Abstract
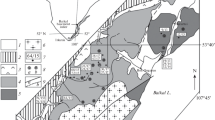
The Muratdagi region is rich in antimony deposits having the following common characteristics: post Miocene age, location on the down-thrown blocks next to normal faults, in the vicinity of active or fossil thermal springs, and in contact with carbonate rocks. The isotopic composition of — 7‰. SMOW of the mineralizing fluid calculated from the measured ° 18O of quartz and the fluid inclusion microthermometry, is indicative of meteoric water origin. The ° 13C of the inclusion CO2 of — 19.1 to — 25.4‰ PDB is indicative of interaction with organic material-graphite. The ° 34S of stibnite — 3.6 to — 0.7‰ is, in view of the mineral assemblage, indicative of magmatic origin of the sulphur. A tightly confined set of structural, lithological, hydrological and geochemical features define a sequence of geochemical processes; formation of acid and reducing fluid, leaching and transport of antimony complexes and precipitation of stibnite within defined lithological units. The set of processes seems to have taken place within a space of 5000 m lateral and 1000 m vertical extension.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aral, H. (1989) Antimony mineralization in the Northern Muratdagi (western Turkey). Econ. Geol. 84:780–787
Bingol, E. (1977) The geology and petrology of Muratdagi area (in Turkish). Bull Geo. Soc. Turkey 20/2:13–67
Clayton, R.N., Mayeda, T.K. (1963) The use of bromine pentafluoride in the extraction of oxygen from oxides and silicates for isotope analysis: Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 27:43–52
Deines, P. (1980) The isotopic composition of reduced organic carbon. In: Fritz, P., Fontes, J.C. (eds.) Handbook of environmental isotope geochemistry, vol 1. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 329–406
Diu, Y., Saukov, A.A. (1961) Physicochemical factors in the genesis of antimony deposits. Geochemistry 6:510–516
Friedman, I., O'Neil, J.M. (1977) Compilation of stable isotope fractionation factors of geochemical interest. Data of geochemistry, 6th edn. US Geol. Surv. Prof. Pap. 440-KK,
Gokçe, A. (1986) Geology of the Cebrail (Gediz-Kuthaya) Antimony deposit. Bull. of the Faculty of Engineering, Cumhuriyet Univ. Serie A, Earth Sci. 3/1:27–35
Gokçe, A. (1987) Geology of the antimony mineralization in the Muratdagi (gediz-KUTHAYA) region. Bull. of the Faculty of Engineering. Cumhuriyet Univ. Serie A, Earth Sci. 4/1:65–85
IAEA (1981) Stable isotope hydrology. Gat, J.R., Gonfiantini, R. (eds.) Technical Reports Series No 210. IAEA, Vienna
Ileri, S., Koksoy, M. (1977) Mechanisms of formation of antimony deposits in Turkey: Yerbilimeri (in Turkish). Publication of the Institute of Earth Sciences of Hacettepe Univ. 3:35–114
Manucharyaants, B.O., Naumov, V.B., Khodokovskiy, I.C., Verandinkiy, V.I. (1970) Physicochemical conditions of formation of hydrothermal deposits of antimony and mercury. Geokhimiya 11:1291–1301
Ohmoto, H., Rye, R.O. (1979) Isotopes of sulphur and Carbon in: Barnes, H.L., (ed.) Geochemistry of hydrothermal ore deposits, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York, pp 505–567
Robinson, B.W., Farrand, M.G. (1982) Sulphur isotopes and the origin of stibnite mineralisation in New England, Australia. Mineral. Deposita 7:161–174
Robinson, B.W., Kusakabe, M. (1975) Quantitative preparation of sulphur dioxide for 34S/32S analyses from sulphides by combustion with cuprous oxide. Analytical Chemistry 47:1179–1181
Shepherd, T.J., Rankin, A.H., Alderton, D.H.M. (1985) A practical guide to fluid inclusion studies. Blackie, London, 235 pp
Tunnel, G. (1963) Geochemical processes in the formation of mercury and antimony ores. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 28:1019–1037
Winkler, H.G.F. (1974) Petrogenesis of metamorphic rocks. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, 320 pp
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gokçe, A., Spiro, B. Stable isotope study of antimony deposits in the Muratdagi region, western Turkey. Mineral. Deposita 29, 361–365 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00191042
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00191042