Abstract
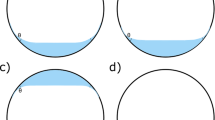
In order to ascertain the tamponade effect of air and silicone oil we examined the contact angles subtended by ex vivo human retina, Teflon and Perspex to find a suitable experimental material which would mimic the surface properties of the retina at a three-phase interface. Using the captive bubble technique to measure the contact angle, it was found that air subtended a larger contact angle (38.8°) with the retina than did silicone oil (18.2°). On coating the Perspex surface with protein (PCP), it was observed that the surface properties were modified such that PCP subtended contact angles with air (43.0°) and silicone oil (16.4°) similar to those subtended by ex vivo human retina. Using PCP as an experimental material that mimics ex vivo human retina, spherical chambers were employed in order to examine qualitatively and to quantify the arc of contact obtained with air and silicone oil. It was found that air gave a greater arc of contact for the same percentage fill than silicone oil.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ando F, Miyake Y, Oshima K, Yamanaka A (1986) Temporary use of intraocular silicone oil in the treatment of complicated retinal detachment. Graefe's Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 224(1):32–33
Baier R (1982) Conditioning surfaces to suit the biomedical environment: recent progress. J Biomech Eng 104:257–271
Bonnet M, Santamaria E, Mouche J (1987) Intraoperative use of pure perfluoropropane gas in the management of proliferative vitreoretinopathy. Graefe's Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 225(4):299–302
Chang S, Lincoff H, Zimmerman NJ, Fuchs W (1989) Giant retinal tears. Surgical techniques and results using perfluorocarbon liquids. Arch Ophthalmol 107(5):761–766
Chang S, Reppucci V, Zimmerman NJ, Heinemann MH, Coleman DJ (1989) Perfluorocarbon liquids in the management of traumatic retinal detachments. Ophthalmology 96(6):785–791
De Juan E Jr, McCuen B, Tiedman J (1985) Intraocular tamponade and surface tension. Surv Ophthalmol 30:47–51
Eckardt C (1992) Treatment of complicated retinal detachment. Intraoperative use of perfluorodecalin. Ophthalmology 89(1):22–26
Fisher YL, Shakin JL, Slakter JS, Sorenson JA, Shafer DM (1988) Perfluoropropane gas, modified panretinal photocoagulation, and vitrectomy in the management of severe proliferative vitreoretinopathy. Arch Ophthalmol 106(9):1255–1260
Fleury J, Bonnet M (1989) C3F8 in the treatment of retinal detachment associated with vitreoretinal proliferation. J Fr Ophthalmol 12(2):89–94
Glaser BM (1988) Editorial: Silicone oil for proliferative vitreoretinopathy. Does it help or hinder? Arch Ophthalmol 106:323–324
Gonvers M (1985) Temporary silicone oil tamponade in the management of retinal detachment with proliferative vitreoretinopathy. Am J Ophthalmol 100:239–245
Grey RHB, Leaver PK (1977) Results of silicone oil injection in massive preretinal retraction. Trans Ophthalmol Soc UK 97:238–241
King RN, Andrade J, Ma SM (1985) Interfacial tensions at acrylic hydrogel-water interfaces. J Colloid Interface Sci 103:62–75
Kreiger AE, Lewis H (1992) Management of giant retinal tears without scleral buckling. Use of radical dissection of the vitreous base and perfluoro-octane and intraocular tamponade. Ophthalmology 99(4):491–497
Lincoff H, Coleman J, Kreissig I et al. (1983) The perfluorocarbon gases in the treatment of retinal detachment. Ophthalmology 90:546–551
Lopez R, Chang S (1992) Long-term results of vitrectomy and perfluoro-carbon gas for the treatment of severe proliferative vitreoretinopathy. Am J Ophthalmol 113(4):424–428
Parver LM, Lincoff H (1978) Mechanics of intraocular gas. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 17(1):77–79
Peterson J (1988) The physical and surgical aspects of silicone oil in the vitreous cavity. Graefe's Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 225:452–456
Scott JD (1975) Treatment of massive vitreous traction. Trans Ophthalmol Soc UK 95:429–432
Shackenraad JM, Arends J, Busscher HJ et al. (1989) Kinetics of cell spreading on protein precoated substrata: a study of interfacial aspects. Biomaterials 10(1):43–50
Silicone Oil Study Group (1985) Proliferative vitreoretinopathy. Am J Ophthalmol 99:593–599
Silicone Oil Study Group (1992) Report 2. Vitrectomy with silicone oil or perfluoropropane gas in eyes with severe proliferative vitreoretinopathy: results of a randomized clinical trial. Arch Ophthalmol 110(6):780–792
Valk P van der, van Pelt AWJ, Busscher HJ et al. (1983) Interaction of fibroblasts and polymer surfaces: relationship between surface free energy and fibroblast spreading. J Biomed Mater Res 17:807–817
Wiedemann P, Leinung C, Hilgers RD, Heimann K (1991) Daunomycin and silicone oil for the treatment of proliferative vitreoretinopathy. Graefe's Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 229(2):150–152
Williams DF (1992) Materials for ophthalmology. In: Williams DF (ed) Medical and dental materials. (Materials science and technology: a comprehensive treatment, vol 14) VCH, Weinheim, pp 415–429
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fawcett, I.M., Williams, R.L. & Wong, D. Contact angles of substances used for internal tamponade in retinal detachment surgery. Graefe's Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 232, 438–444 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00186587
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00186587