Abstract
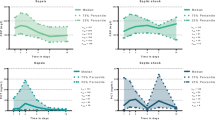
This prospective study of 35 multitraumatized intensive care unit patients requiring mechanical ventilation examined the relative utility of four biochemical parameters with a physiological scoring system for predicting lethal outcome. Levels of serum phospholipase A2 (PLA2), serum amyloid A (SAA), polymorphonuclear granulocyte elastase (PMN elastase), and C-reactive protein (CRP) were determined at short intervals during the patient's hospitalization. The first specimen was obtained at the time of admission, and subsequent specimens were drawn at 8 h intervals for the first 48 h and then twice daily until death or convalescence. Calculations of the APACHE II score used the most deranged variables during the first 24 h of admission to assess patient outcome. Additional calculations of the APACHE II score at the time of each blood draw served as an indicator of patient status. The results indicate that during the first 24 h after admission none of the four examined biochemical parameters gives reliable information about the outcome. The APACHE II score provided the earliest indicator of patient outcome (83% sensitivity, 65% specificity). PMN elastase provided useful information first at 32 h (83% sensitivity, 45% specificity) and better at 132 h (86% sensitivity, 86% specificity). CRP was of intermediate use in predicting outcome initially at 72 h (83% sensitivity, 50% specificity) and later at 132 h (86% sensitivity, 93% specificity). PLA2 and SAA were not useful as early indicators of lethal outcome.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ARDS:
-
adult respiratory distress syndrome
- APACHE II:
-
acute physiology and chronic health evaluation
- CRP:
-
C-reactive protein
- E-α1-PI:
-
elastase α1-proteinase inhibitor
- ICU:
-
intensive care unit
- IL:
-
interleukin
- PLA2 :
-
phospholipase A2
- PMN:
-
polymorpho nuclear granulocyte
- SAA:
-
serum amyloid A
- TNF-α:
-
tumor necrosis factor-α
References
Aufenanger J, Münscher G, Ensenauer R, Kattermann R (1993) Nephelometrische Bestimmung von Serum Amyloid A (SAA). GIT Labor-Medizin 11:367–368
Crowl RM, Stoller TJ, Conroy RR, Stoner CR (1991) Induction of phospholipase A2 gene expression in human hepatoma cells by mediators of the acute phase response. J Biol Chem 266:2647–2651
Dofferhoff ASM, Bom VJJ, de Vries-Hospers HG, van Ingen J, vd Meer J, Hazenberg BPC, Mulder POM, Weits J (1992) Patterns of cytokines, plasma endotoxin, plasminogen activator inhibitor, and acute-phase proteins during the treatment of severe sepsis in humans. Crit Care Med 20:185–192
Gosling P, Dickson GR (1992) Serum C-reactive protein in patients with serious trauma. Injury 23:483–486
Hafner G, Dreher M, Lütgehaus M, Ehrenthal W, Heubner A, Swars H, Prellwitz W (1991) Determination of human granulocyte elastase by the immunoactivation method on the Hitachi 717 automated analyser. Eur J Clin Chem Clin Biochem 29:179–183
Henderson AR (1993) Chemistry with confidence: should clinical chemistry require confidence intervals for analytical and other data? Clin Chem 39:929–935
Hoffmann GE, Neumann U (1989) Modified photometric method for the determination of phospholipase A activities. Klin Wochenschr 67:106–109
Jochum M, Fritz H, Nast-Kolb D, Inthorn D (1990) Granulozyten-Elastase als prognostischer Parameter. Dtsch Ärztebl87:B-1106-B-1110
Kisilevsky R (1991) Serum amyloid A (SAA), a protein without a function: some suggestions with reference to cholesterol metabolism. Med Hypotheses 35:337–341
