Abstract
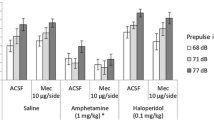
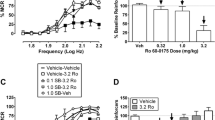
The ability of serotonin2 (5-HT2) antagonists to block the excitatory effects of mescaline on the acoustic startle reflex were analyzed. Mescaline (20 mg/kg) caused a consistent increase in the amplitude of the acoustic startle reflex. This effect was blocked in a dose-related fashion by the 5-HT2 antagonist ritanserin (ED50 dose=0.25 mg/kg IP). In contrast, even a high dose of ritanserin (2.0 mg/kg) did not block the excitatory effects of amphetamine on startle. Other 5-HT2 antagonists (ketanserin, cinanserin, LY 53857) also blocked mescaline's effect, whereas the 5-HT1 antagonist pindolol (5 mg/kg) did not. These results support the hypothesis that the behavioral effects of hallucinogens are mediated by agonist actions at 5-HT2 receptors.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams LM, Geyer MA (1981) Effects of 6-hydroxydopamine lesions of locus coeruleus on startle in rats. Psychopharmacology 73:394–398
Aghajanian GK (1980) Mescaline and LSD facilitate the activation of locus coeruleus neurons by peripheral stimuli. Brain Res 186:492–498
Aghajanian GK, Haigler HJ (1974) Mode of action of LSD on serotonergic neurons: In: Advances in biochemical psychopharmacology. Raven, New York, pp 167–177
Aghajanian GK, Haigler HJ, Bloom FE (1972) Lysergic acid diethylamide and serotonin: direct actions on serotonin-containing neurons in rat brain. Life Sci 2:615–622
Aghajanian GK, Foote WE, Sheard MH (1968) Lysergic acid diethylamide: sensitive neuronal units in the midbrain raphe. Science 161:706–708
Aghajanian GK, Foote WE, Sheard MH (1969) Action of psychotogenic drugs on single midbrain raphe neurons. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 171:178–187
Aghajanian GK, Sprouse JC, Rasmussen K (1987) Physiology of the midbrain serotonin system. In: Psychopharmacology, the third generation of progress. Raven, New York (in press)
Appel JB, White FJ, Holohean AM (1982) Analyzing mechanism(s) of hallucinogenic drug action with drug discrimination procedures. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 6:529–536
Astrachan DI, Davis M (1981) Spinal modulation of the acoustic startle response: the role of norepinephrine, serotonin and dopamine. Brain Res 206:223–228
Astrachan DI, Davis M, Gallager DW (1983) Behavior and binding: correlations between α1-adrenergic stimulation of acoustic startle and α1-adrenoceptor occupancy and number in rat lumbar spinal cord. Brain Res 260:81–90
Balestriere A, Fontanari D (1959) Acquired and cross tolerance to mescaline, LSD-25 and BOL-148. Arch Gen Psychiatry 1:279
Bennett JP, Snyder SH (1976) Serotonin and lysergic acid diethylamide binding in rat brain membranes: relationship to postsynaptic serotonin receptors. Mol Pharmacol 12:373
Braff DL, Geyer MA (1980) Acute and chronic LSD effects on rat startle: data supporting an LSD — rat model of schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 15:909–916
Browne RG, Ho BT (1975) Role of serotonin in the discriminative stimulus properties of mescaline. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 3:429–435
Cassella JV, Davis M (1986) The design and calibration of a startle measurement system. Physiol Behav 36:377–383
Cholden LS, Kurland A, Savage C (1955) Clinical reactions and tolerance to LSD in chronic schizophrenia. J Nerv Ment Dis 122:211–221
Cohen ML, Fuller RW, Kurz KD (1983) LY53857, a selective and potent serotonergic (5-HT2) receptor antagonist, does not lower blood pressure in the spontaneously hypertensive rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 227:327–332
Colpaert FC, Janssen PAJ (1983) A characterization of LSD-antagonist effects of pirenerone in the rat. Neuropharmacology 22:1001–1005
Colpaert FC, Meert TF, Niemegeers CJE, Janssen PAJ (1985) Behavioral and 5-HT antagonist effects of ritanserin: a pure and selective antagonist of LSD discrimination in rat. Psychopharmacology 86:45–54
Commissaris RL, Semeyn DR, Moore KE, Rech RH (1980a) The effects of 2,5-dimethoxy-4-methylamphetamine (DOM) on operant behavior: Interactions with other neuroactive agents. Commun Psychopharmacol 4:393–404
Commissaris RL, Lyness WH, Moore KE, Rech RH (1980b) Enhancement of the behavioral effects of 2,3-dimethoxy-4-methylamphetamine (DOM) by pretreatment with p-chlorophenylalanine. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 13:605–608
Davis M, Sheard MH (1974a) Effects of lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD) on habituation and sensitization of the startle response in the rat. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 2:675–683
Davis M, Sheard MH (1974b) Biphasic dose-response effects of N-N-dimethyltryptamine on the rat startle reflex. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 2:827–829
