Abstract
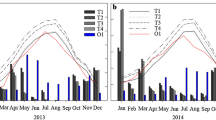
In recent decades, the biostatistical analysis of relationships among tree growth and macroclimatic factors has developed remarkably. In this discipline, the parametrisation of tree growth is generally based on the records of annual ring widths measured on breast height transverse sections of tree stems (ARI). The present research enables the stem volume annual increment (AVI) to be evaluated as a dendroclimatic indicator in comparison with ARI. The research is a part of a broader investigation into the ecobiological characteristics of Turkey oak in the Gargano region (southern Italy). The results indicate that AVI is no better than ARI as a means of highlighting expressive relationships among the examined macroclimatic factors (monthly precipitation and monthly averages of temperature daily maxima and minima) and the Turkey oak annual stem growth. In the examined stands, the most growthinfluencing factors are the autumn and spring rainfalls. Regarding the stem breast height radial increment, the most effective temperature factors are the June averages of daily minima and maxima.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brugnoli A, Gandolfo C (1991) Analisi dendroclimatica sull'abete rosso [Picea abies (L.) Karst.] del Trentino orientale: primi risultati. Monti Boschi 6: 51–56
Castellani C (1978–79) Studio sull'incremento diametrico stagionale di alcune delle più importanti specie forestali che popolano i boschi italiani. Ann Ist Sper Assestamento For Alpic 7: 1–106
Chalupa V (1969) Start, duration and end of growing activity of forest trees. Pr Vulhm 37: 43–67
Chalupa V (1979) Initiation of cambial activity and seasonal course of radial growth of forest trees in relation to development of leaves and air temperature. Pr Vulhm 54: 29–48
Corona P, Ferrara A, la Marca O (1989) Un sistema di misura delle ampiezze anulari: il dendrocronografo SMIL 3. It For Mont 44: 391–404
Fabbio G, Frattegiani M, Manetti MC (1988) Il metodo di analisi del fusto. Stima della superficie di sezioni legnose trasversali. Ann Ist Sper Selvic 19:71–108
Gadbin C (1992) Intérêt du choix des carottes de sondage en dendroclimatologie. Dendrochronologia 10: 29–40
Guiot J, Tessier L, Serre Bachet F (1982) Application de la modélisation ARMA en dendroclimatologie. CR Acad Sci Paris 294: 133–136
Guiot J (1990) Methods and programs of statistics for paleoclimatology and paleoecology. Labeyrie G. (ed) Université d'Aix Marseille, Marseille
Guiot J (1991) The bootstrapped response function. Tree Ring Bull 51: 39–42
Hinckley TM, Thompson D, Mcginnes NP, Hinckley A (1976) Stem growth of a dominant white oak. Central Hardwood Forest Conference. Proceedings of First Meeting at Southern Illinois University, Fralish, Weaver and Schlesinger, pp 187–200
Le Blanc DC (1990a) Relationships between brest-height and wholestem growth indices for red spruce on Whiteface Mountain, New York. Can J For Res 20: 1399–1407
Le Blanc DC (1990b) Red spruce decline on Whiteface Mountain, New York. Relationships with elevation, tree age, and competition. Can J For Res 20: 1408–1414
Le Blanc D, Nicholas NS, Zedaker SM (1992) Prevalence of individual-tree growth decline in red spruce populations of the southern Appalachian Mountains. Can J For Res 22: 905–914
La Marca O, Leone V, Moretti N (1989) Prove di diradamento in fustaie di cerro: primi risultati. Doc Reg Basilicata 1–3: 249–277
Leone V, Vita F, Zito G (1981) Valutazione delle condizioni climatiche stazionali e rimboschimento a fini produttivi: applicazione al territorio pugliese. Cellul Carta 12: 13–30
Lo Monaco A, Schirone A, Schirone B (1988) Osservazioni sulla sensitività media degli alberi nei boschi governati a ceduo. Atti 2∘ Colloquio ‘Approcci metodologici per la definizione dell'ambiente fisico e biologico mediterraneo’, Castro Marina, pp 193–201
Lorenz M, Eckstein D (1988) Wachstumsreaktionen von Einzelbäumen in Douglasien-, Fichtenund Kieferbeständen in norddeutschen Waldschadensgebieten. Forst Holz 43: 8–12
Martinelli N, Pignatelli O, Romagnoli M (1994) Primo contributo allo studio dendroclimatologico del cerro (Quercus cerris L.) in Sicilia (in press)
Messaudene M (1989) Approche dendroclimatologique et productivité de Quercus afares (Pomel) et Quercus canariensis (Willd) dans les massifs forestiers de l'Akfadou et de Beni-ghobri en Algérie. Thèse de Doctorate en Sciences, Université d'Aix Marseille, Marseille
Nola P (1991) Primo approccio alla dendroclimatologia della quercia [Quercus robur L. e Quercus petraea (Mattuschka) Liebl.] in Pianura Padana (Italia settentrionale). Dendrochronologia 9: 71–94
Nola P (1992) Dendroecologia di Quercus robur L. nella valle sublacuale del fiume Ticino. Tesi di Dottorato, Università di Pavia, Pavia
Romagnoli M (1993) Ricerche dendroclimatiche sul cerro del Lazio. Tesi di Dottorato, Università della Tuscia, Viterbo
Santini A, Bottacci A, Gellini R (1994) Preliminary dendroecological survey on pedunculate oak (Quercus robur L.) stands in Tuscany (Italy). Ann Sci For 51: 1–10.
Schirone B, Romagnoli M (1990) Prime indagini dendroclimatologiche sul cerro dell'Alto Lazio. Atti Convegno ‘Effetti degli inquinanti atmosferici e del clima sugli ambienti naturali e sui manufatti’, Bressanone, pp 59–61
Serre Bachet F (1982) The Mediterranean area. In: Hughes MK, Kelly PM, Pilcher JR, La Marche VC (eds) Climate from tree rings, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 151–155
Serre Bachet F, Tessier L (1989) Response function analysis for ecological study. In: Cook O, Kariukstis R (eds) Methods dendrochron, pp 247–257
Waring RH, Schlesinger WH (1985) Forest ecosystems concepts and management. Academic Press, New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Corona, P., Romagnoli, M. & Torrini, L. Stem annual increments as ecobiological indicators in Turkey oak (Quercus cerris L.). Trees 10, 13–19 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00197774
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00197774