Summary
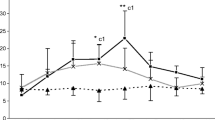
A study was carried out on leukocyte enzyme activity from prints of skin cut wounds of guinea pigs at various time intervals after the injury. The following enzymes were examined: alkaline and acid phosphatase, succine, lactate, and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenases. Cytochemical analysis revealed a rapid increase in enzyme activity in the 4th h after the wound occurred, which can be explained by the alteration in leukocyte metabolism induced by the damaging agent, i.e., the skin trauma inflicted. The rise in lactate dehydrogenase and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase activity is the most characteristic feature. In accordance with these changes in enzyme activity, some conclusions can be made about certain intracellular alterations. There is a close relationship between the course and the degree of these cellular changes and the time interval between the injury and examination of the enzyme activity. These changes make it possible to draw conclusions concerning the vital character and the interval after inflicting as well.
Zusammenfassung
Es wurde eine Untersuchung der Enzymaktivität der alkalischen und sauren Phosphatase, der Sukzinat- und Laktatdehydrogenase, und der Glucose-6-Phosphatdehydrogenase in den Leukozyten von Abdrücken von Hautschnittwunden bei Meerschweinchen nach verschiedenen Zeitabschnitten nach Verletzung durchgeführt. Die zytochemische Analyse zeigt eine merkliche Steigerung der Aktivität der untersuchten Enzyme um die vierte Stunde nach der Verletzung der Haut. Diese Steigerung der Enzymaktivität wird auf die eingetretene Umwandlung des normal verlaufenden metabolischen Prozesses in den Leukozyten, hervorgerufen durch die Einwirkung eines schädigenden Agents — der Verletzung der Haut — zurückgeführt. Am demonstrativsten ist diese Steigerung der Enzymaktivität bei der Laktatdehydrogenase und der Glucose-6-Phosphatdehydrogenase. Auf Grund der Veränderungen in der Aktivität der untersuchten Enzyme kann man Schlußfolgerungen auf die sich entwickelnden Veränderungen in der Zelle selbst ziehen. Die Entwicklung und der Grad dieser Veränderungen stehen in enger Abhängigkeit von der verstrichenen Zeit von dem Moment der Schädigung bis zum Moment der Untersuchung der entsprechenden Enzymaktivität. Aus diesen Veränderungen kann man sowohl darauf schließen, ob die Verletzung zu Lebzeiten geschah, als auch auf die Zeitdauer ihres Bestehens.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Berg S (1972) Die Altersbestimmung von Hautverletzung. Z Rechtsmed 70:121–135
Berg S, Ebel R (1969) Altersbestimmung subkutaner Blutungen. Münch Med Wochenschr 1185–1190
Gadzhiev A, Kadiev B, Silin E (1976) Influence on peripheral leukocyte peroxidase activity of the time interval after death. In: Smol'yaninov WM (ed) First Allunion Congress on Forensic Medicine. Department of Health, Moscow, pp 233–234 (Russ)
Gerebtzoff M (1968) Contribution histochimique à l'étude de la lactate dehydrogénase et ses iso-enzymes. Pathol Biol Paris 16:601–609
Gerebtzoff M (1966) Détection histochimique d'isoenzymes de la LDH dans le nerf et le ganglion spinal. C R Soc Biol (Paris) 160:1323–1325
Hizhnjakova K (1983) Dynamics of craniocerebral injury pathomorphology. Medizina, Moscow, pp 19–25 (Russ)
Hou-Jensen K (1968) Histochemical demonstration of some hydrolysic enzymes as vital reaction in medicolegal practice. J Forensic Med 15:91–105
Kömpf J, Oehmichen M, Smidt V (1983) Enzymaktivität isolierten Leukozytenpopulationen. Z Rechtsmed 90:115–125
Oboznaja E, Pushkar N, Markova O, Pankov E (1981) Frozencell cytochemistry. Naukova dumka, Kiev, pp 7–16 (Russ)
Ojala K, Lempinen M, Hirvonen J (1969) A comparative study of the charakter and rapidity of the vital reaction in the incised wounds of human skin and subcutaneous tissue. J Forensic Med 16:29–34
Nachlas M, Tsou K, De Souza E, Cheng C, Seligman A (1957) Cytochemical demonstration of succinic dehydrogenase by the use of a new p-nitrophenyl substituted ditetrazole. J Histochem Cytochem 3:420
Padykula H, Herman E (1955) Factors affecting the activity of adenosine triphosphatase and other phosphatases as measured by histochemical techniques. J Histochem Cytochem 3:161
Padykula H, Herman E (1955) The specificity of the histochemical method for adenosine triphosphatase. J Histochem Cytochem 3:170
Raekallio J (1961) Histochemical studies on vital and post-mortem skin wounds. University of Helsinki, Helsinki, pp 7–11
Raekallio J (1965) Die Altersbestimmung mechanisch bedingter Hautwunden mit enzymhistochemischen Methoden. Max Schmidt-Römhild, Lübeck, S 11–16
Wachstein M (1946) Alkaline phosphatase activity in normal and abnormal human blood and bone marrow cells. J Lab Clin Med 31:1–17
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lasarov, I. Enzymaktivität von Leukozyten aus Schnittwunden der Haut mit verschiedener Wundaltersbestimmung. Z Rechtsmed 100, 157–164 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00200756
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00200756