Knaus WA, Draper EA, Wagner DP, Zimmerman JE (1985) APACHE II: a severity of disease classification system. Crit Care Med 13:818–829
Koeniger R, Hoffmann GE, Schmid TO (1989) Serum activities of phospholipase A in acute posttraumatic pulmonary insufficiency. Klin Wochenschr 67:212–216
Lalli E, Meliconi R, Conte R, Mancini A, Uguccioni M, Stefanini GF, Gasbarrini G (1992) Serum markers of immune activation and liver allograft rejection. Dig Dis Sci 37:1116–1120
Mozes G, Friedman N, Shainkin-Kestenbaum R (1989) Serum amyloid A: an extremely sensitive marker for intensity of tissue damage in trauma patients and indicator of acute response in various diseases. J Trauma 29:71–74
Nast-Kolb D, Jochum M, Waydhas C, Schweiberer L (1991) Die klinische Wertigkeit biochemischer Faktoren beim Polytrauma. Hefte Unfallheilkd 215:1–162
Nuytinck JKS, Goris RJA, Redl H, Schlag G, van Munster PJJ (1986) Posttraumatic complications and inflammatory mediators. Arch Surg 121:886–890
Ogawa M, Arakawa H, Yamashita S-I, Sakamoto K, Ikei S (1992) Postoperative elevations of serum interleukin 6 and group II phospholipase A2: group II phospholipase A2 in serum is an acute phase reactant. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol 75:109–115
Ohmann C, Groß-Weege W (1992) Scoring-Systeme auf der chirurgischen Intensivstation. Chirurg 63:1021–1028
Pruzanski W, Vadas P (1991) Phospholipase A2 — a mediator between proximal and distal effectors of inflammation. Immunol Today 12:143–146
Püttmann M, Scheel M, Ensenauer R, Kattermann R (1993) Automated determination of serum phospholipase A on a BM-Hitachi 911 analyzer. Ann Biol Clin 50:409
Rhee KJ, Baxt WG, Mackenzie JR, Willits NH, Burney RE, O'Malley RJ, Reid N, Schwabe D, Storer DL, Weber R (1990) APACHE II scoring in the injured patient. Crit Care Med 18:827–830
Saile R, Kabbaj O, Visvikis S, Steinmetz J, Steinmetz A, Férard G, Fruchart J-C, Metais P (1990) Variations in apolipoproteins serum amyloid A, A-I, A-II, and C-III in severely head- injured patients. J Clin Chem Clin Biochem 28:519–525
Schild A, Pscheidl E, v Hintzenstern U (1989) Phospholipase A — a parameter of sepsis? Klin Wochenschr 67:207–211
Stahl WM (1987) Acute phase protein response to tissue injury. Crit Care Med 15:545–550
Teasdale G, Jennett B (1974) Assessment of coma and impaired consciousness — a practical scale. Lancet 13:81–83
Teschner M, Schaefer RM, Penzel W, Heidland A (1987) Serum Phospholipase A-Aktivität als prognostischer Indikator bei septischen Patienten. Dtsch Ges Klin Chemie Mitteilungen 5:232–235
Thomas L, Messinger M (1993) Pathobiochemie und Labordiagnostik der Entzündung. Lab Med 17:179–194
Trentz O, Oestern H-J, Hempelmann G, Kolbow H, Sturm J, Trentz OA, Tscherne H (1978) Kriterien für die Operabilität von Polytraumatisierten. Unfallheilk 81:451–458
Waydhas C, Nast-Kolb D, Duswald K-H, Lehnert P, Schweiberer L (1989) Prognostic value of serum phospholipase A in the multitraumatized patient. Klin Wochenschr 67:203–206
Waydhas C, Nast-Kolb D, Trupka A, Kerim-Sade C, Kanz G, Zoller J, Schweiberer L (1992) Traumascores: Reproduzierbarkeit und Zuverlässigkeit. Unfallchir 95:67–70
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ensenauer, R., Püttmann, M., Quintel, M. et al. Comparison of serum phospholipase A2, polymorphonuclear granulocyte elastase, C-reactive protein and serum amyloid A with the APACHE II score in the prognosis of multiple injured patients. Clin Investig 72, 843–849 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00190738
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00190738