Abstract
To study patient compliance in hypertensive outpatients amlodipine (5 mg once daily) and slow release nifedipine (20 mg twice daily) were compared in an open, crossover study in general practices.
Four methods of assessment for patient compliance (pill count, taking compliance, days with correct dosing, timing compliance) were used in both study arms. For the latter three assessment a special device, the medication event monitoring system, was used to record the time and date of each opening and closure of the container.
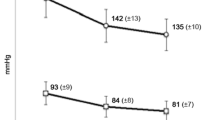
The compliance of the 320 hypertensive patients with once-daily amlodipine was markedly superior to twice-daily slow release nifedipine. Therapeutic coverage was also significantly better for amlodipine in the hypertensive patients. Amlodipine was better tolerated than nifedipine slow release.
Patient compliance and therapeutic coverage with the calcium antagonist amlodipine given once daily was superior to slow release nifedipine b. d. in hypertensive outpatients recruited in general practice.
Statistical Unit: Léon Kaufmann, Marie-Paule Derde, Data Investigation Company Europe, Brussels
Participating Investigators: D. Abbate, G. Armand, C.I. Authelet, J.L. Badot, J. Baeck, P. Baeck, P. Bastin, C.I. Bernard, P. Bernard, B. Beyssens, J. Bosly, P. Boudart, J. Bourdeaudhuy, W. Callens, L. Carolides, Y. Catry, E. Cerstelotte, F. Charlier, H. Charloteaux, J.M. Chaudron, L. Christiaen, G. Cornette, P. Cranskens, R. Creteur, N. De Cock, M. De Corte, A. De Vos, P. Defrance, P. Delhaye, G. Deneckere, M. Dobbeleir, A. Dufour, P. Dumont, L. D'Haen, H. D'Haenens, P. Eloy, P. Evrard, C. Fellemans, G. Geeraerts, L. Gielen, D. Grand, J. Grosjean, J. Guffens, R. Guillaume, R. Hacquaert, V. Hamoir, W. Hens, M. Hondeghem, M.C. Humblet-Koch, L. Leven, W. Janssens, L. Jeanfils, J. Jodogne, B. Jortay, W. Ketels, J.M. Krzesinski, E. Langendries, J. Lannoy, M. Leeman, J. Leire, P. Lempereur, L. Lenaerts, F. Lustman, R. Martens, Y. Maus, M. Meroueh, J.P. Meurant, P. Meurant, A. Michiels, E. Mievis, H. Moors, K. Naesens, P. Neels, J. Neven, W. Odeurs, W. Pardon, M. Peduzzi, J. Piette, D. Plessers, P. Putzeys, A. Quoidbach, A. Renaerts, G. Rits, M. Ruhwiedel, M. Salavracos, M. Seret, P. Sibille, M. Taziaux, J. Teucq, H. Therasse, F. Tihon, F. Vandenput, J. Van Elsen, J.P. Van Liefferinge, J. Van Neck, M. Van Pelt, T. Van Vlaenderen, G. Vandenbeylaardt, M. Vandewoude, F. Veldeman, D. Ven, F. Verbruggen, A. Vlaeminck, P. Werion, J. Westerlinck.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cramer JA, Spilker B (1991) Compliance in medical practice and clinical trials. In: Cramer JA, Spilker B (eds) Raven Press, New York
Urquhart J (1992) Ascertaining how much compliance is enough with outpatient antibiotic regimens. Postgrad Med J 68 [Suppl 3]: S49-S59
Vander Stichele R (1991) Measurement of patient compliance and the interpretation of randomised clinical trials. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 41: 27–35
Onesti G (1983) Treatment of mild hypertension and the problem of compliance. Curr Med Res Opin 8 [Suppl 3]: 77–80
Horwitz RI, Viscoli CM, Berkman L, et al (1990) Treatment adherence and risk of death after a myocardial infarction. Lancet 336: 542–545
Psaty BM, Koepsell TD, Wagner EH, et al (1990) The relative risk of incident coronary heart disease associated with recently stopping the use of beta blockers. JAMA 263: 1653–1657
Miller RR, Olson HG, Amserdam EA, Mason DT (1975) Propranolol withdrawal rebound phenomenon. Exacerbation of coronary events after abrupt cessation of antianginal therapy. N Engl J Med 293: 416–418
