Abstract
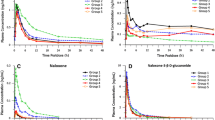
In a closed metabolic ward the pharmacokinetics of methadone and its primary metabolite (EDDP) were studied in 20 long-term opiate addicts. After administration of the daily oral dose of methadone HCl (mean 60 mg, range 10–225 mg) blood samples were taken and analysed, using a newly developed high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) method. The steady-state plasma concentrations of the 20 subjects varied from 65–630 ng·ml−1 and from 5 to 55 ng·ml−1, whereas the peak concentrations were 124–1255 ng·ml−1 and 10 – 301 ng·ml−1 for methadone and EDDP, respectively. The calculated ratios between the area under the curve (AUC(0–24 h)) for methadone and the AUC(0–24 h) for EDDP varied from 5.9 to 44.6, indicating interindividual differences in metabolic activity. In 19 out of 20 subjects the pharmacokinetics of methadone are best described using a two-compartment model. The mean body clearance was 1.64 ml·min−1·kg−1, whereas the mean elimination rate constant (β) and plasma half-life (t 1/2β) were 0.026·h−1 (range 0.013–0.053·h−1) and 31.2 h (range 13–53 h), respectively. Differences of gender were also found. A poor correlation was found between the methadone dose and the steady-state level. A much better correlation was found between the normalized steady-state level and the body clearance.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dole VP, Nyswander ME (1965) A medical treatment for diacetylmorphine (heroin) addiction. J Am Med Assoc 193:646–650
Nilsson MI, Grönbladh L, Widerlöv E, Ångg»rd E (1983) Pharmacokinetics of methadone maintenance treatment: characterization of therapeutic failures. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 25:497–501
Ångg»rd E, Nilsson MI, Holmstrand J, Gunne LM (1979) Pharmacokinetics of methadone during maintenance therapy: pulse labeling with deuterated methadone in the steady-state. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 16:53–57
Nilsson MI, Ångg»rd E, Holmstrand J, Gunne LM (1982) Pharmacokinetics of methadone during maintenance treatment: adaptive changes during the inductive phase. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 22: 343–349
Meresaar U, Nilsson MI, Holmstrand J, Ångg»rd E (1981) Single dose pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of methadone in man studied with a stable isotope method. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 20:473–478
Olsen GD, Wilson JE, Robertson GE (1981) Respiratory and ventilatory effects of methadone in healthy women. Clin Pharmacol Ther 29:373–380
Denson DD, Concilus RR, Warden G, Prithvi RP (1990) Pharmacokinetics of continuous intravenous infusion of methadone in the early postburn period. J Clin Pharmacol 30:70–75
Wolff K, Hay AWM, Raistrick D, Calvert R (1993) Steady-state pharmacokinetics of methadone in opioid addicts. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 44:189–194
Plummer JL, Gourlay GK, Cherry DA, Cousins MJ (1988) Estimation of methadone clearance: application in the management of cancer pain. Pain 33:313–322
Verebely K, Volavka J, Mulé S, Resnick R (1975) Methadone in man: pharmacokinetic and excretion studies in acute and chronic treatment. Clin Pharmacol Ther 18:180–190
Ångg»rd E, Gunne LM, Holmstrand J, McMahon RE, Sandberg CG, Sullivan HR (1975) Disposition of methadone in methadone maintenance. Clin Pharmacol Ther 17:258–266
Säwe J, Hansen J, Ginman C, Hartvig P, Jakobsson PA, Nilsson MI, Rane A, Ångg»rd E (1981) Patient-controlled dose regimen of methadone for chronic cancer pain. BMJ 282:771–779
Horns WH, Rado M, Goldstein A (1975) Plasma levels and symptom complaints in patients maintained on daily dosage of methadone hydrochloride. Clin Pharmacol Ther 17:636–649
Pohland A, Boaz HE, Sullivan HR (1971) Synthesis and identification of metabolites resulting from the biotransformation of dl-methadone in man and in rat. J Med Chem 14:194–197
Beckett AH, Taylor JF, Casy AF, Hassan MMA (1968) The biotransformation of methadone in man: synthesis and identification of a major metabolite. J Pharm Pharmacol 20:754–762
Gibaldi M, Perrier D (1982) Pharmacokinetics—drugs and the pharmaceutical sciences. Marcel Dekker, New York
Proost JH, Meijer DKF (1992) MW/Pharm, an integrated software package for drug dosage regimen calculation and therapeutic drug monitoring. Comput Biol Med 22:155–163
Inturissi CE, Colburn WA, Kaiko RF, Houde RW, Foley KM (1987) Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of methadone in patients with chronic pain. Clin Pharmacol Ther 41:392–401
Jacob P, Rigod JF, Pond SM, Benowitz NL (1981) Determination of methadone and its primary metabolite in biologic fluids using gas chromatography with nitrogen-phosphorus detection. J Anal Toxicol 5:292–295
Kintz P, Mangin P, Lugnier AA, Chaumont AJ (1990) A rapid and sensitive gas chromatographic analysis of methadone and its primary metabolite. J Toxicol Clin Exp 10:15–20
Kreek MJ, Bencsath FA, Field FH (1980) Effects of liver disease on urinary excretion of methadone and metabolites in maintenance patients: quantitation by direct probe chemical ionization mass spectrometry. Biomed Mass Spectrometry 7:385–395
Pierce TL, Murray AGW, Hope W (1992) Determination of methadone and its metabolites by high performance liquid chromatography following solid-phase extraction in rat plasma. J Chromat Sci 30:443–447
Sullivan HR, Due SL (1973) Urinary metabolites of dl-methadone in maintenance subjects. J Med Chem 16:909–913
Wolff K, Sanderson M, Hay AWM, Raystrick D (1991) Methadone concentrations in plasma and their relationship to drug dosage. Clin Chem 37:205–209
Loimer N, Schmid R (1992) The use of plasma levels to optimize methadone maintenance treatment. Drug Alcohol Depend 30:241–246
Bellward GD, Warren PM, Howard W, Axelson JE, Abbott FS (1977) Methadone maintenance: effect of urinary pH on renal clearance in chronic high and low doses. Clin Pharmacol Ther 22:92–99
Nilsson MI, Widerlöv E, Meresaar U, Ångg»rd E (1982) Effect of urinary pH on the disposition of methadone in man. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 22:337–342
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Vos, J.W., Ufkes, J.G.R., van Wilgenburg, H. et al. Pharmacokinetics of methadone and its primary metabolite in 20 opiate addicts. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 48, 361–366 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00194951
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00194951