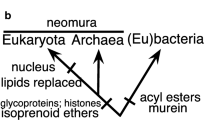
Summary
Phylogenetic analyses of ribosomal RNA sequences have played an important role in the study of early evolution of life. However, Loomis and Smith suggested that the ribosomal RNA tree is sometimes misleading—especially when G+C content differs widely among lineages—and that a protein tree from amino acid sequences may be more reliable. In this study, we analyzed amino acid sequence data of elongation factor-1α by a maximum likelihood method to clarify branching orders in the early evolution of eukaryotes. Contrary to Sogin et al.'s tree of small-subunit ribosomal RNA, a protozoan species, Entamoeba histolytica, that lacks mitochondria was shown to have diverged from the line leading to eukaryotes with mitochondria before the latter separated into several kingdoms. This indicates that Entamoeba is a living relic of the earliest phase of eukaryotic evolution before the symbiosis of protomitochondria occurred. Furthermore, this suggests that, among eukaryotic kingdoms with mitochondria, Fungi is the closest relative of Animalia, and that a cellular slime mold, Dictyostelium discoideum, had not diverged from the line leading to Plantae-Fungi-Animalia before these three kingdoms separated.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adachi J, Hasegawa M (1992) Computer science monographs, No. 27, MOLPHY: Programs for molecular phylogenetics I—PROTML: maximum likelihood inference of protein phylogeny. Institute of Statistical Mathematics, Tokyo
Alarcon CM, Donelson JE (1991) Translational elongation factor 1α (EF-1α) of Onchocerca volvulus. Mol Biochem Parasitol 48:105–108
Auer J, Spicker G, Böck A (1990) Nucleotide sequence of the gene for the translation elongation factor 1α from the extreme thermophilic archaebacterium Thermococcus celer. Nucleic Acids Res 18:3989–3989
Baldacci G, Guinet F, Tillit J, Zaccai G, de Recondo AM (1990) Functional implications related to the gene structure of the elongation factor EF-Tu from Halobacterium marismortui. Nucleic Acids Res 18:507–511
Cavalier-Smith T (1987) Eukaryotes with no mitochondria. Nature 326:332–333
Cavalier-Smith T (1991) The evolution of cells. In: Osawa S, Honjo T (eds) Evolution of life: fossils, molecules, and culture. Springer-Verlag, Tokyo, pp 271–304
Dayhoff MO, Schwartz RM, Orcutt BC (1978) A model of evolutionary change in proteins. In: Dayhoff MO (ed) Atlas of protein sequence and structure, vol 5, suppl 3. National Biomedical Research Foundation, Washington DC, pp 345–352
De Meester F, Bracha R, Huber M, Keren Z, Rozenblatt S, Mirelman D (1991) Cloning and characterization of an unusual elongation factor-1α cDNA from Entamoeba histolytica. Mol Biochem Parasitol 44:23–32
Douglas SE, Murphy CA, Spencer DF, Gray MW (1991) Cryptomonad algae are evolutionary chimaeras of two phylogenetically distinct unicellular eukaryotes. Nature 350:148–151
Felsenstein J (1978a) The number of evolutionary trees. Syst Zool 27:27–33
Felsenstein J (1978b) Cases in which parsimony and compatibility methods will be positively misleading. Syst Zool 27:401–410
Felsenstein J (1981) Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: a maximum likelihood approach. J Mol Evol 17:368–376
Fukami-Kobayashi K, Tateno Y (1991) Robustness of maximum likelihood tree estimation against different patterns of base substitutions. J Mol Evol 32:79–91
Gouy M, Li W-H (1989) Molecular phylogeny of the kingdoms Animalia, Plantae, and Fungi. Mol Biol Evol 6:109–122
Hasegawa M, Cao Y, Adachi J, Yano T (1992) Rodent polyphyly? Nature 355:595
Hasegawa M, Fujiwara M (1993) Relative efficiencies of the maximum likelihood, maximum parsimony, and neighbor joining methods for estimating protein phylogeny. Mol Phyl Evol (in press)
Hasegawa M, Iida Y, Yano T, Takaiwa F, Iwabuchi M (1985) Phylogenetic relationships among eukaryotic kingdoms inferred from ribosomal RNA sequences. J Mol Evol 22:32–38
Hasegawa M, Kishino H, Hayasaka K, Horai S (1990) Mitochondrial DNA evolution in primates: transition rate has been extremely low in lemur. J Mol Evol 31:113–121
Hasegawa M, Kishino H, Saitou N (1991) On the maximum like-lihood method in molecular phylogenetics. J Mol Evol 32: 443–445
Hayashi Y, Urade R, Utsumi S, Kito M (1989) Anchoring of peptide elongation factor EF-1α by phosphatidylinositol at the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. J Biochem 106:560–563
Hendriks L, De Baere R, Van de Peer Y, Neefs J, Goris A (1991) The evolutionary position of rhodophyte Porphyra umbilicalis and the basidiomycete Leucosporidium scottii among other eukaryotes as deduced from complete sequences of small ribosomal subunit RNA. J Mol Evol 32:167–177
Herzog M, Maroteaux L (1986) Dinoflagellate 17S rRNA sequence inferred from the gene sequence: evolutionary implications. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:8644–8648
Hovemann B, Richer S (1988) Two genes encode related cytoplasmic elongation factors 1-α (EF-1) in Drosophila melanogaster with continuous and stage specific expression. Nucleic Acids Res 16:3175–3194
Iwabe N, Kuma K, Hasegawa M, Osawa S, Miyata T (1989) Evolutionary relationship of archaebacteria, eubacteria, and eukaryotes inferred from phylogenetic trees of duplicated genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:9355–9359
