocal laser scanning microscopy after immunofluorescent staining. The arrays of MTs in the tracheids during formation of the primary wall were not well ordered and the predominant orientation changed from longitudinal to transverse. During formation of the secondary wall, the arrays of MTs were well ordered and their orientation changed progressively from a flat S-helix to a steep Z-helix and then to a flat S-helix as the differentiation of tracheids proceeded. The orientation of cellulose microfibrils (MFs) on the innermost surface of cell walls changed in a similar manner to that of the MTs. These results provide strong evidence for the co-alignment of MTs and MFs during the formation of the semi-helicoidal texture of the cell wall in conifer tracheids.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- MT:
-
cortical microtubule
- MF:
-
cellulose microfibril
- S1, S2 and S3:
-
the outer, middle and inner layers of the secondary wall
References
Abe H, Funada R, Ohtani J, Fukazawa K (1995) Changes in the arrangement of microtubules and microfibrils in differentiating conifer tracheids during the expansion of cells. Ann Bot 75:305–310
Abe H, Ohtani J, Fukazawa K (1991) FE-SEM observation on the microfibrillar orientation in the secondary wall of tracheids. Int Assoc Wood Anat Bull NS 12:431–438
Abe H, Ohtani J, Fukazawa K (1992) Microfibrillar orientation of the innermost surface of conifer tracheid walls. Int Assoc Wood Anat Bull NS 13:411–417
Abe H, Ohtani J, Fukazawa K (1994) A scanning electron microscopic study of changes in microtubule distributions during secondary wall formation in tracheids. Int Assoc Wood Anat J 15:185–189
Emons AMC, Derksen J, Sassen MMA (1992) Do microtubules orient plant cell wall microfibrils? Physiol Plant 84:486–493
Fujita M, Saiki H, Harada H (1974) Electron microscopy of microtubules and cellulose microfibrils in secondary wall formation of poplar tension wood fibers. Mokuzai Gakkaishi 20:147–156
Giddings TH Jr, Staehelin LA (1991) Microtubule-mediated control of microfibril deposition: a re-examination of the hypothesis. In: Lloyd CW (ed) The cytoskeletal basis of plant growth and form. Academic Press, London, pp 85–99
Green PB (1980) Organogenesis — a biophysical view. Annu Rev Plant Physiol 31:51–82
Gunning BES, Hardham RH (1982) Microtubules. Annu Rev Plant Physiol 33:651–698
Harada H, Côté WA Jr (1985) Structure of wood. In: Higuchi T (ed) Biosynthesis and biodégradation of wood components. Academic Press, Orlando, pp 1–42
Hepler KH, Palevitz BA (1974) Microtubules and microfilaments. Annu Rev Plant Physiol 25:309–362
Ledbetter MC, Porter KR (1963) A “microtubule” in plant cell fine structure. J Cell Biol 19:239–250
Lloyd CW (1984) Toward a dynamic helical model for the influence of microtubules on wall patterns in plants. Int Rev Cytol 86:1–51
Neville AC, Levy S (1984) Helicoidal orientation of cellulose microfibrils in Nitella opaca internode cells: ultrastructure and computed theoretical effects of strain reorientation during wall growth. Planta 162:370–384
Neville AC, Levy S (1985) The helicoidal concept in plant cell wall ultrastructure and morphogenesis. In: Brett CT, Hillman JR (eds) Biochemistry of plant cell walls. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 99–124
Nobuchi T, Fujita M (1972) Cytological structure of differentiating tension wood fibres of Populus euroamericana. Mokuzai Gakkaishi 18:137–144
Prodhan AKMA, Funada R, Ohtani J, Abe H, Fukazawa K (1995a) Orientation of microfibrils and microtubules in developing tension-wood fibres of Japanese ash (Fraxinus mandshurica var. japonica). Planta 196:577–585
Prodhan AKMA, Ohtani J, Funada R, Abe H, Fukazawa K (1995b) Ultrastructural investigation of tension wood fibre in Fraxinus mandshurica Rupr. var. japonica Maxim. Ann Bot 75:311–317
Robards AW, Kidwai P (1972) Microtubules and microfibrils in xylem fibres during secondary cell wall formation. Cytobiologie 6:1–21
Roberts IN, Lloyd CW, Roberts K (1985) Ethylene-induced microtubule reorientations: mediation by helical arrays. Planta 164:439–447
Roland JC, Mosiniak M (1983) On the twisting pattern, texture and layering of the secondary cell walls of lime wood. Proposal of an unifying model. Int Assoc Wood Anat Bull NS 4:15–26
Roland JC, Reis D, Vian B, Satiat-Jeunemaitre B, Mosiniak M (1987) Morphogenesis of plant cell walls at the supramolecular level: internal geometry and versatility of helicoidal expression. Protoplasma 140:75–91
Seagull RW (1991) Role of the cytoskeletal elements in organized wall microfibril deposition. In: Haigler CH, Weimer PJ (eds) Biosynthesis and biodegradation of cellulose. Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York, pp 143–163
Vian B, Reis D (1991) Relationship of cellulose and other cell wall components: supramolecular organizaton. In: Haigler CH, Weimer PJ (eds) Biosynthesis and biodegradation of cellulose. Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York, pp 25–50
Wardrop AB (1964) The structure of formation of cell wall in xylem. In: Zimmermann MA (ed) The formation of wood in forest trees. Academic Press, New York, London, pp 87–134
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The authors thank Mr. T. Itoh of the Electron Microscope Laboratory, Faculty of Agriculture, Hokkaido University, for his technical assistance. This work was supported in part by a Grant-in-Aid from the Ministry of Education, Science and Culture, Japan (no. 06404013).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abe, H., Funada, R., Imaizumi, H. et al. Dynamic changes in the arrangement of cortical microtubules in conifer tracheids during differentiation.. Planta 197, 418–421 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00202666
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00202666