Summary
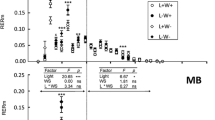
Shoot development was investigated on branches of Larix laricina (Du Roi) K. Koch trees growing in their 8th year in two plantations and in a natural stand approximately 12 years old. Expansion of throughout-crown series of short and long shoots was measured weekly, and later colour change and natural fall of leaves were assessed. Similar shoots were collected at intervals and dissected, the long shoots by 25-leaf segments. Leaf area and weight, as well as time of bud formation, were determined. Increasing acropetal trends were evident in time to bud burst: duration of short-shoot leaf-cluster expansion; size of leaf clusters and number, area and weight of leaves per cluster; duration and rate of long-shoot elongation; number, area and weight of leaves on long shoots; time to terminal-bud formation on long shoots. Along each long shoot, stem and leaf elongation and lateral-axis formation progressed acropetally. Lateral axes were most numerous on second to fourth 25-leaf segments. On longer shoots, some axes in middle segments developed as sylleptic short shoots rather than as lateral buds. Leaves of short shoots and basal leaves on long shoots turned yellow and abscissed sooner than axial leaves on long shoots. Colour change and loss among axial leaves were acropetal along shoots and up the crown. Thus, last-formed leaves, in axils of some of which lastformed lateral buds occurred, were held longest.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baldwin HI (1955) Course of seasonal height growth in European larch. Fox For Not 60: 1
Bonnet-Masimbert M (1982) Effect of growth regulators, girdling, and mulching on flowering of young European and Japanese larches under field conditions. Can J For Res 12: 270–279
Champagnat P (1965) Rameaux courts et rameaux longs: problémes physiologiques. In: Ruhland W (ed) Differentiation and development I: Encyclopedia of plant physiology, vol 15. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 1165–1171
Clausen JJ, Kozlowski TT (1967) Seasonal growth characteristics of long and short shoots of tamarack. Can J Bot 45: 1643–1651
Clausen JJ, Kozlowski TT (1970) Observations on growth of long shoots in Larix laricina. Can J Bot 48: 1045–1048
Cook DB (1941) Five seasons' growth of conifers. Ecology 22: 285–296
Ford ED, Deans JD, Milne R (1987) Shoot extension in Picea sitchensis. I. Seasonal variation within a forest canopy. Ann Bot 60: 531–542
Frampton CV (1960) Some aspects of the developmental anatomy of the “long” shoot in Larix decidua Mill., with particular reference to seasonal periodicity. New Phytol 54: 175–191
Fraser DA (1962) Apical and radial growth of white spruce (Picea glauca [Moench] Voss) at Chalk River, Ontario, Canada. Can J Bot 40: 659–668
Friesner RC (1943) Correlation of elongation in primary, secondary and tertiary axes of Pinus strobus and P. resinosa. Butler Univ Bot Stud 6: 1–9
Fujimoto S (1978) Studies on the shoot formation in Larix leptolepis Gordon. Hokkaido Univ Coll Exp For Res Bull 35: 1–28
Geiger R (1965) The climate near the ground. Harvard University Press, Cambridge MA
Hallé F, Oldeman RAA, Tomlinson PB (1978) Tropical trees and forests. An architectural analysis. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Kienholz R (1941) Seasonal course of height growth in some hardwoods in Connecticut. Ecology 22: 249–258
Kozlowski TT, Clausen JJ (1966) Shoot growth characteristics of heterophyllous woody plants. Can J Bot 44: 827–843
Larcher W (1975) Physiological plant ecology. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Maillette L (1982) Structural dynamics of silver birch. I. The fates of buds. J Appl Ecol 19: 203–218
McCurdy WD, Powell GR (1987) Syllepsis in Larix laricina: association of sylleptic branching with cross-sectional stem growth and stem form of saplings. Can J For Res 18: 1609–1619
Mitchell AF (1965) The growth in early life of the leading shoot of some conifers. Forestry 38: 121–136
Owens JN, Molder M (1979) Bud development in Larix occidentalis. I. Growth and development of vegetative long shoot and vegetative short shoot buds. Can J Bot 57: 687–700
Powell GR (1987) Syllepsis in Larix laricina: an analysis of tree leaders with and without sylleptic long shoots. Can J For Res 17: 490–498
Powell GR, Vescio SA (1986) Syllepsis in Larix laricina: occurrence and distribution of sylleptic long shoots and their relationships with age and vigour in young plantation-grown trees. Can J For Res 16: 597–607
Powell GR, Tosh KJ, Remphrey WR (1984) Occurrence and distribution of cones borne laterally on long shoots of Larix laricina. Can J Bot 62: 771–777
Remphrey WR, Powell GR (1984a) Crown architecture of Larix laricina saplings: quantitative analysis and modelling of (nonsylleptic) order 1 branching in relation to development of the main stem. Can J Bot 62: 1904–1915
Remphrey WR, Powell GR (1984b) Crown architecture of Larix laricina saplings: shoot preformation and neoformation and their relationships to shoot vigour. Can J Bot 62: 2181–2192
Remphrey WR, Powell GR (1985) Crown architecture of Larix laricina saplings: sylleptic branching on the main stem. Can J Bot 63: 1296–1302
Remphrey WR, Powell GR (1987) Crown architecture of Larix laricina saplings: an analysis of higher-order branching. Can J Bot 65: 268–279
Remphrey WR, Powell GR (1988) Crown architecture of Larix laricina saplings: production and disposition of foliage and their simulation. Can J Bot 66 (in press)
Simak M, Jeansson E (1987) Research on Larix laricina in Sweden. In: Northern forest silviculture and management, IUFRO S1.05-12 Symposium, Finland, preprint pp 15
Sweet GB (1965) Provenance differences in Pacific coast Douglas-fir. I. Seed and seedling characteristics. Silvae Genet 14: 46–56
Tosh KJ, Powell GR (1986) Proliferated, bisporangiate, and other atypical cones occurring on young, plantationgrown Larix laricina. Can J Bot 64: 469–475
Wareing PF (1980) Root hormones and shoot growth. In: Little CHA (ed) Control of shoot growth in trees. Proc IUFRO Workshop, Maritimes For Res Centre, Fredericton NB, pp 237–256
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Powell, G.R. Shoot elongation, leaf demography and bud formation in relation to branch position on Larix laricina saplings. Trees 2, 150–164 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00196020
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00196020