Iwabe N, Kuma K, Kishino H, Hasegawa M, Miyata T (1991) Evolution of RNA polymerases and branching patterns of the three major groups of archaebacteria. J Mol Evol 32:70–78
Kimura M, Ohta T (1973) Eukaryote-prokaryote divergence estimated by 5S ribosomal RNA sequences. Nature New Biol 243:199–200
Kishino H, Hasegawa M (1989) Evaluation of the maximum like-lihood estimate of the evolutionary tree topologies from DNA sequence data, and the branching order in Hominoidea. J Mol Evol 29:170–179
Kishino H, Hasegawa M (1990) Converting distance to time: an application to human evolution. Methods Enzymol 183:550–570
Kishino H, Miyata T, Hasegawa M (1990) Maximum likelihood inference of protein phylogeny and the origin of chloroplasts. J Mol Evol 30:151–160
Krieg PA, Varnum SM, Wormington WM, Melton DA (1989) The mRNA encoding elongation factor 1α (EF-1α) is a major transcript at the midblastula transition in Xenopus. Dev Biol 133:93–100
Lechner K, Böck A (1987) Cloning and nucleotide sequence of the gene for an archaebacterial protein synthesis elongation factor Tu. Mol Gen Genet 208:523–528
Li W-H (1989) A statistical test of phylogenies estimated from sequence data. Mol Biol Evol 6:424–435
Liboz T, Bardet C, Le Van Thai A, Axelos M, Lescure B (1989) The four members of the gene family encoding the A. thaliana translation elongation factor. Plant Mol Biol 14:107–110
Linz JE, Lira LM, Sypherd PS (1986) The primary structure and the functional domains of an elongation factor-1α from Mucor racemosus. J Biol Chem 261:15022–15029
Loomis WF, Smith DW (1990) Molecular phylogeny of Dictyostelium discoideum by protein sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:9093–9097
McCarroll R, Olsen GJ, Stahl YD, Woese CR, Sogin ML (1983) Nucleotide sequence of the Dictyostelium discoideum small-subunit ribosomal ribonucleic acid inferred from the gene sequence: evolutionary implications. Biochemistry 22:5858–5868
Miyata T, Iwabe N, Kuma K, Kawanishi Y, Hasegawa M, Kishino H, Mukohata Y, Ihara K, Osawa S (1991) Evolution of archaebacteria: Phylogenetic relationships among archaebacteria, eubacteria, and eukaryotes. In: Osawa S, Honjo T (eds) Evolution of life: fossils, molecules, and culture. Springer-Verlag, Tokyo, pp 337–351
Montandon PE, Stutz E (1990) Structure and expression of the Euglena gracilis nuclear gene coding for the translation elongation factor EF-1a. Nucleic Acids Res 18:75–82
Nagashima K, Kasai M, Nagata S, Kaziro Y (1986) Structure of the two genes coding for polypeptide chain elongation factor 1-α (EF-1-α) from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene 45:265–273
Pokalsky AR, Hiatt WR, Ridge N, Rasmussen R, Houck CM, Shewmaker CK (1989) Structure and expression of elongation factor 1α in tomato. Nucleic Acids Res 17:4661–4673
Sakamoto Y, Ishiguro M, Kitagawa G (1986) Akaike information criterion statistics. D Reidel Publ Comp, Dordrecht
Schwartz RM, Dayhoff MO (1978) Origins of prokaryotes, eukaryotes, mitochondria, and chloroplasts. Science 199:395–403
Sogin ML, Elwood HJ, Gunderson JH (1986) Evolutionary diversity of eukaryotic small-subunit rRNA genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:1383–1387
Sogin ML, Gunderson JH, Elwood HJ, Alonso RA, Peattie DA (1989a) Phylogenetic meaning of the kingdom concept: An unusual ribosomal RNA from Giardia lamblia. Science 243: 75–77
Sogin ML, Edman U, Elwood H (1989b) A single kingdom of eukaryotes. In: Fernholm B, Bremer K, Jörnvall H (eds) The hierarchy of life. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 133–143
Sundstrom P, Smith D, Sypherd PS (1990) Sequence analysis and expression of the two genes for elongation factor 1-α from the dimorphic yeast Candida albicans. J Bacteriol 172: 2036–2045
Tesch A, Klink F (1990) Cloning and sequencing of the gene coding for the elogation factor 1α from the archaebacterium Thermoplasma acidophilum. FEMS Microbiol Lett 71:293–298
Uetsuki T, Naito A, Nagata S, Kaziro Y (1989) Isolation and characterization of the human chromosomal gene for polypeptide chain elongation factor 1-α. J Biol Chem 264:5791–5798
van Hemert FJ, Amons R, Pluijms WJM, van Ormondt H, Möller W (1984) The primary structure of elongation factor EF-1α from the brine shrimp Artemia. EMBO J 3:1109–1113
Vossbrinck CR, Maddox JV, Friedman S, Debrunner-Vossbrinck BA, Woese CR (1987) Ribosomal RNA sequence suggests microsporidia are extremely ancient eukaryotes. Nature 326:411–414
Woese CR (1987) Bacterial evolution. Microbiol Rev 51:221–271
Yang F, Demma M, Warren V, Dharmawardhane S, Condeelis J (1990) Identification of an actin-binding protein from Dictyostelium as elongation factor 1a. Nature 347:494–496
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Offprint requests to: M. Hasegawa
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hasegawa, M., Hashimoto, T., Adachi, J. et al. Early branchings in the evolution of eukaryotes: Ancient divergence of entamoeba that lacks mitochondria revealed by protein sequence data. J Mol Evol 36, 380–388 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00182185
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00182185