Abstract
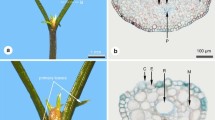
Morphological and histological observations were made on eight dwarf mutants arising either as seedlings from sexual reproduction or from somatic bud mutations (witches'-brooms in the crowns of normal trees). The most predominate morphological trait contributing to the expression of dwarfism in all taxa was the reduction of final internode lengths along the shoot axis. In taxa of sexual origin, with the exception of Prunus, there was a consistent reduction in the number of preformed leaves contained in the winter buds. In addition, in two taxa (Liquidambar and Tsuga) there was an almost complete absence of neoformed leaves and sylleptic branches on current year shoots. Conversely, in mutants of somatic origin there was no apparent reduction in the number of preformed leaves. Genetic dwarfness in this group resulted solely from decreases in final internode length. Significant differences in the cellular basis of dwarfism between mutants of different genetic origins are clearly evident. In dwarf trees arising from sexual reproduction, reduction in final internode length is attributed predominately to inhibition of mitotic activity in developing internodes resulting in highly significant decreases in final cell number, and not cell length. In mutants of somatic origin, the reduction in length of mature internodes results from a decrease in final cell length, rather than a decrease in cell number. Physiological mechanisms associated with the genetic expression of these morphogenetic differences are suggested.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brown CL, Sommer HE (1992) Shoot growth and development of trees possessing diverse patterns of shoot development. Am J Bot 79: 335–346
Brown CL, McAlpine RG, Kormanik PP (1967) Apical dominance and form in woody plants: a reappraisal. Am J Bot 54: 153–162
Fordham AJ (1967) Dwarf conifers from witches'-brooms. Arnoldia 24: 29–50
Harting MG (1845) Recherches micrométriques sur le développement des parties élémentaires de la tige annuelle des plantes dicotylédonées. Ann Sci Nat Bot 3e Ser 4: 210–279
Holmsen TW (1960) Pith development in normal and short internode seedlings of Prunus persica var. Lovell. Am J Bot 47: 173–175
Johnson AG, Pauley SS, Cromell WH (1968) Pine dwarf segregates from witches'-brooms. Proc Int Plant Prop Soc 18: 265–270
Kormanik PP, Steinbeck K, Brown CL (1966) A new variety of sweetgum. USFS Res Note SE-55, Asheville, N.C.
Lam OC, III, Brown CL (1974) Shoot growth and histogenesis of Liquidambar styraciflua L. under different photoperiods. Bot Gaz (Chicago) 135: 149–154
Ledbetter MC (1960) Anatomical and morphological comparisons of normal and physiologically dwarfed seedlings of Rhodotypos tetrapetala and Prunus persica. Contr Boyce Thompson Inst 20: 437–458
Liernur AGM (1927) Hexenbesen: Ihre Morphologie und Entstehung. Proefschrift Universiteit Te Utrechet, Rotterdam
Moll JW (1876) The influence of cell division and cell elongation on growth (in Dutch). Academich Proefschrift, L. E. Bosh en Zoom, Utrecht
Powell GR (1991) Preformed and neoformed extension of shoots and sylleptic branching in relation to shoot length in Tsuga canadensis. Trees 5: 107–116
Sachs RM (1965) Stem elongation. Annu Rev Plant Physiol 16: 73–96
Waxman S (1975) Witches'-brooms sources of new and interesting dwarf forms of Picea, Pinus, and Tsuga species. Acta Hort 54: 25–32
Wetmore RH, Garrison R (1966) The morphological ontogeny of the leafy shoot. In: Cutter EG (ed) Trends in plant morphogenesis. Longmans, London, pp187–199
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brown, C.L., Sommer, H.E. & Wetzstein, H. Morphological and histological differences in the development of dwarf mutants of sexual and somatic origin in diverse woody taxa. Trees 9, 61–66 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00202123
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00202123