National Pharmaceutical Council (NPC) (1992) Non-compliance with medication regimens: an economic tragedy. June 1992, 2: 1–2
Purcell H, Waller DG, Fox K (1989) Therapeutic focus. Calcium antagonists in cardiovascular disease. Br J Clin Pract 43: 369–379
Cappucio FP, Markandu MD, Sagnella GA, et al (1991) Effects of amlodipine on urinary sodium excretion, renin-angiotension-aldosterone system, atrial natriuretic peptide and blood pressure in hypertension. J Hum Hypertens 5: 115–119
Vandewoude MFJ, Lambert M, Vryens R (1991) Open evaluation of amlodipine in the monotherapeutic treatment of systolic hypertension in the elderly. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 17: S28-S29
Abernathy Dr (1992) Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of amlodipine. Cardiology 80: 31–36
Leonetti G, Rupoli L, Chianca R, et al (1991) Acute, chronic and postwithdrawal antihypertensive and renal effects of amlodipine in hypertensive patients. J Hypertens 9: S394-S395
Ueda S, Meredith P, Hawie C, Elliott H. A comparative assessment of the duration of action of amlodipine and nifedipine GITS in normotensive subjects. Br J Clin Pharmacol (in press)
Cruickshank JM, McAinsh J (1992) Patient compliance on taking cardiovascular drug therapy. Acta Therapeutica 18: 53–60
Gatley MS (1968) To be taken as directed. J R Coll Gen Pract 16: 39
Cramer JA, Mattson RH, Prevey ML, et al (1989) How often is medication taken as prescribed? JAMA 261: 3273–3277
Lange Anderson K, Piatkowski W, Green KA, Ottmann W (1985) Working ability and exercise tolerance during treatment of mild hypertension. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 56: 41–47
Asphund J, Danielson M, Ohman P (1984) Patients compliance in hypertension — the importance of number of tablets. Br J Clin Pharmacol 17: 547–552
Addison DJ, Frewin DB, Penhall RK (1979) Compliance and beta-blocker therapy: a study of hypertension patients attending the cardiac and renal outpatient clinics at a large hospital. Current Therapeutics 20: 19–24
Moore MA (1988) Improving compliance with anti-hypertensive therapy. Am Fam Physician 37: 142–148
Sneddon PL, Farral DL (1989) Medication compliance in elderly patients. Pharm J 243 (6553): R18-R20
Guerrero D, Rudd P, Bryant-Kosling C, Middleton BE (1993) Antihypertensive Medication-Taking. Investigation of a simple regimen. Am J Hypertens 6: 586–592
Pullar T, Kurnar S, Tindall H, Feely M (1989) Time to stop counting the tablets. Clin Pharmacol Ther 46: 163–168
Rudd P, Byyny RL, Zachary V, et al (1989) The natural history of medication compliance in a drug trial: limitations of pill counts. Clin Pharmacol Ther 46: 169–176
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Additional information
Advisory Board: Pierre Block, Division of Cardiology, Universiteit Brussels, A.Z.-V.U.B. University Hospital Brussels, Belgium; Guy De Backer, Universiteit Gent, Gent; Jean-Paul Degaute, Hypertension Clinic, Hôpital Erasme, Université Libre de Bruxelles, Brussels, Belgium; Jean-Marie R. Detry, Division of Cardiology, University of Louvain, St. Luc University Hospital, Brussels, Belgium; Roland Six, Department of Internal Medicine, Vrije Universiteit Brussel, A.Z.-V.U.B., Brussels, Belgium.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Detry, J.M., Block, P., De Backer, G. et al. Patient compliance and therapeutic coverage: comparison of amlodipine and slow release nifedipine in the treatment of hypertension. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 47, 477–481 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00193697
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00193697