Davis M, Wagner AR (1969) Habituation of startle response under incremental sequence of stimulus intensities. J Comp Physiol Psychol 67:486–492
Davis M, Walters JK (1977) Psilocybin: Biphasic dose-response effects on the acoustic startle reflex in the rat. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 6:427–431
Davis M, Svensson TH, Aghajanian GK (1975) Effects of d-and l-amphetamine on habituation and sensitization of the acoustic startle response in rats. Psychopharmacologia 43:1–11
Davis M, Astrachan DI, Gendelman PM, Gendelman DS (1980a) 5-Methoxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamine: Spinal cord and brainstem mediation of excitatory effects on acoustic startle. Psychopharmacology 70:123–130
Davis M, Astrachan DI, Kass E (1980b) Excitatory and inhibitory effects of serotonin on sensorimotor reactivity measured with acoustic. Science 209:521–523
Davis M, Gendelman DS, Tischler MD, Gendelman PM (1982) A primary acoustic startle circuit: lesion and stimulation studies. J Neurosci 2:791–805
Davis M, Cassella JV, Wrean WH, Kehne JH (1986) Serotonin receptor subtype agonists: differential effects on sensorimotor reactivity measured with acoustic startle. Psychopharmacol Bull 22:837–843
Dwoskin LP, Sparber SB (1983) Behaviorally inactive doses of mianserin antagonize the supressant effect of lysergic acid diethylamide on a fixed-ratio operant. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 225:77–85
Engel G, Gothert M, Hoyer D, Schlicker E, Hillenbrand K (1986) Identity of inhibitory presynaptic 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) autoreceptors in the rat brain cortex with 5-HT1B binding sites. Naunyn-Schmiedberg's Arch Pharmacol 332:1–7
Freedman DX (1961) Effects of LSD-25 on brain serotonin. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 134:160–166
Gallager DW, Aghajanian GK (1975) Effects of chlorimipramine and lysergic acid diethylamide on efflux of precursor-formed 3H-serotonin: Correlations with serotonergic impulse flow. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 193:785–795
Geyer MA, Petersen LR, Rose GJ, Horwitt DD, Light RK, Adams LM, Zook JA, Hawkins RL, Mandell AJ (1978) The effects of lysergic acid diethylamide and mescaline-derived hallucinogens on sensory-integrative function: Tactile startle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 207:837–847
Geyer MA, Rose GJ, Petersen LR (1979) Mescaline increases startle responding equally in normal and raphe-lesioned rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 10:293–298
Glennon RA, Hauck AE (1985) Mechanistic studies on DOM as a discriminative stimulus. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 23:937–941
Glennon RA, Young R, Jacyno JM, Slusher M, Rosecrans JA (1983a) DOM-stimulus generalization to LSD and other hallucinogenic indolealkylamines. Eur J Pharmacol 86:453–459
Glennon RA, Young R, Rosecrans JA (1983b) Antagonism of the effects of the hallucinogen DOM and the purported 5-HT agonist quipazine by 5-HT2 antagonists. Eur J Pharmacol 91:189–196
Glennon RA, Titeler M, McKenney JD (1984) Evidence for 5-HT2 involvement in the mechanism of action of hallucinogenic agents. Life Sci 34:2505–2511
Haigler HJ, Aghajanian GK (1973) Mescaline and LSD: direct and indirect effects on serotonin-containing neurons in brain. Eur J Pharmacol 21:53–60
Haigler HJ, Aghajanian GK (1974a) Lysergic acid diethylamide and serotonin: A comparison of effects on serotonergic neurons and neurons receiving a serotonergic input. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 188:688–699
Haigler HJ, Aghajanian GK (1974b) Peripheral serotonin antagonists: Failure to antagonize serotonin in brain areas receiving a prominent serotonergic input. J Neurol Transm 35:257–273
Heym J, Rasmussen K, Jacobs BL (1984) Some behavioral effects of hallucinogens are mediated by a postsynaptic serotonergic action: evidence from single unit studies in freely moving cats. Eur J Pharmacol 101:57–68
Isbel H, Belleville RE, Fraser HF, Wikler A, Logan CR (1956) Studies on lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD-25). I. Effects in former morphine addicts and development of tolerance during chronic intoxication. Arch Neurol Psychiatry 76:468–478
Kehne JH, Davis M (1985) Central noradrenergic involvement in yohimbine excitation of acoustic startle: effects of DSP4 and 6-OHDA. Brain Res 330:31–41
Kuhn DM, White FJ, Appel JB (1978) The discriminative stimulus properties of LSD: Mechanisms of action. Neuropharmacology 17:257–263
Laduron PM, Janssen FM, Leysen JE (1982) In vivo binding of [3H]ketanserin on serotonin S2-receptors in rat brain. Eur J Pharmacol 81:43–48
Lee EHY, Geyer MA (1980) Persistent effects of chronic administration of LSD on intracellular serotonin content in rat mid-brain. Neuropharmacology 19:1005–1007
