Summary
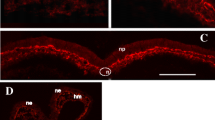
Changes in the distribution of extracellular matrix components have been investigated immunohistochemically during neural crest development in the rat. Inside the ectodermal epithelium basal lamina components are formed resulting in a separation of neurectoderm and epidermal ectoderm. Within the presumptive neural crest area fibronectin, hyaluronan and chondroitin sulphate become apparent. Upon subsequent neural crest migration the basal lamina becomes disrupted. As the neural crest cells take part in mesectoderm formation, fragments of the basal lamina remain attached to their surface, as is demonstrated with antibodies against laminin and collagen type IV. The extracellular matrix is therefore active both in the separation of neuroectoderm from epidermal ectoderm and in mesectoderm formation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson CB, Meier S (1982) Effect of hyaluronidase treatment on the distribution of cranial neural crest cells in the chick embryo. J Exp Zool 221:329–335
Baroffio A, Dupin E, LeDouarin NM (1989) A clonal analysis of the differentiation of neural crest cells. Cell Diff Dev 27 [Suppl]:105
Bertrand P, Delpech B (1985) Interaction of hyaluronectin with hyaluronic acid oligosaccharides. J Neurochem 45:434–439
Bilozur ME, Hay ED (1988) Neural crest migration in 3D extracellular matrix utilizes laminin, fibronectin, or collagen. Dev Biol 125:19–33
Boucaut JC, Darribere T, Poole TJ, Aoyama H, Yamada KM, Thiery JP (1984) Biologically active synthetic peptides as probes of embryonic development: a competitive peptide inhibitor of fibronectin function inhibits gastrulation in amphibian embryos and neural cest migration in avian embryos. J Cell Biol 99:1822–1830
Bronner-Fraser M (1986) An antibody to a receptor for fibronectin and laminin perturbs cranial neural crest development in vivo. Dev Biol 117:528–536
Bronner-Fraser M, Callier T (1988) A monoclonal antibody against a laminin-heparan sulphate proteoglycan complex perturbs cranial neural crest migration in vivo. J Cell Biol 106:1321–1330
Darribere T, Yamada KM, Johnson KE, Boucaut JC (1988) The 140-kDa fibronectin receptor complex is required for mesodermal cell adhesion during gastrulation in the amphibian Pleuradeles waltlii. Dev Biol 126:182–194
Delpech A, Delpech B, Girard N, Bertrand P, Chauzy C (1987) Hyaluronectin and hyaluronic acid during the development of rat brain cortex. In: Wolff JR et al. (eds) “Mesenchymal-epithelial interactions in neural development”. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg. Nato ASI Series, vol H5, pp 77–87
Derby MA (1978) The major derivations of trunk neural crest cells encounter extracellular environments differing in glycoaminoglycan preceding their differentiation. Dev Biol 66:321–336
Duband JL, Thiery JP (1982a) Distribution of fibronectin in the early phase of avian cephalic neural crest cell migration. Dev Biol 93:308–323
Duband JL, Thiery JP (1982b) Appearance and distribution of fibronectin during chick embryo gastrulation and neurulation. Dev Biol 94:337–350
Erickson CA (1987) Behavior of neural crest cells on embryonic basal laminae. Dev Biol 120:38–49
Erickson CA, Weston JA (1983) An SEM analysis of neural crest migration in the mouse. J Embryol Exp Morphol 74:97–118
Fisher M, Solursh M (1977) Glycosaminoglycan localization and role in maintenance of tissue spaces in the early chick embryo. J Embryol Exp Morphol 42:195–207
Fisher M, Solursh M (1979) The influence of the substratum on the mesenchyme spreading in vitro. Exp Cell Res 123:1–14
Girard N, Delpech A, Delpech B (1986) Characterization of hyaluronic acid on tissue sections with hyaluronectin. J Histochem Cytochem 34:529–541
Hay ED (1984) Cell-matrix interaction in the embryo: cell shape, cell surface, cell skeletons, and their role in differentiation. In: Revel JP (ed) The role of extracellular matrix in development. Alan R Liss, New York, pp 1–31
Heath L, Breaden A, Wild A, Thorogood P (1989) Monoclonal antibodies against premigratory neural crest. Cell Diff Dev 27 [Suppl]:202
Laurie GW, Leblond CP, Martin GR (1982) Localization of type IV collagen, laminin, heparan sulphate proteoglycan and fibronectin to the basal lamina of basement membranes. J Cell Biol 95:340–344
Leivo I, Vaheri A, Timpl R, Wartiovaara J (1980) Appearance and distribution of collagens and laminin in the early mouse embryo. Dev Biol 76:108–114
Luckenbill-Edds L, Carrington JL (1988) Effect of hyaluronic acid on the emergence of neural crest cells from the neural tube of the quail, Coturnix coturnix japonica. Cell Tissue Res 252:573–579
Martins-Green M (1988) Origin of the dorsal surface of the neural tube by progressive delamination of epidermal ectoderm and neuroepithelium: implication for neurulation and neural tube defects. Development 103:687–706
