Abstract
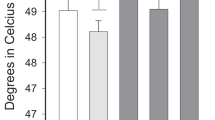
Twelve subjects (8 male) took part in a randomised double blind four way crossover design study comparing four treatments: (i) morphine sulphate 10 mg, (ii) morphine sulphate 15 mg, (iii) lorazepam 1 mg (positive control) and (iv) placebo. Cognitive function was assessed using choice reaction time, number vigilance, memory scanning, immediate and delayed word recall, word recognition, picture recognition, critical flicker fusion threshold (CFFT) and subjective measures of alertness, calmness and contentment. Lorazepam produced a marked impairment in the tests of attention and memory. CFFT was reduced from 1–4 h but this only reached significance at 4 hours. The subjective measures suggested impaired alertness but this did not reach significance. The effects of morphine were less dramatic; both doses of morphine produced significant impairment at 1 hour on tests of secondary memory retrieval (delayed word recall and picture recognition sensitivity). CFFT was reduced for the whole observation period (6 h) achieving statistical significance at 4 hours. Morphine 15 mg produced a significant improvement in accuracy on the choice reaction time test at the 2, 4 and 6 h assessments. These results show minimal impairment of cognitive and psychomotor function after single oral doses of morphine and with possible improvement in one test. Further studies are required to examine the effect of repeated doses.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Curran H V, Allen D, Lader M (1987) The effects of single doses of alpidem and lorazepam on memory and psychomotor performance in normal humans. J Psychopharmacology 2:81–89
Evans W O, Smith R P (1964) Some effects of morphine and amphetamine on intellectual functions and mood. Psychopharmacologia 6:49–56
Hanks G W (1991) Morphine pharmacokinetics and analgesia after oral administration. Postgrad Med J 67:S60–63
Hanks G W, Hoskin P J, Aherne G W, Turner P (1987) Explanation for potency of repeated oral doses of morphine? Lancet 723–726
Hindmarch I, Kerr J S, Sherwood N (1990) The effects of antidiarrhoeal drugs and analgesics in psychomotor performance, mood and sleep. Pharmacopsychoecologia 3:1–7
Kerr B, Hill H, Coda B, Calogera M, Chapman C R, Hunt E, Buffington V, Mackie A (1991) Concentration-related effects of morphine on cognition and motor control in human subjects. Neuropsychopharmacology 5:157–166
Lasagna L (1981) Heroin: a medical ‘me-too’. N Engl J Med 304:1539–1540
Link C G G, Leigh T J, Dennison J K (1993) The effects of BRL 46470A, a novel 5-HT3 receptor antagonist, and lorazepam on psychometric performance and the EEG. Br J Clin Pharmacol 35:395–399
O'Neill W M, Hanks G W, White L, Simpson P M, Wesnes K A (1995) The cognitive and psychomotor effects of opioid analgesics. I. A randomized controlled trial of single doses of dextropropoxyphene, lorazepam and placebo in healthy subjects. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 48:447–453
Preston G C, Broks P, Traub M, Ward C, Poppleton P, Stahl S M (1988) Effects of lorazepam on memory, attention and sedation in man. Psychopharmacology 95:208–215
Subhan Z, Harrison C, Hindmarch I (1986) Alprazolam and Lorazepam: single and multiple-dose effects on psychomotor skills and sleep. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 29:709–712
World Health Organisation (1990) Cancer pain relief and palliative care. Technical Report Series 804, Geneva
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hanks, G.W., O'Neill, W.M., Simpson, P. et al. The cognitive and psychomotor effects of opioid analgesics. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 48, 455–460 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00194334
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00194334