Leysen JE, Niemegeers JE, VanNueten JM, Laduron PM (1982) [3H]Ketanserin (R 41 468), a selective 3H-ligand for serotonin2 receptor binding sites. Mol Pharmacol 21:301–314
Leysen JE, Gommeren W, VanGompel P, Wynants J, Janssen PFM, Laduron PM (1985) Receptor-binding properties in vitro and in vivo of ritanserin a very potent and long acting serotonin-S2 antagonist. Mol Pharmacol 27:600–611
McCall RB, Aghajanian GK (1979) Serotonergic facilitation of facial motoneuron excitation. Brain Res 169:11–27
McCall RB, Aghajanian GK (1980) Hallucinogens potentiate responses to serotonin and norepinephrine in the facial motor nucleus. Life Sci 26:1149–1156
Miliaressis TE, St-Laurent J (1974) Effets de l'Amide de l'Acide Lysergique-25 sur la Réaction de Sursaut chez le rat. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 52:126–129
Mokler DJ, Commissaris RL, Warner MR, Rech RH (1983) Blockade of the behavioral effects of lysergic acid diethylamide, 2,5-dimethoxy-4-methylamphetamine, quipazine and lisuride by 5-hydroxytryptamine antagonists. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 227:557–562
Mokler DJ, Stoudt KW, Rech RH (1985) The 5-HT2 antagonist pirenperone reverses disruption of FR-40 by hallucinogenic drugs. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 22:677–682
Nielsen EB, Ginn SR, Cunningham KA, Appel JB (1985) Antagonism of the LSD cue by putative serotonin antagonists: Relationship to inhibition of in vivo [3H]spiroperidol binding. Behav Brain Res 16:171–176
Pazos A, Cortes R, Palacios M (1985) Quantitative autoradiographic mapping of serotonin receptors in the rat brain. II. Serotonin-2 receptors. Brain Res 346:231–249
Rasmussen K, Aghajanian GK (1986) Effect of hallucinogens on spontaneous and sensory-evoked locus coeruleus unit activity in the rat: Reversal by selective 5-HT2 antagonists. Brain Res 385:395–400
Rasmussen K, Glennon RA, Aghajanian GK (1986) Phenethylamine hallucinogens in the locus coeruleus: Potency of action correlates with rank order of 5-HT2 binding affinity. Eur J Pharmacol 132:79–82
Rogawski MA, Aghajanian GK (1979) Response of central monoaminergic neurons to lisuride: comparison with LSD. Life Sci 24:1289–1298
Rosecrans JA, Lovell RA, Freedman DX (1967) Effects of lysergic acid diethylamide on the metabolism of brain 5-hydroxytryptamine. Biochem Pharmacol 16:2011–2021
Shannon M, Battaglia G, Glennon RA, Titeler M (1984) 5-HT1 and 5-HT2 binding properties of derivatives of the hallucinogen 1-(2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-2-aminopropane (2,5-DMA). Eur J Pharmacol 102:23–29
Sietnieks A (1985) Involvement of 5-HT2 receptors in the LSD- and L-5-HTP-induced suppression of lordotic behavior in the female rat. J Neural Transm 61:65–80
Stoff DM, Wyatt RJ, Uretsky SH, Gillin JC (1976) para-Chlorophenylalanine potentiates facilitatory effects of mescaline on shuttlebox escape/avoidance in rats. Psychopharmacology 47:287–292
Tilson HA, Baker TG, Chamberlain JH, Marquis WJ, Rech RH (1975) Behavioral and neuropharmacological analysis of amphetamine and 2,5-dimethoxy-4-methylamphetamine in rats. Psychopharmacologia 44:229–239
Tricklebank MD, Forler C, Fozard JR (1984) The involvement of subtypes of 5-HT1 receptor and of catecholaminergic systems in the behavioural response to 8-hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino)-tetralin in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol 106:271–282
Trulson ME, Jacobs BL (1979) Dissociations between the effects of LSD on behavior and raphe unit activity in freely moving cats. Science 205:515–518
Trulson ME, Ross CA, Jacobs BL (1977) Lack of tolerance to the depression of raphe unit activity by lysergic acid diethylamide. Neuropharmacology 16:771–774
Trulson ME, Heym J, Jacobs BL (1981) Dissociations between the effects of hallucinogenic drugs on behavior and raphe unit activity in freely moving cats. Brain Res 215:275–293
White SR, Neuman SR (1980) Facilitation of spinal motoneuron excitability by 5-hydroxytryptamine and noradrenaline. Brain Res 185:1–9
Winter JC (1975) Blockade of the stimulus properties of mescaline by a serotonin antagonist. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther 214:250–253
Winter JC (1978) Stimulus properties of phenethylamine hallucinogens and lysergic acid diethylamide: the role of 5-hydroxytryptamine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 204:416–423
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Davis, M. Mescaline: excitatory effects on acoustic startle are blocked by serotonin2 antagonists. Psychopharmacology 93, 286–291 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00187244
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00187244