Abstract
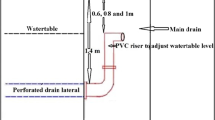
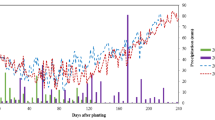
Experiments were conducted during the winter seasons of 1983–1984 and 1984–1985 to identify suitable irrigation regimes s for wheat grown after rice in soils with naturally fluctuating shallow water table (SWT) at a depth of 0.4 to 0.9 m and medium water table (MWT) at a depth of 0.8 to 1.3 m. Based on physiological stages, the crop was subjected to six irrigation regimes viz., rainfed (I0); irrigation only at crown root initiation (I1); at only crown root initiation and milk (I2); at crown root initiation, maximum tillering and milk (I3); at crown root initiation, maximum tillering, flowering and milk (I4); and at crown root initiation, maximum tillering, flowering milk and dough (I5). Tube-well water with an EC <0.4 dsm−1 was used for irrigation. Based on 166 mm effective precipitation during the cropping season, 1983–1984 was designated as a wet year and 1984–1985 with 51 mm as a dry year. The change in profile soil water content ΔW (depletion) in the wet year was less (23%) under SWT and 10% under MWT as compared to the dry year. The ground water contribution (GWC) to evapotranspiration (ET) was 58% under SWT and 42% under MWT conditions in both the years. The GWC in the wet year was 20% under SWT and 23% under MWT. Of the total net water use (NWU), about 85% was ET and 15% drainage losses. The NWU was highest (641 and 586 mm) in I5 under SWT and MWT conditions, respectively, but not the yield (5069 kg ha−1). Compared to I5, NWU in I2 treatment decreased by 10% in the wet and 25% in the dry year. A similar trend was observed in the I3 treatment under MWT condition. However, there was no statistically significant difference between yields of the I1 to I5 treatments of either water table depth during the wet year. This was also true during the dry year for the I2 to I5 treatments. Under SWT, in I2, the grain yield was 5130 kg ha−1 and under I3 regime, 5200 kg ha−1. Under MWT in I3, the yield was 5188 kg ha−1 and under I4 regime, 5218 kg ha−1. Thus it appears that in the Tarai region where the water table remains shallow (<0.9 m) and medium (<1.3 m) for most of the wheat growing season applications of more than 120 and 180 mm irrigation under SWT and MWT conditions, respectively were not necessary. Irrigation given only at crown root initiation and milk stages under shallow water table conditions, and at crown root initiation, maximum tillering and milk stages under medium water table conditions, appears to be as effective as frequent irrigations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrawal PK, Singh AK, Chaturvedi GS, Singh SK (1986) Performance of wheat and triticale cultivars in a variable soil-water environment. II. Evapotranspiration, water use efficiency, harvest index and grain yield. Field Crops Res 13:301–315
Bohm W (1976) In situ estimation of root length at natural soil profile. J Agric Sci 87:365–368
Bohm W (1979) Methods of studying root systems. In: Ecological Studies, No 33. Springer, Berlin, pp 188
Chaudhary TN, Bhatnagar VK (1980) Wheat root distribution, water extraction pattern and grain yield as influenced by time and rate of irrigation. Agric Water Manage 3:115–124
Chaudhary TN, Bhatnagar VK, Prihar SS (1974) Growth response of crops to depth and salinity of ground water and soil submergence. I. Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Agron J 66:32–35
Chaudhary PN, Kumar V (1980) The sensitivity of growth and yield of dwarf wheat to water stress at three growth stages. Irrig Sci 1:223–227
Day AD, Intalap S (1970) Some effect of soil moisture stress on the growth of wheat. Agron J 62:27–32
Hillel D, Krentos VD, Stylianou Y (1972) Procedure and test of an internal drainage method for measuring soil hydraulic characteristics in situ. Soil Sci 114:395–400
Joshi NL (1976) Effect of various management practices in rice on the performance of rice and succeeding wheat. PhD Thesis, GB Pant University of Agric and Tech, Pantnagar, pp 127
Kessler J (1974) Determining hydraulic conductivity of soil. In: Anonymous (editor), Drainage principles and appliction. The Netherlands, Vol III (24)
Mishra RK, Chaudhary TN (1985) Effect of limited water input on root growth, water use and grain yield of wheat. Field Crops Res 10:125–134
Mishra HS, Rathore TR, Pant RC (1990) Effect of intermittent irrigation on ground water table contribution, irrigation requirement and yield of rice in Mollisols of Tarai region. Agric Water Manage 18:231–241
Mishra HS, Rathore TR, Pant RC (1991) Effect of varying water regimes on soil physical properties and yield of rice in Mollisols of Tarai region. Agric Water Manage 20:71–80
Mishra RD, Sharma KC, Wright BC, Singh UP (1969) Critical stages in irrigation requirement of wheat variety “Lerma Rojo”. Indian J Agric Sci 39:898–906
Saini BC, Ghildyal BP (1978) Seasonal water use by winter wheat grown under shallow water table conditions. Agric Water Manage 1:263–276
Schneider AD, Musick JT, Dusak DA (1969) Efficient irrigation with limited water. Trans Am Soc Agric Engg 12:23–82
Sharma DK, Kumar A, Singh KN (1990) Effect of irrigation scheduling on growth, yield and evapotranspiration of wheat in sodic soils. Agric Water Manage 18:267–276
Tripathi RP, Mishra RK (1986) Wheat root growth and seasonal water use as affected by irrigation under shallow water table conditions. Plant and Soil 92:181–188
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mishra, H.S., Rathore, T.R. & Tomar, V.S. Water use efficiency of irrigated wheat in the Tarai region of India. Irrig Sci 16, 75–80 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00189163
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00189163