Martins-Green M, Erickson CA (1986) Development of neural tube basal lamina during neural crest emigration in the trunk of the mouse embryo. JEEM 98:219–236
Martins-Green M, Erickson CA (1987) Basal lamina is not a barrier to neural crest cell emigration: documentation by TEM and by immunofluorescent and immunogold labelling. Development 101:517–533
Morriss GM, Solursh M (1978) Regional differences in mesenchymal cell morphology and glycosaminoglycans in early neuralfold stage rat embryos. J Embryol Exp Morphol 46:37–52
Newgreen DF (1982) Adhesion to extracellular materials by neural crest cells at the stage of initial migration. Cell Tissue Res 227:297–317
Newgreen DF (1985) Control of the timing of commencement of migration of embryonic neural crest cells. Exp Biol Med 10:209–221
Newgreen DF, Gibbins IL, Sauter J, Wallenfels B, Wuetz R (1982) Ultrastructural and tissue-culture studies on the role of fibronectin, collagen and glycosaminoglycans in the migration of neural crest cells in the fowl embryo. Cell Tissue Res 221:521–549
Newgreen DF, Scheel M, Kastner V (1986) Morphogenesis of sclerotome and neural crest in avian embryos. In vivo and in vitro studies of notochordal extracellular material. Cell Tissue Res 244:299–313
Newgreen DF, Thiery JP (1980) Fibronectin in early avian embryos: synthesis and distribution along the migration pathways of neural crest cells. Cell Tissue Res 211:269–291
Nichols DH (1981) Neural crest formation of the mouse embryo as observed using a new histological technique. J Embryol Exp Morphol 64:105–120
Nichols DH (1986) Mesenchymal formation from the trigeminal placodes of the mouse embryo. Am J Anat 176:19–31
Pintar JE (1978) Distribution and synthesis of glycosaminoglycans during quail neural crest morphogenesis. Dev Biol 67:444–464
Poelmann RE (1980) Differential mitosis and degeneration patterns in relation to the alterations in the shape of the embryonic ectoderm of early post-implantion mouse embryos. J Embryol Exp Morphol 55:33–51
Revel JP, Brown SS (1976) Cell junctions in development, with particular reference to the neural tube. In: Cold Spring Harbor Symp Quant Biol, vol XL, pp 443–455
Rovasio RA, Delouvee A, Yamada KM, Timpl R, Thiery JP (1983) Neural crest cell migration: requirements for exogenous fibronectin and high cell density. J Cell Biol 96:462–473
Smits-Van Prooije AE, Vermeij-Keers C, Dubbeldam JA, Mentink MMT, Poelmann RE (1987) The formation of mesoderm and mesectoderm in presomite stage rat embryos cultured in vitro, using WGA-Au as a marker. Anat Embryol 176:71–77
Smits-Van Prooije AE, Vermeij-Keers C, Poelmann RE, Mentink MMT, Dubbeldam JA (1988) The formation of mesoderm and mesecto-derm in 5- to 41-somite rat embryos cultured in vitro, using WGA-AU as a marker. Anat Embryol 177:245–256
Sternberg J, Kimber SJ (1986) Distribution of fibronectin, laminin and entactin in the environment of migrating neural crest cells in early mouse embryos. J Embryol Exp Morphol 91:267–282
Tan SS, Morriss-Kay GM (1986) Analysis of cranial neural crest cell migration and early fates in postimplantation rat chimaeras. J Embryol Exp Morphol 98:21–58
Thiery JP, Duband JL (1986) Role of tissue environment and fibronectin in the patterning of neural crest derivatives. Trends in Neuroscience 565–570
Thiery JP, Duband JL, Delouvee A (1982) Pathways and mechanisms of avian trunk neural crest cell migration and localization. Dev Biol 93:324–343
Timpl R, Rohde H, Robey PG, Rennard SI, Foidart JM, Martin GR (1979) Laminin — a glycoprotein from basement membranes. J Biol Chem 254:9933–9937
Tosney KW (1978) The early migration of neural crest cells in the trunk region of the avian embryo: an electron microscopic study. Dev Biol 62:317–333
Tosney KW (1982) The segregation and early migration of cranial neural crest cells in the avian embryo. Dev Biol 89:13–24
Toole BP, Underhill CB, Mikuni-Takagaki Y, Orkin RW (1980) Hyaluronate in morphogenesis. In: Pratt R, Christiansen M (ed) Current research trends in prenatal craniofacial development. Elsevier-North Holland, Amsterdam
Tucker RP (1986) The role of glycosaminoglycans in anuran pigment cell migration. J Embryol Exp Morphol 92:145–164
Verwoerd CDA, VanOostrom CG (1979) Cephalic neural crest and placodes. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol 58:1–74
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Poelmann, R.E., Gittenberger-de Groot, A.C., Mentink, M.M.T. et al. The extracellular matrix during neural crest formation and migration in rat embryos. Anat Embryol 182, 29–39 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00187525
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00187525