Abstract
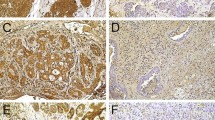
The development and progression of cancer are known to be regulated by various oncogenes and tumour suppressor genes. We analysed 63 primary malignant salivary gland tumours for the expression of p53 and c-erbB-2 proteins. Immunohistochemically, 7 of 63 tumours (11%) showed diffuse nuclear staining for p53 protein, and all 7 were also positive for c-erbB-2 protein. The overexpression of p53 protein correlated closely with the overexpression of c-erbB-2 protein (P<0.001). Overexpression of both p53 and c-erbB-2 proteins (coexpression) was found in tumours of certain histological types, such as adenocarcinoma, carcinoma in pleomorphic adenoma, and salivary duct carcinoma. Furthermore, it is noteworthy that coexpression was associated with high-grade carcinoma, advanced tumour stage, and a high Ki-67 labelling index (%) which is a marker of cell proliferation. In adenocarcinoma, we attempted to clarify the relationship between coexpression and histological grade. Coexpression was associated with histological grades showing high mitotic indices and necrotic areas, which reflected high cell-proliferative activity. These results suggest that the accumulation of genetic alterations, such as those involving p53 and c-erbB-2, plays an important part in the progression of malignant salivary gland tumours.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Azuma M, Kasai Y, Tamatani T, Sato M (1992) Involvement of p53 mutation in the development of human salivary gland pleomorphic adenomas. Cancer Lett 65:61–71
Baas IO, Mulder JR, Offerhaus GJA, Vogelstein B, Hamilton SR (1994) An evaluation of six antibodies for immunohistochemistry of mutant p53 gene product in archival colorectal neoplasmas. J Pathol (Lond) 172:5–12
Barbareschi M, Leonardi E, Mauri FA, et al (1992) p53 and c-erbB-2 protein expression in breast carcinomas: an immunohistochemical study including correlations with receptor status, proliferation markers, and clinical stage in human breast cancer. Am J Clin Pathol 98:408–418
Barnes DM, Dublin EA, Fisher CJ, et al (1993) Immunohistochemical detection of p53 protein in mammary carcinoma: an important new independent indicator of prognosis. Hum Pathol 24:469–476
Brambilla E, Gazzeri S, Mor D, et al (1993) Immunohistochemical study of p53 in human lung carcinomas. Am J Pathol 143:199–210
Cattoretti G, Rilke F, Andoreola S, et al (1988) p53 expression in breast cancer. Int J Cancer 41:178–183
Deguchi H, Hamano H, Hayashi Y (1993) c-myc, ras p21, and p53 expression in pleomorphic adenoma and its malignant form of the human salivary glands. Acta Pathol Jpn 43:413–422
Delahunt B, Bethwaite PB, Thornton A, Ribas JL (1995) Proliferation of renal cell carcinoma assessed by fixation-resistant polyclonal Ki-67 antibody labeling. Cancer 75:2714–2719
Ellis GL, Auclair PL (1991) Classification of salivary gland neoplasms. In: Ellis GL, Auclair PL, Guepp DR (eds) Surgical pathology of the salivary glands. Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 318–332
Fearon ER, Volgelstein B (1990) A genetic model for colorectal tumorigenesis. Cell 61:759–767
Haerslev T, Jacobsen GK (1995) An immunohistochemical study of p53 with correlations to histopathological parameters, c-erbB-2, proliferating cell nuclear antigen, and prognosis. Hum Pathol 26:295–301
Hurlimann J, Saraga EP (1994) Expression of p53 protein in gastric carcinomas. Am J Surg Pathol 18:1247–1253
Ishii K, Nakajima T (1994) Evaluation of malignant grade of salivary gland tumors: studies by cytofluorometric nuclear DNA analysis, histochemistry for nucleolar organizer regions and immunohistochemistry for p53. Pathol Int 44:287–296
Isola J, Visakorpi T, Holli K, Kallioniemi O-P (1992) Association of overexpression of tumor suppressor protein p53 with rapid cell proliferation and poor prognosis in node-positive breast cancer patients. J Natl Cancer Inst 84:1109–1114
Kernohan NM, Blessing K, King G, Corbett IP, Miller ID (1991) Expression of c-erbB-2 oncoprotein in salivary gland tumors: an immunohistochemical study. J Pathol (Lond) 163:81–85
Martin HM, Filipe MI, Morris RW, et al (1992) p53 Expression and prognosis in gastric carcinoma. Int J Cancer 50:859–862
Midgley CA, Fisher CJ, Bartek J, Vojtesek B, Lane D, Barenes DM (1992) Analysis of p53 expression in human tumors: an antibody raised against human p53 expressed in Escherichia coli. J Cell Sci 101:183–189
Murakami M, Ohtani I, Hojo H, Wakasa H (1992) Immunohistochemical evaluation with Ki-67: an application to salivary gland tumours. J Laryngol Otol 106:35–38
Nagao T, Kondo F, Sato T, Nagato Y, Kondo Y (1995) Immunohistochemical detection of aberrant p53 expression in hepatocelluar carcinoma. Hum Pathol 26:326–333
Press MF, Pike MC, Hung G, Zhou JY, Ma Y, George J, Dietz-Band J, James W, Slamon JG, Batsakis JG, El-Naggar AK (1994) Amplication and overexpression of HER-2/neu in carcinomas of the salivary gland: correlation with poor prognosis. Cancer Res 54:5675–5682
Sasano H, Miyazaki S, Gooukon Y, et al (1992) Expression of p53 in human esophageal carcinoma: an immunohistochemical study with correlation to proliferating cell nuclear antigen expression. Hum Pathol 23:1238–1243
Seifert G (1991) Histological typing of salivary gland tumours. (World Health Organization) Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Shrestha P, Huang JW, Tsuji T, Shinozaki F, Maeda K, Sasaki K, Ueno K, Yamada K, Mori M (1992) Rare expression of the c-erbB-2 oncoprotein in salivary gland tumors: immunohistochemical study. J Oral Pathol Med 21:477–480
Slamon DJ, Godolphin W, Jones LA, et al (1989) Studies of the HER-2/neu proto-oncogene in human breast and ovarian cancer. Science 244:707–712
Spiro RH, Huvos AG, Strong EW (1982) Adenocarcinoma of salivary gland origin: clinicopathologic study of 204 patients. Am J Surg 144:423–431
Sugano S, Mukai K, Tsuda H, Hirohashi S, Furuya S, Shimosato Y, Ebihara S, Takeyama I (1992) Immunohistochemical study of c-erbB-2 oncoprotein overexpression in human major salivary gland carcinoma: an indicator of aggressiveness. Laryngoscope 102:923–927
Thackray AC, Lucas RB (1974) Tumors of the major salivary glands. Armed Forces Institute of Pathology, Washington, DC
Van den Berg FM, Tigges AJ, Schipper MEI, et al (1989) Expression of the nuclear oncogene p53 in colon tumours. J Pathol (Lond) 157:193–199
Wiltschke C, Kindas-Mueggen I, Steininger A, Reiner A, Reiner G, Preis PN (1994) Coexpression of HER-2/neu and p53 is associated with a shorter disease-free survival in node-positive breast cancer patients. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 120:737–742
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kamio, N. Coexpression of p53 and c-erbB-2 proteins is associated with histological type, tumour stage, and cell proliferation in malignant salivary gland tumours. Vichows Archiv A Pathol Anat 428, 75–83 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00193934
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00193934